Causal relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on Mendelian randomization analysis
-
摘要:目的
基于双向两样本孟德尔随机化(MR)方法分析胃食管反流病(GERD)与慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)的因果关系。
方法从全基因组关联研究(GWAS)中获取GERD与COPD的遗传变异信息, 并以此作为工具变量。采用逆方差加权法(IVW)、加权中位数法和MR-Egger回归分析法进行MR分析,并通过敏感性分析验证结果的稳健性。
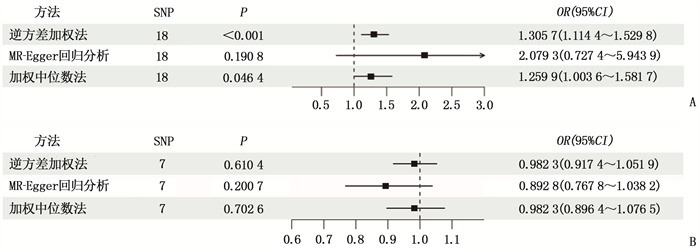
结果遗传预测的GERD与COPD发生风险具有显著正相关性,而COPD与GERD发生风险无统计学关联。正向IVW结果显示比值比(OR)=1.305 7, 95%置信区间(95%CI)为1.114 4~1.529 8, P=0.000 9; 逆向IVW结果显示OR=0.982 3, 95%CI为0.917 4~1.051 9, P=0.610 4。敏感性分析未发现任何潜在偏倚。
结论MR分析显示GERD是COPD的一个风险因子,治疗GERD可能有助于预防或延缓COPD的进展。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the causal relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on the bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR).
MethodsGenetic variation information of GERD and COPD was obtained from Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) and used as instrumental variables. Inverse variance-weighted (IVW), weighted median and MR-Egger methods were used for MR analysis, and sensitivity analysis was performed to validate the robustness of the results.
ResultsA significant positive correlation was observed between genetically predicted GERD and the incidence risk of COPD, but there was no statistical association between COPD and the incidence risk of GERD. Positive IVW result showed that the odds ratio (OR) was 1.305 7, the 95% confidence interval (95%CI) was 1.114 4 to 1.529 8, and the P value was 0.000 9; the reverse IVW result showed that the OR was 0.982 3, the 95%CI was 0.917 4 to 1.051 9, and the P value was 0.610 4. Sensitivity analysis did not find any potential bias.
ConclusionMR analysis shows that GERD is a risk factor for COPD, and treating GERD may help prevent or delay the progression of COPD.
-
-
表 1 工具变量信息
暴露 单核苷酸多态性 效应位点 其他位点 P Beta SE F COPD rs11846838 A G 4.67E-08 0.062 2 0.011 4 29.850 8 rs12449174 A G 2.91E-08 0.148 6 0.026 8 30.767 2 rs13270042 G A 2.28E-08 0.098 7 0.017 7 31.242 3 rs28929474 T C 2.06E-18 0.326 6 0.037 3 76.635 5 rs3025383 C T 2.33E-08 -0.084 5 0.015 1 31.195 0 rs7671167 T C 1.88E-08 0.062 9 0.011 2 31.611 1 rs8089390 T C 2.17E-08 -0.070 4 0.012 6 31.332 0 GERD rs111472920 T G 4.47E-08 0.098 7 0.018 0 30.066 9 rs12706746 A G 4.24E-09 0.036 9 0.006 3 34.306 1 rs12939066 T C 3.13E-11 0.041 5 0.006 2 44.803 6 rs13167137 T G 2.82E-08 -0.032 8 0.005 9 30.906 1 rs1473115 T C 3.95E-10 0.039 6 0.006 3 39.510 2 rs15071 T C 1.01E-08 -0.042 8 0.007 5 32.566 0 rs1858828 T G 3.23E-08 0.032 7 0.005 9 30.717 9 rs3072 T C 1.86E-08 -0.034 5 0.006 1 31.987 4 rs62046253 T C 1.30E-08 -0.035 2 0.006 2 32.233 1 rs62442944 T G 3.49E-08 0.041 8 0.007 6 30.250 0 rs6683411 A G 4.82E-08 0.032 4 0.005 9 30.156 9 rs6710685 T C 1.96E-09 0.039 1 0.006 5 36.184 9 rs6762606 T C 4.18E-08 -0.035 9 0.006 5 30.504 4 rs6809836 A G 3.70E-09 0.038 3 0.006 5 34.719 3 rs6991878 T C 2.71E-08 -0.033 8 0.006 1 30.702 5 rs72704785 A G 6.81E-09 0.045 9 0.007 9 33.757 6 rs7552188 T C 1.07E-08 0.041 3 0.007 2 32.903 0 rs769671 T C 9.28E-10 -0.038 5 0.006 3 37.345 7 表 2 敏感性分析结果
暴露 结局 SNPs/个 异质性检验 MR-Egger多效性检验 MR-PRESSO离群值检测 Q P 截距值 P 残差平方和 P 离群SNP GERD COPD 18 17.926 12 0.393 5 -0.017 9 0.392 7 20.311 47 0.404 9 无 COPD GERD 7 5.513 072 0.479 9 0.009 4 0.222 2 7.259 081 0.524 4 无 GERD: 胃食管反流病; COPD: 慢性阻塞性肺疾病; SNPs: 单核苷酸多态性; MR-PRESSO: 孟德尔随机多态性残差和离群值。 -
[1] MARET-OUDA J, MARKAR S R, LAGERGREN J. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Review[J]. Jama, 2020, 324(24): 2536-2547. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.21360
[2] 燕晶晶, 李颖, 于明娟, 等. 胃食管反流病的诊治研究进展[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2023, 32(9): 1309-1314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2023.09.030 [3] RAHERISON C, GIRODET P O. Epidemiology of COPD[J]. Eur Respir Rev, 2009, 18(114): 213-221. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00003609
[4] CHEN Y. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and non-digestive tract diseases[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 9(5): 685-692. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2015.1012495
[5] 樊建勇, 秦燕. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病与胃食管反流病相互作用的研究进展[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2020, 19(01): 88-91. [6] GARCíA RODRíGUEZ L A, RUIGóMEZ A, MARTíN-MERINO E, et al. Relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and COPD in UK primary care[J]. CHEST, 2008, 134(6): 1223-1230. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0902
[7] LICCARDI G, SALZILLO A, CALZETTA L, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux and COPD exacerbations: Is cholinergic-mediated oesophago-bronchial reflex a possible link[J]. RESPIROLOGY, 2016, 21(8): 1496-1497. doi: 10.1111/resp.12896
[8] AN J, GHARAHKHANI P, LAW M H, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux GWAS identifies risk loci that also associate with subsequent severe esophageal diseases[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 4219. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11968-2
[9] KURKI M I, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population[J]. NATURE, 2023, 613(7944): 508-518. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05473-8
[10] ZAGKOS L, DIB M J, PINTO R, et al. Associations of genetically predicted fatty acid levels across the phenome: A mendelian randomisation study[J]. PLoS Med, 2022, 19(12): e1004141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004141
[11] CHEN X, KONG J, DIAO X, et al. Depression and prostate cancer risk: A Mendelian randomization study[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(23): 9160-9167. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3493
[12] WANG S, ZHU H, PAN L, et al. Systemic inflammatory regulators and risk of acute-on-chronic liver failure: A bidirectional mendelian-randomization study[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1125233. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1125233
[13] 张晓莉, 李晗瑜, 郑松柏. 重视老年人胃食管反流病及其相关疾病的诊治[J]. 国际老年医学杂志, 2023, 44(4): 385-389. [14] LEE A S, LEE J S, HE Z, et al. Reflux-Aspiration in Chronic Lung Disease[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2020, 17(2): 155-164. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201906-427CME
[15] LEE A S, RYU J H. Aspiration Pneumonia and Related Syndromes[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2018, 93(6): 752-762. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.03.011
[16] SAKAE T M, PIZZICHINI M M, TEIXEIRA P J, et al. Exacerbations of COPD and symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Bras Pneumol, 2013, 39(3): 259-271. doi: 10.1590/S1806-37132013000300002
[17] 李路, 杨阳, 孙亚男, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者心功能不全相关危险因素及其与预后的关系[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(15): 43-48, 52. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20211756 [18] LI X, LIN S, WANG Z, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic cough: A possible mechanism elucidated by ambulatory pH-impedance-pressure monitoring[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2019, 31(12): e13707. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13707
[19] CIBELLA F, CUTTITTA G. Nocturnal asthma and gastroesophageal reflux[J]. Am J Med, 2001, 111(Suppl 8A): 31s-36s.
[20] 阿卜杜喀迪尔·阿卜杜热合曼, 柔孜麦麦提·艾则孜, 合贝尔江·力提甫. 胃食管反流病相关呼吸系统疾病研究进展[J]. 新疆医学, 2022, 52(2): 207-210. [21] REYNOLDS C J, DEL GRECO M F, ALLEN R J, et al. The causal relationship between gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomisation study[J]. Eur Respir J, 2023, 61(5): 2201585. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01585-2022
[22] ZHU J, ZHOU D, WANG J, et al. A Causal Atlas on Comorbidities in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study[J]. CHEST, 2023, 164(2): 429-440. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.02.038
[23] LEE A L, GOLDSTEIN R S. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in COPD: links and risks[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2015, 10: 1935-1949.
[24] BECKER B S, BURAKOFF R. The effect of verapamil on the lower esophageal sphincter pressure in normal subjects and in achalasia[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1983, 78(12): 773-775.
[25] HONGO M, TRAUBE M, MCALLISTER R G JR, et al. Effects of nifedipine on esophageal motor function in humans: correlation with plasma nifedipine concentration[J]. GASTROENTEROLOGY, 1984, 86(1): 8-12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(84)90583-3
[26] BERQUIST W E, RACHELEFSKY G S, KADDEN M, et al. Effect of theophylline on gastroesophageal reflux in normal adults[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1981, 67(5): 407-411. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90087-7
[27] STEIN M R, TOWNER T G, WEBER R W, et al. The effect of theophylline on the lower esophageal sphincter pressure[J]. Ann Allergy, 1980, 45(4): 238-241.
[28] JOHANNESSON N, ANDERSSON K E, JOELSSON B, et al. Relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter and stimulation of gastric secretion and diuresis by antiasthmatic xanthines. Role of adenosine antagonism[J]. Am Rev Respir Dis, 1985, 131(1): 26-30.
[29] 顾章明, 孙丽. 氟哌噻吨美利曲辛片联合舒肝解郁胶囊对难治性胃食管反流患者疗效及焦虑、抑郁状态的影响[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2019, 23(12): 32-35. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201912010 [30] 殷江龙, 彭卓嵛, 石林韬, 等. 基于Citespace中医药治疗胃食管反流病相关研究的可视化分析[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(22): 65-71. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20221681 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王梓杭,姜红丽,史绪生. 全球重症病人早期康复研究热点的可视化分析. 循证护理. 2024(14): 2554-2561 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴洪,温贤秀,雷花,毛孝容,潘俊青,曹海霞,卢婷,蓝梅. 新型冠状病毒肺炎患者早期康复及干预措施研究进展. 实用医院临床杂志. 2022(02): 211-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋宇杰,徐悦蓉,董佳颖,张明明. 新型冠状病毒肺炎所致心血管系统损伤的研究进展. 实用临床医药杂志. 2021(15): 114-118 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
