Value of combined application of ultrasound elastography, color Doppler blood flow imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in differential diagnosis of breast occupying lesions
-
摘要:目的
探讨超声弹性成像(UE)、彩色多普勒血流显像(CDFI)及超声造影(CEUS)技术联合应用对乳腺占位性病变的鉴别诊断价值。
方法回顾性选取2022年1—12月收治的乳腺占位性病变患者95例,病灶数量共113个。治疗前对患者行UE、CDFI和CEUS检查; 对影像学图像进行分析,以病理检查为“金标准”,分析其诊断准确率; 采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析UE、CDFI和CEUS单独和联合检查对乳腺占位性病变的鉴别效能。
结果对95例乳腺占位性病变患者行病理组织活检,有38例患者存在共48个恶性结节, 57例患者无恶性结节。根据病理检查结果将患者分为恶性组和良性组。相较于良性组,恶性组患者的结节数量更多,最大肿瘤直径更大,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。采用UE诊断出恶性病变52个,良性病变61个; 采用CDFI诊断出恶性病变62个,良性病变51个; 采用CEUS诊断出恶性病变57个,良性病变56个; 3种方法联合诊断出恶性病变56个,良性病变57个。CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断灵敏度、特异度、准确率、阳性预测值以及阴性预测值均高于UE和CDFI, 指标联合诊断效能最高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。UE、CDFI和CEUS诊断乳腺占位性病变的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.750、0.639和0.840; Delong检验结果发现,联合诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=4.15, P < 0.01)、UE(Z=3.81, P < 0.01)、CEUS(Z=2.68, P=0.02), CEUS诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=3.17, P < 0.01)、UE(Z=2.31, P=0.02), UE诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=2.05, P=0.04)。
结论UE、CDFI和CEUS对于乳腺占位性病变的良恶性均有较高的鉴别诊断价值,且UE、CDFI和CEUS联合诊断的灵敏度和特异度均高于单独诊断。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the value of combined application of ultrasound elastography (UE), color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the differential diagnosis of breast occupying lesions.
MethodsA total of 95 patients with breast occupying lesions from January to December 2022 were retrospectively selected, with 113 lesions in total. Before treatment, UE, CDFI and CEUS examinations were performed for the patients; the images were analyzed, and pathological examination was used as the "gold standard" to analyze diagnostic accuracy of images; the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the differential efficiencies of UE, CDFI, and CEUS examinations alone and their combination for breast occupying lesions.
ResultsPathological tissue biopsies were performed in 95 patients with breast occupying diseases, and 38 patients had 48 malignant nodules, while 57 patients had no malignant nodules. According to the pathological examination results, the patients were divided into malignant group and benign group. Compared with the benign group, the malignant group had more nodules and larger diameter of the largest tumor, and the difference were statistically significant (P < 0.05). A total of 52 malignant lesions and 61 benign lesions were diagnosed by UE; 62 malignant lesions and 51 benign lesions were diagnosed by CDFI; 57 malignant lesions and 56 benign lesions were diagnosed by CEUS; 56 malignant lesions and 57 benign lesions were diagnosed by the combination of the three methods. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of CEUS in the diagnosis of breast occupying lesions were significantly higher than those of UE and CDFI, and the diagnostic efficacy of the three methods in combination was the highest (P < 0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) of UE, CDFI and CEUS for diagnosis of breast occupying lesions was 0.750, 0.639 and 0.840 respectively; the Delong test results showed that the combined diagnostic efficiency was significantly higher than CDFI (Z=4.15, P < 0.01), UE (Z=3.81, P < 0.01) and CEUS (Z=2.68, P=0.02), diagnostic efficiency of CEUS was significantly higher than that of CDFI (Z=3.17, P < 0.01) and UE (Z=2.31, P=0.02), and diagnostic efficiency of UE was significantly higher than that of CDFI (Z=2.05, P=0.04).
ConclusionUE, CDFI and CEUS have high differential diagnostic value for benign and malignant breast occupying lesions, and the sensitivity and specificity of the combined diagnosis of UE, CDFI and CEUS are higher than those of individual diagnosis.
-
乳腺占位性病变包括良性病变与恶性病变,良性病变包括纤维腺瘤、腺样增生和乳头状瘤等,而恶性病变即乳腺癌,在临床中表现为乳房肿块,其发病率在女性恶性肿瘤中居于首位[1-3]。对于不同性质的乳腺病变需要进行鉴别诊断。随着医疗水平的进步,临床上乳腺占位性病变的诊断准确率有了极大的提高。超声弹性成像(UE)、彩色多普勒血流显像(CDFI)及超声造影(CEUS)技术均对乳腺病变的性质有一定的鉴别效果[4-6]。本研究探讨3种超声成像技术单独和联合应用在诊断乳腺占位性病变中的价值,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性选取2022年1—12月在本院治疗的95例乳腺占位性病变患者为研究对象,年龄37.5~55.7岁,平均(45.64±5.81)岁。纳入标准: ①经临床筛查发现乳腺占位性病变且经病理学检查确诊者; ②检查前1个月内未接受放化疗者; ③均行UE、CDFI和CEUS检查且图像清晰者。排除标准: ①术前接受新辅助化疗者; ②存在乳房手术史或外伤史者; ③合并其他恶性肿瘤者; ④妊娠期或哺乳期患者; ⑤临床资料不完整者。所有患者经病理学检查共发现病灶113个,其中良性结节65个,恶性结节48个。
1.2 方法
UE检查: 采用Aixplorer V彩色多普勒超声诊断仪(法国声科影像公司)对患者进行检查。选择线阵探头并将探头频率设置为5~15 MHz, 患者取仰卧位,采用探头对病灶的部位、大小、形态进行弹性成像检查,根据测量乳腺肿物的组织硬度来判断其有无恶性可能。
CDFI检查: 采用同一彩色多普勒超声诊断仪对患者进行检查。探头频率为5~15 MHz, 患者取仰卧位,采用探头对病灶的部位、大小、形态以及血供情况进行检查并记录。若病灶内部血流信号存在异常,且频谱显示血供丰富(血管>3支),呈穿支血流,血流阻力指数(RI)>0.70, 则有恶性可能。
CEUS检查: 将彩色多普勒超声诊断仪调整为造影模式,并将其机械指数设置为0.07, 采用21G套管针经肘静脉行静脉通路建立,并注入2.5 mL造影剂,选取病灶内最清晰区域进行观察,记录动脉相、门脉相以及延迟相变化趋势。若造影显示形态不规则,边界欠清晰,呈不均匀增强,造影后结节面积较二维增大,则判断为恶性。
阅片由2名具有10年以上经验的影像科医师独立进行,若存在意见分歧,则进行讨论,获得最终结论。以病理检查结果为金标准,探讨不同影像学方法的诊断效能。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行数据分析,计量资料以(x±s)表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验,计数资料以[n(%)]表示,组间比较采用χ2检验; 采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析UE、CDFI和CEUS检查对乳腺占位性病变良恶性的诊断效能,通过Delong检验比较不同评分方法单独及联合诊断的曲线下面积(AUC)的差异; P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
对95例乳腺占位性病变患者行病理组织活检,有38例患者存在恶性结节共48个,包括浸润性导管癌41个,原位癌3个,导管内癌3个,髓样癌1个; 57例患者无恶性结节,有良性结节共65个,包括纤维腺瘤46个,纤维脂肪瘤9个,纤维囊性乳腺病7个,不典型增生2个,导管内乳头状瘤1个。根据病理检查结果将患者分为恶性组和良性组,相比于良性组,恶性组患者的结节数量更多,最大肿瘤直径更大,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 2组一般资料比较(x±s)一般资料 恶性组(n=38) 良性组(n=57) 年龄/岁 44.63±5.73 46.31±5.89 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 23.49±3.14 23.24±3.02 结节数量/个 1.26±0.19* 1.14±0.14 最大肿瘤直径/cm 1.57±0.29* 1.45±0.20 与良性组比较, * P < 0.05。 2.2 UE、CDFI和CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断结果
采用UE诊断出恶性病变52个,良性病变61个; 采用CDFI诊断出恶性病变62个,良性病变51个; 采用CEUS诊断出恶性病变57个,良性病变56个; UE、CDFI和CEUS联合诊断出恶性病变56个,良性病变57个。见表 2。
表 2 UE、CDFI和CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断结果检查方式 检查结果 金标准 合计 恶性 良性 UE 恶性 36 16 52 良性 12 49 61 CDFI 恶性 34 28 62 良性 14 37 51 CEUS 恶性 43 14 57 良性 5 51 56 3个指标联合 恶性 45 11 56 良性 3 54 57 2.3 UE、CDFI和CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断效能
CEUS对乳腺占位性病变诊断灵敏度、特异度、准确率、阳性预测值以及阴性预测值均高于UE和CDF, 3个指标联合诊断效能最高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 UE、CDFI和CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断效能项目 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 准确率/% 阳性预测值/% 阴性预测值/% UE 75.00(36/48) 75.38(49/65) 75.22(85/113) 69.23(36/52) 80.33(49/61) CDFI 70.83(34/48) 56.92(37/65) 62.83(71/113) 54.84(34/62) 72.55(37/51) CEUS 89.58(43/48) 78.46(51/65) 83.18(94/113) 75.43(43/57) 91.07(51/56) 3个指标联合 93.75(45/48) 83.08(54/65) 87.61(99/113) 80.35(45/56) 94.74(54/57) χ2 12.15 13.16 25.29 10.37 13.02 P 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.02 < 0.01 2.4 UE、CDFI和CEUS诊断乳腺占位性病变的ROC曲线
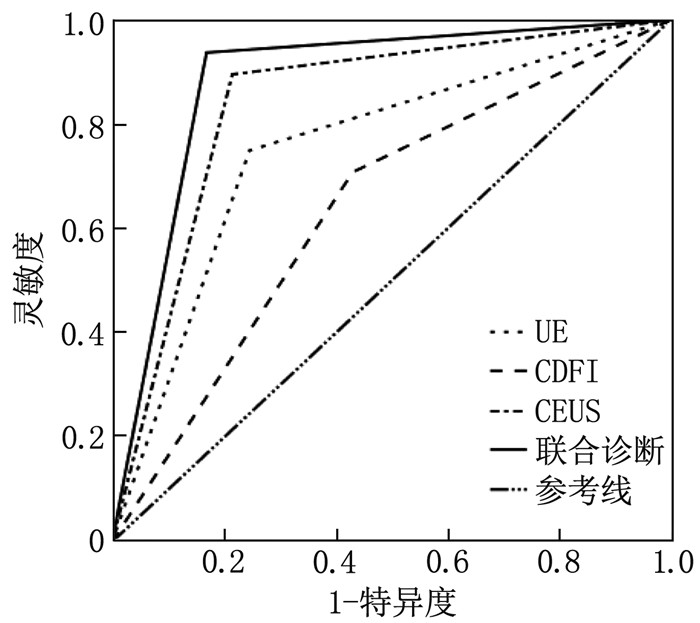
UE、CDFI和CEUS诊断乳腺占位性病变的AUC分别为0.750、0.639和0.840, 3个指标联合诊断的AUC为0.884。Delong检验比较4种模型的诊断效能,结果发现联合诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=4.15, P < 0.01)、UE(Z=3.81, P < 0.01)、CEUS(Z=2.68, P=0.02), CEUS诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=3.17, P < 0.01)、UE(Z=2.31, P=0.02), UE诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=2.05, P=0.04)。见表 4、图 1。
表 4 UE、CDFI和CEUS诊断乳腺占位性病变的ROC曲线指标指标 AUC 95%CI 灵敏度/% 特异度/% P CDFI 0.639 0.536~0.742 70.83 56.92 0.01 UE 0.752 0.658~0.845 75.00 75.38 < 0.01 CEUS 0.840 0.763~0.918 89.58 78.46 < 0.01 联合诊断 0.884 0.817~0.951 93.75 83.08 < 0.01 3. 讨论
乳腺结节在治疗前首先需要对结节性质进行鉴定,然后才能根据结节的性质进行治疗方案的选择。对于良性结节,临床上一般选择定期复诊,而针对恶性结节,则需要根据患者肿瘤发展情况进行手术治疗或者其他综合性治疗[7-8]。彩色多普勒超声在乳腺良恶性肿块的鉴别中具有较高的价值,其原因为肿瘤增长具有持续性,其组织中的血管生长因子不断释放,刺激肿瘤组织中不断产生新生毛细血管,并随着肿瘤的发展,血管数量增加,分布状态也发生变化,其形态和功能相较于正常组织变得异常,发生扩张、扭曲以及动静脉短路等状况[9-10]。
UE、CDFI和CEUS均是常用的临床超声成像技术,对于乳腺结节的性质均有一定的鉴别诊断价值。UE是一种基于人体组织生物学特性的影像学技术,其通过收集被检组织的信号信息,对其进行编码、分析,形成对应的超声图像,再由专业的影像学医师通过图像对组织内部情况进行解读,明确组织分布情况和弹性水平[11]。由于不同性质的乳腺结节具有明显不同的弹性系数,且乳腺结节与正常组织之间也有明显差异,因此UE能够对乳腺的病变情况进行较为准确的观察和分析[12]。本研究中, UE对乳腺结节的良恶性诊断准确率为75.22%, 刘迪等[13]关于磁共振成像、超声弹性成像和X线的研究显示, UE在乳腺癌临床诊断中的准确率为80.29%, 与本研究结果较为一致。
CDFI是基于乳腺肿瘤具有不同于正常组织新生血管的病理学基础的一种影像学技术,能够反映肿瘤新生血管程度,对于乳腺占位性病变具有一定的鉴别诊断作用[14-15]。研究[16]显示,不同性质的乳腺肿瘤的血流分级之间存在显著差异,其血流丰富程度越高,恶性的可能性越高,与本研究结果较为一致。值得注意的是, CDFI的诊断准确率并不理想,其原因可能是CDFI对于血流速度在1 cm/s以下的低速血流反映效果差,因此在对血流丰富程度进行评价时存在一定的偏差,导致其对乳腺良恶性结节的诊断效能较低[17]。近年来, CEUS作为一种新兴的影像学技术,被广泛应用于乳腺肿瘤的良恶性鉴别诊断,并取得了良好的效果,其不仅能够展示靶器官的微观和宏观周期性变化情况,还能够解决超声对微血管灵敏度较差的问题; 同时, CEUS能够展示典型的良性、恶性增强模式,有助于展示钙化区域周围的微循环情况,是一种可靠的鉴别诊断方法[18]。有学者[19]研究表明, CEUS的增强模式和时间强度曲线仅能显示乳腺病灶的新生血管情况,而与病灶的良恶性无关; 此外, CEUS会低估乳腺肿瘤的实际大小,而恶性肿瘤在超声造影后的面积测量值会显著大于造影前,而良性肿瘤的面积在造影前后无显著差异。
本研究中, CEUS对于乳腺占位性病变的鉴别诊断的灵敏度较高,达到89.58%, 高于CDFI的诊断效能,其原因为CEUS能够对病灶的血流灌注情况进行动态观察,能清晰观察到微小血管以及低速血流[20-22]。一般情况下,若受检组织未出现增强情况,则可排除恶性病变可能。王剑桥等[23]关于乳腺良恶性病变的研究显示, CEUS诊断乳腺良恶性病变的AUC为0.770, 与本研究得到的0.840具有一定的差异性,出现该结果的原因可能为本研究中纳入病例主要为乳腺占位性病变患者,而王剑桥等研究中纳入的病例主要为乳腺导管内病变患者, CEUS对于不同的病变类型具有不同的诊断效能。
本研究通过对3种影像学方法进行ROC曲线分析发现, 3种影像学方法对于乳腺占位性病变的性质均有一定的鉴别诊断效能,其中CEUS的诊断效能较高,其灵敏度和特异度分别为89.58%和78.46%, 均高于UE和CDFI。3种影像学方法联合诊断的整体效能最高,其AUC为0.884, 灵敏度和特异度分别为93.75%和83.08%; Delong检验结果发现联合诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=4.15, P < 0.01)、UE(Z=3.81, P < 0.01)、CEUS(Z=2.68, P=0.02), CEUS诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=3.17, P < 0.01)、UE(Z=2.31, P=0.02), UE诊断效能显著高于CDFI(Z=2.05, P=0.04); 上述结果提示在临床上对乳腺占位性病变的性质进行诊断鉴别时,可以优先采用CEUS进行诊断,其在乳腺占位性病变方面诊断效能较高,有条件者可以结合以上多种影像学方式的优势,对其进行综合分析,以提高诊断准确度。
综上所述, UE、CDFI和CEUS对于乳腺占位性病变的良恶性均有较高的鉴别诊断价值,且UE、CDFI和CEUS联合诊断的灵敏度和特异度均高于单独诊断。
-
表 1 2组一般资料比较(x±s)
一般资料 恶性组(n=38) 良性组(n=57) 年龄/岁 44.63±5.73 46.31±5.89 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 23.49±3.14 23.24±3.02 结节数量/个 1.26±0.19* 1.14±0.14 最大肿瘤直径/cm 1.57±0.29* 1.45±0.20 与良性组比较, * P < 0.05。 表 2 UE、CDFI和CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断结果
检查方式 检查结果 金标准 合计 恶性 良性 UE 恶性 36 16 52 良性 12 49 61 CDFI 恶性 34 28 62 良性 14 37 51 CEUS 恶性 43 14 57 良性 5 51 56 3个指标联合 恶性 45 11 56 良性 3 54 57 表 3 UE、CDFI和CEUS对乳腺占位性病变的诊断效能
项目 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 准确率/% 阳性预测值/% 阴性预测值/% UE 75.00(36/48) 75.38(49/65) 75.22(85/113) 69.23(36/52) 80.33(49/61) CDFI 70.83(34/48) 56.92(37/65) 62.83(71/113) 54.84(34/62) 72.55(37/51) CEUS 89.58(43/48) 78.46(51/65) 83.18(94/113) 75.43(43/57) 91.07(51/56) 3个指标联合 93.75(45/48) 83.08(54/65) 87.61(99/113) 80.35(45/56) 94.74(54/57) χ2 12.15 13.16 25.29 10.37 13.02 P 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.02 < 0.01 表 4 UE、CDFI和CEUS诊断乳腺占位性病变的ROC曲线指标
指标 AUC 95%CI 灵敏度/% 特异度/% P CDFI 0.639 0.536~0.742 70.83 56.92 0.01 UE 0.752 0.658~0.845 75.00 75.38 < 0.01 CEUS 0.840 0.763~0.918 89.58 78.46 < 0.01 联合诊断 0.884 0.817~0.951 93.75 83.08 < 0.01 -
[1] KATSURA C, OGUNMWONYI I, KANKAM H, et al. Breast cancer: presentation, investigation and management[J]. Br J Hosp Med (Lond), 2022, 83(2): 1-7.
[2] WEIDLE U H, BIRZELE F, KOLLMORGEN G, et al. Mechanisms and targets involved in dissemination of ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 2016, 13(6): 407-423. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20004
[3] 钟志方, 孙景敏, 韩正祥. ABVS与VTI技术在乳腺占位性病变鉴别诊断中的应用[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2022, 37(9): 90-93, 98. [4] 路祥芬, 胡晓华. 非肿块型乳腺疾病超声弹性成像、剪切波弹性成像检测特征及其鉴别诊断[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2021, 39(5): 764-767. [5] 赵利辉, 忻晓洁. 超微血管成像在乳腺及颈部肿瘤中的应用进展[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2021, 29(1): 89-92. [6] 赵婷, 蒋世亮. 乳腺钼靶、超声造影检查鉴别诊断乳腺非肿块样强化病变的良恶性质的对比分析[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2021, 39(4): 512-516. [7] 陈剑琼, 肖榕, 周玮珺, 等. 灰阶超声影像组学在诊断乳腺结节良恶性中的应用价值[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2022, 57(2): 325-328. [8] JANNUSCH K, BRUCKMANN N M, GEUTING C J, et al. Lung nodules missed in initial staging of breast cancer patients in PET/MRI-clinically relevant[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(14): 3454. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143454
[9] LIU H, HOU C J, TANG J L, et al. Deep learning and ultrasound feature fusion model predicts the malignancy of complex cystic and solid breast nodules with color Doppler images[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 10500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37319-2
[10] 粟世桃, 黄健源, 黄炫彰, 等. 乳腺结节超声BI-RADS分类3~5类的量化评分研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2021, 37(1): 27-30. [11] 张凌霄, 杨宗利, 邵娟娟. 高频彩色多普勒超声联合弹性成像诊断乳腺结节的临床价值分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2021, 31(6): 993-996. [12] 彭刿, 马良, 庞蓉. 超声、UE及PET/CT诊断乳腺癌良恶性病变的价值观察[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(12): 84-86. [13] 刘迪, 贺松, 牛向欣, 等. 磁共振成像、超声弹性成像、X线在乳腺癌临床诊断中的应用价值研究[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2021, 39(5): 749-753. [14] ZHANG G, LEI Y M, LI N, et al. Ultrasound super-resolution imaging for differential diagnosis of breast masses[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1049991. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1049991
[15] 杨爽, 刘宏武, 祝艳秋, 等. 超声造影微血管成像对乳腺良恶性病变的诊断效能[J]. 中国医学装备, 2023, 20(3): 94-97. [16] 王洲, 刘芳欣, 殷延华, 等. 声触诊组织成像定量技术联合超声造影诊断乳腺原发性淋巴瘤1例[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2021, 37(1): 157. [17] 刘海华, 夏群, 程扬眉, 等. 高频超声、实时剪切波弹性成像、彩色多普勒血流显像联合检查对BI-RADS 4类乳腺肿块良恶性的诊断价值[J]. 中国医药导报, 2022, 19(28): 147-150. [18] 钟兆明, 唐丽娜, 王瑶琴, 等. 常规超声联合超声造影对乳腺BI-RADS 4类小结节的诊断价值[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2021, 30(11): 955-960. [19] 史宪全, 董云云, 李尚, 等. 常规超声、超声造影及动态增强核磁共振成像评估乳腺浸润性导管癌病灶大小的准确性研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2023, 20(3): 74-79. [20] 左文思, 金林原, 刘新桥, 等. 微血管成像联合超声造影5分法对BI-RADS 4类乳腺肿块的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2021, 37(9): 974-978. [21] 陈艳艳. BI-RADS评分与CEUS检查联合用于乳腺肿块良恶性诊断的价值[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2021, 18(24): 3613-3615. [22] 宋倩, 刘景萍, 冯华梅, 等. 超声造影联合乳腺钼靶X线对乳腺导管内乳头状瘤的诊断价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(6): 13-16. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20210367 [23] 王剑桥, 李睿. 二维超声联合超声造影TIC参数在乳腺导管内病变良/恶性诊断中的应用价值[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2021, 39(1): 7-11. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陈勇辉,蔡冠晖. 超声造影联合弹性成像在BI-RADS 4a类结节穿刺活检中的应用价值. 临床医学工程. 2025(02): 169-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 庞欢,周瑞. 超声普查乳腺结节与甲状腺结节发病率的相关性分析. 影像研究与医学应用. 2025(03): 131-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陶晨韬,鲁小娟,苏继红. 二维超声与彩色多普勒超声鉴别诊断乳腺良恶性结节的价值. 影像研究与医学应用. 2024(22): 103-105+108 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号