Expression levels and clinical significance of cerebrospinal fluid Annexin A2 and S100 calcium binding protein A10 levels in patients with secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery
-
摘要:目的
探讨颅脑术后继发颅内感染患者脑脊液膜联蛋白A2(Annexin A2)和S100钙结合蛋白A10(S100A10)表达水平及临床意义。
方法选取收治的颅脑术后继发颅内感染患者120例为试验组,选取同期颅脑术后未感染的120例患者为对照组。采用酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)检测脑脊液中Annexin A2、S100A10水平; 采用Pearson相关分析法分析Annexin A2、S100A10与各临床指标的相关性; 采用Logistic回归分析法分析颅脑术后继发颅内感染的影响因素; 采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析Annexin A2、S100A10水平对颅脑术后继发颅内感染的预测价值。
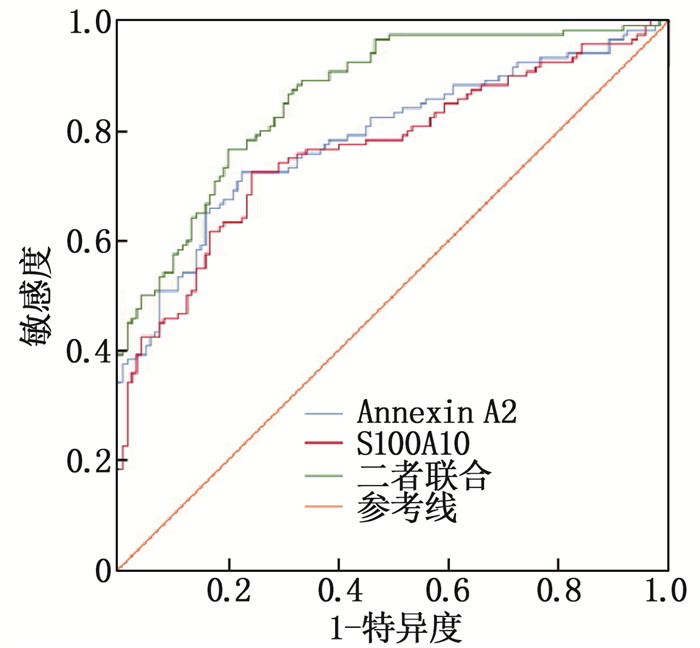
结果试验组的糖尿病占比、脑脊液渗漏占比、血乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)、脑脊液中Annexin A2及S100A10水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。颅内感染患者脑脊液中Annexin A2与S100A10、血LDH水平呈正相关, S100A10水平与LDH水平呈正相关(P<0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,糖尿病、脑脊液渗漏、血LDH、脑脊液中Annexin A2和S100A10均是颅脑术后继发颅内感染的独立影响因素(P<0.05)。ROC曲线显示,脑脊液中Annexin A2、S100A10水平单独预测及二者联合预测颅脑术后继发颅内感染的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.788、0.768、0.865, 其中联合预测AUC大于二者单独预测(P<0.05)。
结论颅脑术后继发颅内感染患者脑脊液中Annexin A2、S100A10表达水平升高,是颅脑术后继发颅内感染的独立影响因素,二者联合预测价值较高。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate expression levels and clinical significance of annexin A2 and S100 calcium binding protein A10 (S100A10) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery.
MethodsA total of 120 patients with secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery were selected as test group, while 120 patients with no infection after craniocerebral surgery in the same period were selected as control group. The levels of Annexin A2 and S100A10 in cerebrospinal fluid were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA). Pearson correlation analysis was applied to analyze the correlations of Annexin A2 and S100A10 with clinical indicators. Logistic regression analysis was applied to analyze the influencing factors of secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was applied to analyze the predictive value of Annexin A2 and S100A10 levels for the occurrence of secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery.
ResultsThe proportions of diabetes and cerebrospinal fluid leakages, blood l actate dehydrogenase (LDH), cerebrospinal fluid Annexin A2 and S100A10 levels in the test group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Annexin A2 in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with intracranial infection was positively correlated with S100A10, LDH, and S100A10 level was positively correlated with LDH (P < 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that diabetes, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, blood LDH, Annexin A2 and S100A10 in cerebrospinal fluid were independent influencing factors for secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery (P < 0.05). ROC results showed that the AUCs of Annexin A2 level or S100A10 level alone in cerebrospinal fluid and their combined prediction for secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery was 0.788, 0.768 and 0.865 respectively, the AUC of combined prediction was larger than that of the single prediction (P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe expression levels of Annexin A2 and S100A10 are increased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery, which are independent influencing factors for secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery. Their combination has higher predictive value for secondary intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery.
-
2型糖尿病(T2DM)是一种慢性代谢性疾病,特征为葡萄糖清除能力异常、持续高血糖及胰岛素敏感性降低。糖尿病前期通常会出现糖耐量受损和空腹血糖受损,约70%的糖尿病前期患者易发展为2型糖尿病(T2DM)[1-3]。目前,患者可服用双胍类和磺脲类药物进行治疗,需规律服药以维持血糖水平,但易导致低血糖、乳酸酸中毒及体质量增加等不良反应,单独使用西药往往难以达到理想疗效[4]。中医将糖尿病归属于“脾瘅”“食郁”等范畴[5], 基于整体观念及治未病理念,强调辨证施治和个体化治疗方案。目前,醒脾化浊方治疗糖尿病前期的临床研究尚显不足。本研究探讨醒脾化浊方对糖尿病前期痰湿体质患者的影响,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2021年1月—2023年12月医院收治的104例糖尿病前期痰湿体质患者为研究对象,采用随机数字表法将其分为西药组(n=52)和联合组(n=52)。纳入标准: ①符合糖尿病前期西医诊断标准[6]者; ②中医辨证为痰湿体质[7]者; ③年龄≥18岁者; ④患者及家属对本研究知情同意。排除标准: ①伴有心、肝、肾等重要脏器疾病者; ②患有严重精神类疾病者; ③伴有急性感染性疾病者; ④对本研究药物过敏者。本研究经医学伦理委员会批准。2组一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性,见表 1。
表 1 2组一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]组别 性别 年龄/岁 病程/月 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 男 女 联合组(n=52) 37(71.15) 15(28.85) 42.58±3.62 8.94±0.52 25.34±3.22 西药组(n=52) 32(61.54) 20(38.46) 43.10±3.75 9.05±0.57 25.71±3.41 1.2 方法
西药组口服二甲双胍(丹东医创药业有限责任公司生产; 国药准字H21022377), 0.5 g/次, 3次/d。联合组在西药组基础上联用醒脾化浊方。药方组成: 党参15 g、麸炒白术30 g、茯苓30 g、半夏10 g、陈皮10 g、炙甘草5 g、薏苡仁30 g、炒苍术10 g、佩兰10 g。采用500 mL水煎,取汁300 mL, 分2次口服。2组均治疗3个月。
1.3 观察指标
1.3.1 临床疗效
治疗3个月后对临床疗效进行评估。显效是指临床症状、体征明显改善,空腹血糖(FPG)<6.1 mmol/L, 餐后2 h血糖(2 hPG)<7.8 mmol/L, 糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)<6.1%; 有效是指临床症状、体征均有好转, FPG<7.0 mmol/L, 2 hPG<1.1 mmol/L, HbAlc为6.1%~6.5%; 无效是指不符合上述标准[8]。
1.3.2 血糖指标
采用葡萄糖氧化酶法检测治疗前后FPG、HbA1c、2 hPG水平。
1.3.3 血脂指标
采用全自动生化分析仪检测甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)水平。
1.3.4 肾功能指标
检测患者治疗前后血肌酐(Scr)、尿素氮(BUN)、β2-微球蛋白(β2-MG)水平。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 23.0软件对数据进行分析,计量资料以(x±s)表示,行t检验; 计数资料以[n(%)]表示,行χ2或Z检验, P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 临床疗效
治疗3个月后,联合组临床治疗总有效率高于西药组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 2组临床疗效比较[n(%)]组别 n 显效 有效 无效 总有效 联合组 52 29(55.77) 19(36.54) 4(7.69) 48(92.31)* 西药组 52 17(32.69) 22(42.31) 13(25.00) 39(75.00) 与西药组比较, * P<0.05。 2.2 2组血糖指标比较
治疗3个月后, 2组患者FPG、HbA1c、2 hPG水平均降低,且联合组低于西药组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 2组血糖指标比较(x±s)组别 n FPG/(mmol/L) HbA1c/% 2 hPG/(mmol/L) 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 联合组 52 6.58±0.19 6.03±0.11*# 6.56±0.16 5.94±0.05*# 8.73±0.84 7.92±0.76*# 西药组 52 6.54±0.18 6.29±0.13* 6.60±0.19 6.21±0.07* 8.75±0.89 8.25±0.80* FPG: 空腹血糖; 2 hPG: 餐后2 h血糖; HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白。与治疗前比较, * P<0.05; 与西药组比较, #P<0.05。 2.3 2组血脂指标比较
治疗3个月后, 2组患者TG、TC、LDL-C水平较治疗前下降,且联合组低于西药组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 2组患者HDL-C水平升高,且联合组高于西药组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), 见表 4。
表 4 2组血脂指标水平比较(x±s)组别 n TG/(mmol/L) TC/(mmol/L) LDL-C/(mmol/L) HDL-C/(μmol/L) 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 联合组 52 0.82±0.12 0.57±0.06*# 2.67±0.31 2.30±0.23*# 2.89±0.22 2.31±0.15*# 703.56±21.34 756.61±27.61*# 西药组 52 0.80±0.11 0.68±0.08* 2.69±0.32 2.42±0.27* 2.90±0.24 2.49±0.18* 705.48±21.59 742.15±25.17* TG: 甘油三酯; TC: 总胆固醇; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。与治疗前比较, * P<0.05; 与西药组比较, #P<0.05。 2.4 2组肾功能指标比较
治疗3个月后,患者Scr、BUN、β2-MG水平均降低,且联合组低于西药组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05), 见表 5。
表 5 2组肾功能指标比较(x±s)组别 n Scr/(μmol/L) BUN/(mmol/L) β2-MG/(mg/L) 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 治疗前 治疗3个月后 联合组 52 113.54±5.24 88.95±3.58*# 6.23±0.67 4.10±0.42*# 6.21±0.50 4.29±0.32*# 西药组 52 112.27±5.57 96.61±3.94* 6.41±0.69 5.16±0.51* 6.16±0.48 4.93±0.41* Scr: 血肌酐; BUN: 尿素氮; β2-MG: β2-微球蛋白。与治疗前比较, * P<0.05; 与西药组比较, #P<0.05。 3. 讨论
痰湿体质患者脾虚是关键病机,脾虚则运化失常,痰浊水湿内聚,中医以健脾益气、清热除湿为主要治则[9]。痰湿体质的糖尿病前期患者临床表现为口甜腻、饮水量增多、食欲亢进等[10]。醒脾化浊方中党参可补益肺、脾、肾之气,生津止渴; 白术补气健脾,燥湿利水; 茯苓健脾安神、益肾、利水祛湿; 半夏燥湿化痰、消痞散结; 陈皮健脾开胃、燥湿化痰; 炙甘草具有补气养阴、清热生津的功效; 薏苡仁具有利水渗湿、健脾止泻之效; 炒苍术可燥湿健脾、祛风除湿;佩兰和中化湿、醒脾开胃,诸药共奏益气健脾、化痰祛湿之功。
现代药理学研究[11]发现,槲皮素是一种黄酮类化合物,目前已知含有槲皮素的中药有100余种,本研究中使用的醒脾化浊方中党参、茯苓等中药均富含槲皮素。在糖尿病斑马鱼模型中,槲皮素通过调节同型半胱氨酸途径、抑制脂质过氧化、清除自由基等发挥降糖作用。甘草富含20余种三萜类化合物和300余种黄酮类化合物,其中甘草素、异甘草素、甘草苷等通过调节磷脂酰肌醇3′-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Akt)、核因子-κB(NF-κB)等信号通路发挥调节糖代谢异常的作用。JIA W J等[12]研究指出,在糖尿病小鼠蔗糖、麦芽糖、淀粉耐受性测定中,党参提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶和酵母α-糖苷酶具有较强的抑制活性作用,可显著降低餐后血糖水平。茯苓是我国批准的降糖药物之一,含有三萜类和多糖类化合物,能够增强β细胞功能,增强胰岛素敏感性,降低餐后血糖水平。
肾为五脏阴阳之本,具有藏精纳气、主水液代谢之功能。高血糖环境可导致肾细胞损伤,进而引发肾小球滤过功能障碍,最终造成肾小球硬化和肾小管间质纤维化[13]。因此,对于糖尿病前期患者而言,不仅需调整饮食及控制血糖、血压和血脂,还应选择具有保护和改善肾功能作用的药物进行治疗。本研究结果显示,联合治疗后,患者肾功能指标均得到有效改善。首先,足细胞是肾小球血液滤过屏障的重要组成部分,其损伤是肾小球硬化的主要因素之一。醒脾化浊方中陈皮所含的橙皮苷能够修复足细胞,抑制转化生长因子-β1(TGF-β1)/整合素连接激酶(ILK)/Akt信号通路,减少足细胞表面蛋白表达的异常变化[14]。其次,槲皮素能够抑制TGF-β1和血清结缔组织生长因子(CTGF)的过度表达,从而改善肾功能。再次,槲皮素还能通过激活Hippo通路抑制系膜细胞增殖,对肾脏具有保护作用。最后,茯苓中的茯苓多糖可促进Klotho蛋白的表达,从而保护肾脏功能[15]。
综上所述,糖尿病前期的影响因素包括腹部肥胖、血脂异常等,其中TG、HDL-C等血脂指标与胰岛素抵抗密切相关,对糖尿病前期患者具有较高的诊断价值[16]。在糖尿病前期痰湿体质患者中,二甲双胍联合醒脾化浊方能够有效改善患者血糖指标水平,并发挥肾脏保护作用。
-
表 1 对照组和试验组临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
临床资料 对照组(n=120) 试验组(n=120) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 42.13±13.25 41.88±13.19 0.146 0.884 男 66(55.00) 68(56.67) 0.068 0.795 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 21.84±6.57 22.16±6.35 0.384 0.702 高血压 49(40.83) 58(48.33) 1.336 0.242 糖尿病 24(20.00) 50(41.67) 13.207 < 0.001 高脂血症 15(12.50) 17(14.17) 0.144 0.704 脑脊液渗漏 26(21.67) 55(45.83) 15.672 < 0.001 手术持续时间≥3 h 32(26.67) 48(31.67) 0.726 0.394 手术类型 择期手术 58(48.33) 65(54.17) 0.817 0.366 急诊手术 62(51.67) 55(45.83) 脑脊液外引流术 13(10.83) 20(16.67) 1.722 0.189 血降钙素原/(μg/L) 2.66±0.85 2.86±0.92 1.749 0.082 血降钙素原/(mg/L) 7.71±2.24 8.18±2.11 1.673 0.096 乳酸脱氢酶/(U/L) 189.95±58.94 306.37±94.39 11.460 < 0.001 膜联蛋白A2/(ng/L) 1.49±0.46 2.10±0.62 8.656 < 0.001 S100钙结合蛋白/(ng/L) 1.01±0.31 1.38±0.43 7.646 < 0.001 表 2 多因素Logistic回归分析颅脑术后继发颅内感染的影响因素
变量 β SE Wald OR 95%CI P 上限 下限 糖尿病 1.584 0.520 9.286 4.876 1.760 13.509 0.002 脑脊液渗漏 1.568 0.484 10.493 4.795 1.857 12.378 0.001 乳酸脱氢酶 0.021 0.003 41.649 1.021 1.015 1.028 < 0.001 膜联蛋白A2 2.402 0.523 21.089 11.050 3.963 30.806 < 0.001 S100钙结合蛋白A10 2.742 0.608 20.313 15.515 4.709 51.117 < 0.001 表 3 脑脊液中Annexin A2、S100A10水平对颅脑术后发生继发颅内感染的预测价值
指标 AUC 95%CI 敏感度/% 特异度/% 临界值 P 膜联蛋白A2 0.788 0.731~0.838 72.50 77.50 1.85 ng/L < 0.001 S100钙结合蛋白A10 0.768 0.709~0.820 72.50 75.83 1.33 ng/L < 0.001 二者联合 0.865 0.815~0.905 76.67 80.00 — < 0.001 -
[1] WANG L Y, CAO X H, SHI L K, et al. Risk factors for intracranial infection after craniotomy: A case-control study[J]. Brain Behav, 2020, 10(7): e01658. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1658
[2] RICE C J, CHO S M, MARQUARDT R J, et al. Clinical course of infectious intracranial aneurysm undergoing antibiotic treatment[J]. Neurol Sci, 2019, 403: 50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2019.06.004
[3] 吴小莉, 王波, 胡昔奇, 等. "四洗法"消毒预防脑室-腹腔分流术后颅内感染的效果分析[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(6): 23-25, 39. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20213904 [4] 叶波, 叶斌. 术后颅内感染相关危险因素及早期炎症指标表达特点分析[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2018, 46(6): 646-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYY201806023.htm [5] DALLACASAGRANDE V, HAJJAR K A. Annexin A2 in Inflammation and Host Defense[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(6): 1499. doi: 10.3390/cells9061499
[6] LOU Y, HAN M, LIU H, et al. Essential roles of S100A10 in Toll-like receptor signaling and immunity to infection[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17(10): 1053-1062. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0278-1
[7] 中华医学会神经外科学分会, 中国神经外科重症管理协作组. 中国神经外科重症患者感染诊治专家共识(2017)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2017, 97(21): 1607-1614. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.21.005 [8] GUERIN B, VORK D L, EGUIGUREN L, et al. Labyrinthine Sequestrum: A Case Report and Review of the Literature[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(3): 340-343. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001676
[9] MO S, WEI L, CHEN H, et al. A chinese case of prevotella intermedia and streptococcus constellatus intracranial mixed infection[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2018, 33(1): 161-166. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0142-x
[10] HUSSEIN K, RABINO G, FEDER O, et al. Risk factors for meningitis in neurosurgical patients with cerebrospinal fluid drains: prospective observational cohort study[J]. Acta Neurochir (Wien), 2019, 161(3): 517-524. doi: 10.1007/s00701-019-03801-y
[11] GU L, YANG X L, YIN H K, et al. Application value analysis of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in the diagnosis of intracranial infection after craniocerebral surgery[J]. World Clin Cases, 2020, 8(23): 5894-5901. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5894
[12] GABEL M, ROYER C, THAHOULY T, et al. Annexin A2 Egress during Calcium-Regulated Exocytosis in Neuroendocrine Cells[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(9): 2059. doi: 10.3390/cells9092059
[13] NA POMBEJRA S, SALEMI M, PHINNEY B S, et al. The Metalloprotease, Mpr1, Engages AnnexinA2 to Promote the Transcytosis of Fungal Cells across the Blood-Brain Barrier[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 296. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00296
[14] ZHOU C M, LUO L M, LIN P, et al. Annexin A2 regulates unfolded protein response via IRE1-XBP1 axis in macrophages during P. aeruginosa infection[J]. Leukoc Biol, 2021, 110(2): 375-384. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3A1219-686RR
[15] FANG W, FA Z Z, XIE Q, et al. Complex Roles of Annexin A2 in Host Blood-Brain Barrier Invasion by Cryptococcus neoformans[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2017, 23(4): 291-300. doi: 10.1111/cns.12673
[16] BHARADWAA, KEMPSTER E, WAISMAN D M. The Annexin A2/S100A10 Complex: The Mutualistic Symbiosis of Two Distinct Proteins[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(12): 1849. doi: 10.3390/biom11121849
[17] ZHANG H, LU D, ZHANG Y, et al. Annexin A2 regulates Mycoplasma bovis adhesion and invasion to embryo bovine lung cells affecting molecular expression essential to inflammatory response[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13(1): 974006.
[18] ZHANG Y, YANG X, ZHU X L, et al. S100A gene family: immune-related prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for low-grade glioma[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2021, 13(11): 15459-15478.
[19] LEE T, BULETKO A B, MATTHEW J, et al. Bloodstream infection is associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage and infectious intracranial aneurysm in left ventricular assist devices[J]. Perfusion, 2020, 35(2): 117-120. doi: 10.1177/0267659119858853
[20] ZHONG X, LI X, SHAO S, et al. A case of infectious intracranial dissecting aneurysm[J]. Neurol India, 2017, 65(2): 405-407. doi: 10.4103/neuroindia.NI_1223_15
[21] 严秀友, 肖炳祥, 冯路, 等. 脑出血血肿清除术后颅内感染影响因素及脑脊液NT-proBNP、NSE、LDH预测价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2022, 32(10): 1509-1513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202210016.htm




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号