Diagnostic efficacy of serum microRNA-375 and microRNA-760 combined with liver enhancement computed tomography in hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨血清微小RNA-375(miR-375)、微小RNA-760(miR-760)联合肝脏增强CT技术对肝细胞癌(HCC)的诊断效能。
方法选取144例HCC患者纳入癌症组,另选取同期144例非肿瘤肝病患者纳入良性组,检测2组患者血清miR-375、miR-760表达水平。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,分析血清miR-375、miR-760表达水平联合肝脏增强CT对HCC的诊断价值。采用Kappa检验分析血清miR-375、miR-760表达水平和肝脏增强CT单独及联合诊断HCC与“金标准”病理结果的一致性。
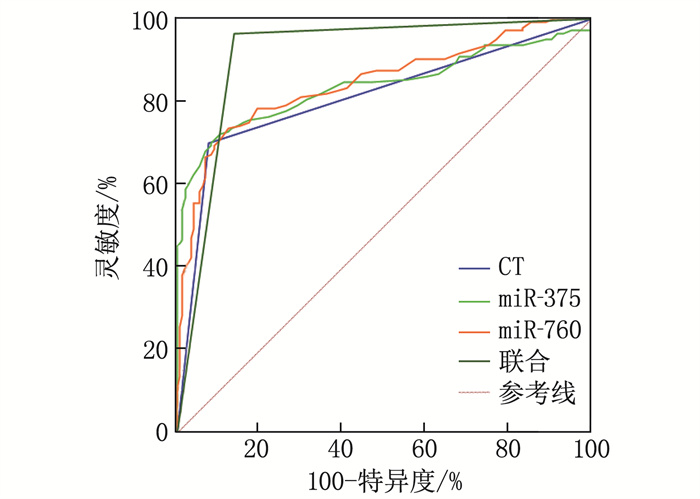
结果癌症组患者血清miR-375、miR-760表达水平均低于良性组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。HCC患者血清miR-375、miR-760表达水平均与肿瘤数目、肿瘤直径、TNM分期、远处器官转移、分化程度、门静脉癌栓、乙型肝炎表面抗原相关(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析结果显示,血清miR-375、miR-760和肝脏增强CT联合诊断HCC的曲线下面积(AUC)显著大于三者单独诊断的AUC(P<0.05), 与病理结果的一致性极高(Kappa=0.826)。
结论HCC患者血清miR-375、miR-760表达水平低于非肿瘤肝病患者,血清miR-375、miR-760水平和肝脏增强CT技术三者联用可显著提升对HCC的诊断效能。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the diagnostic efficacy of serum microRNA-375 (miR-375) and microRNA-760 (miR-760) combined liver enhancement computed tomography(CT) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
MethodsA total of 144 patients with HCC were included in cancer group, and another 144 patients with benign liver tumors in the same period were included in benign group. The expression levels of serum miR-375 and miR-760 were measured in both groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to analyze the diagnostic value of serum miR-375 and miR-760 expression levels combined with liver enhancement CT in HCC. The Kappa test was used to analyze the consistency of lonely detection of serum miR-375, miR-760 levels and liver enhancement CT, and their combined diagnosis for HCC with the gold standard pathological results.
ResultsThe expression levels of serum miR-375 and miR-760 in the cancer group were significantly lower than those in the benign group (P<0.05). The expression levels of serum miR-375 and miR-760 in patients with HCC were correlated with the number of tumor, tumor diameter, TNM stage, distant organ metastasis, degree of differentiation, portal vein tumor thrombus, and hepatitis B surface antigen (P<0.05). The ROC curve analysis showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of combined diagnosis of HCC using serum miR-375, miR-760, and liver enhancement CT was significantly greater than the AUC of individual diagnosis of the three methods (P<0.05), and there was a high consistency with pathological results (Kappa=0.826).
ConclusionThe expression levels of serum miR-375 and miR-760 in patients with HCC are lower than those in patients with benign liver tumors. The combined use of serum miR-375 and miR-760 levels and liver enhancement CT technology can significantly improve the diagnostic efficacy of HCC.
-
-
表 1 引物序列
基因 上游引物 下游引物 miR-375 5′-AGCCGTTTGTTCGTTCGGCT-3′ 5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′ miR-760 5′-AATCTGGTGGCTGTGCACAC-3′ 5′-CCTTGGGCTTGAATGGAGT-3′ U6 5′-CATCCGATAA AATTGGAACGA-3′ 5′-TTTGTGCGTGTCATCCTTGCG-3′ miR-375: 微小RNA-375; miR-760: 微小RNA-760。 表 2 肝脏增强CT诊断HCC与病理诊断结果的一致性分析
肝脏增强CT 病理诊断结果 Kappa P 肝细胞癌 良性肝肿瘤 肝细胞癌 101 11 0.625 <0.001 良性肝肿瘤 43 133 合计 144 144 表 3 miR-375、miR-760表达水平与HCC患者病理特征的关系($\overline x $ ±s)
病理特征 分类 n miR-375 miR-760 表达水平 t P 表达水平 t P 性别 男 83 0.85±0.19 1.631 0.105 0.80±0.17 0.786 0.433 女 61 0.80±0.17 0.78±0.12 年龄 <50岁 76 0.85±0.20 1.315 0.191 0.81±0.16 1.542 0.125 ≥50岁 68 0.81±0.16 0.77±0.15 肿瘤数目 单发 82 0.86±0.19 2.289 0.024 0.82±0.14 2.793 0.006 多发 62 0.79±0.17 0.75±0.16 肿瘤直径 <5 cm 95 0.87±0.17 3.776 <0.001 0.83±0.17 4.404 <0.001 ≥5 cm 49 0.75±0.20 0.71±0.12 TNM分期 Ⅰ~Ⅱ期 89 0.89±0.20 5.109 <0.001 0.85±0.16 6.248 <0.001 Ⅲ期 55 0.73±0.15 0.69±0.13 远处器官转移 有 118 0.81±0.16 2.834 0.005 0.77±0.14 3.077 0.003 无 26 0.92±0.25 0.87±0.19 分化程度 中/高分化 98 0.85±0.18 2.214 0.028 0.81±0.16 2.591 0.011 低分化 46 0.78±0.17 0.74±0.13 门静脉癌栓 有 31 0.74±0.13 3.031 0.003 0.71±0.12 3.236 0.002 无 113 0.85±0.19 0.81±0.16 乙型肝炎表面抗原 阳性 111 0.81±0.19 2.522 0.013 0.77±0.13 2.991 0.003 阴性 33 0.90±0.14 0.86±0.21 -
[1] VOGEL A, MEYER T, SAPISOCHIN G, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400(10360): 1345-1362. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4
[2] 王丽菲, 罗龙龙, 郑英, 等. 巨噬细胞移动抑制因子在肝细胞癌中的研究进展[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2023, 27(14): 126-130. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20231220 [3] 彭敏. 动态增强CT诊断肝细胞癌的影像表现及应用价值[J]. 现代诊断与治疗, 2021, 32(20): 3311-3312. [4] 刘向东, 闫松果, 孙世松. 动态增强CT扫描与MRI对肝细胞癌的诊断价值及影像学特征分析[J]. 实用癌症杂志, 2023, 38(1): 89-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5930.2023.01.025 [5] WEI J H, LU Y R, WANG R Q, et al. MicroRNA-375: potential cancer suppressor and therapeutic drug[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(9): BSR20211494. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211494
[6] JOKOVIC S M, DOBRIJEVIC Z, KOTARAC N, et al. MiR-375 and miR-21 as potential biomarkers of prostate cancer: comparison of matching samples of plasma and exosomes[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(12): 2320. doi: 10.3390/genes13122320
[7] MANVATI M K S, KHAN J, VERMA N, et al. Association of miR-760 with cancer: an overview[J]. Gene, 2020, 747: 144648. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144648
[8] HUANG X J, LAI S Q, QU F L, et al. CCL18 promotes breast cancer progression by exosomal miR-760 activation of ARF6/Src/PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 2022, 25: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.03.004
[9] 黄伟康, 文戈, 吴水天, 等. CT扫描联合血清AFP-L3、CEA在诊断肝细胞癌中的应用价值分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2021, 31(5): 810-813. [10] 王莉琳, 张永宏, 陈新月. 2010年美国肝病年会(AASLD)肝细胞癌诊疗指南[J]. 北京医学, 2011, 33(3): 236-251. [11] 郑可国, 许达生, 李子平. 肝细胞癌临床CT诊断[M]. 广州: 广东世界图书出版公司, 2003: 22-67. [12] CALDERARO J, SERAPHIN T P, LUEDDE T, et al. Artificial intelligence for the prevention and clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(6): 1348-1361. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.01.014
[13] SUGAWARA Y, HIBI T. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biosci Trends, 2021, 15(3): 138-141. doi: 10.5582/bst.2021.01094
[14] LLOVET J M, BAERE T D, KULIK L, et al. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(5): 293-313. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00395-0
[15] 吴建峰, 李林静, 方春, 等. 个体化碘对比剂注射速率方案在肝脏增强CT中提高增强质量一致性的价值[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2022, 24(3): 456-458. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20210518-00556 [16] LIU C F, LI J, WANG W, et al. MiR-206 inhibits liver cancer stem cell expansion by regulating EGFR expression[J]. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19(10): 1077-1088. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1739808
[17] LIU Y, WANG Q Y, WEN J, et al. MiR-375: a novel multifunctional regulator[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 275: 119323. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119323
[18] NI H W, QIN H, SUN C, et al. MiR-375 reduces the stemness of gastric cancer cells through triggering ferroptosis[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2021, 12(1): 325. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02394-7
[19] WANG C, LUO J, CHEN Z H, et al. MiR-375 impairs the invasive capabilities of hepatoma cells by targeting HIF1α under hypoxia[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(2): 493-502. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06202-9
[20] XU R, YIN S W, ZHENG M, et al. Circular RNA circZFR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating miR-375/HMGA2 axis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(12): 4361-4373. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06805-2
[21] WU X D, CHEN H, LIU N, et al. Curcumin suppresses lung cancer progression via circRUNX1 mediated miR-760/RAB3D axis[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2023, 14(5): 506-516. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14773
[22] WANG Q H, WANG G, XU X D, et al. MiR-760 mediated the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating HMGA2[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2021, 222: 153420. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153420
[23] YIN L N, SUN T T, LIU R B. NACC-1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell malignancy and is targeted by miR-760[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2020, 52(3): 302-309. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmz167
[24] LI J F, QIN Y Y, WANG W J, et al. Peiminine inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer through up-regulating miR-760 via declining the expression of long noncoding RNA LINC00659[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2021, 32(2): 148-156. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000981
-
期刊类型引用(40)
1. 陈龙飞. 浸骨水泥明胶海绵预填注对胸腰椎OVCF患者PKP手术治疗后骨水泥渗漏的影响. 菏泽医学专科学校学报. 2024(04): 12-16+23 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 马福云,马恩波,张昊,戴鸿浩,徐斌斌,孙浩. 3D打印技术在椎体压缩性骨折PKP中的应用效果分析. 青海医药杂志. 2024(08): 18-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 牛丹英,张苗. 早期康复护理对股骨颈骨折术后患者Barthel指数及Harris髋关节评分的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2023(01): 164-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郭永传,马守战,贾思明. 经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的效果观察. 中国实用医刊. 2023(01): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周正龙,陈晓磊. 经皮穿刺骨水泥椎体成形术治疗老年椎体压缩性骨折的临床效果. 临床医学工程. 2023(04): 477-478 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 蔡丽萍. 损害控制在高龄重度骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折围术期患者中的应用. 当代护士(中旬刊). 2023(05): 59-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张慧燕. 格林模式配合微信平台的连续康复护理对老年髋部骨折患者髋关节功能的影响. 医疗装备. 2022(07): 173-175 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈凝,熊虎林,马鑫,魏新祺. 椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折54例的近期疗效. 福建医药杂志. 2022(05): 114-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈志军,黎树佳,丁小科,伍志健,邓征智. 经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎急性压缩性骨折2000例的临床经验总结. 系统医学. 2022(22): 140-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 黄宏伟,黄健,谢永辉,陈钢,李始汉,梁志豪. 两种骨水泥注入器在经皮椎体成形术中治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的临床比较. 中国当代医药. 2021(19): 58-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 房魏,武厚志,张伟. 上海某社区提升骨质疏松症患者用药依从性的干预研究. 上海预防医学. 2021(03): 216-219 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 吴刚,张永锋. 温针灸加补肾通络方对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨代谢及疼痛的影响. 检验医学与临床. 2021(21): 3172-3175 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 赖细梅,胡志容,谢爱婷. 时机理论指导的延续性护理对行经皮椎体成形术的椎体压缩性骨折患者的应用效果. 中西医结合护理(中英文). 2021(06): 166-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 曹运军. 高粘度骨水泥经皮椎体成形术在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者中的应用. 医疗装备. 2020(03): 82-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李英昌,杨夏阳,胡浩,王强. 经皮椎体成形术用于老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折临床治疗的效果分析. 中国社区医师. 2020(04): 95-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 刘艳茹,刘又文. 老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折微创术后再发骨折的相关因素分析. 中国老年学杂志. 2020(05): 987-989 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 刘祥志. 经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的临床效果观察. 中国医药指南. 2020(06): 214 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 夏文卫. 经椎旁间隙入路手术对胸腰椎骨折患者日常生活能力及疼痛程度的影响. 河南医学研究. 2020(05): 819-820 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 贺富文,净惠明,杜秋珊. CT三维重建及薄层扫描诊断良性和恶性脊柱骨折临床性分析. 医学影像学杂志. 2020(01): 167-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 张敏,吕雪,张梦楠,张静. 基于快速康复理念的团队康复模式对缺血型股骨头坏死患者术后肌酸磷酸激酶、Harris评分及改良Barthel指数的影响. 河北医药. 2020(07): 1110-1113 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 李相军. 96例骨质疏松性椎体骨折患者应用脊柱微创手术治疗的临床效果观察. 现代诊断与治疗. 2020(09): 1442-1443 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 李军,黄志雄,王洁艳. 经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的疗效探讨. 黑龙江中医药. 2020(03): 129-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 张恒. 经皮双侧加压空心螺钉内固定对踝关节骨折患者骨折愈合时间及踝关节功能的影响. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报. 2020(17): 2126-2128 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 拉元红. 探讨PVP治疗老年性骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的临床效果. 世界最新医学信息文摘. 2019(01): 77+79 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 宋思桐. 内固定结合椎体成形术治疗脊柱骨折的效果观察. 中国民康医学. 2019(01): 14-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 向峰,刘耀斌,杨红彦. 椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的近期效果及对患者VAS及满意度评分的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2019(06): 55-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 李亚杰. PVP治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折临床分析. 中国城乡企业卫生. 2019(06): 149-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 靳宇飞,朱军,殷翔,赵建华,刘鹏. 老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折微创术后再发骨折的影响因素分析. 创伤外科杂志. 2019(08): 587-590 .  百度学术
百度学术
29. 张笋,肖雪青. 早期肠内营养联合持续性护理干预对年龄>65岁老年髋部骨折患者术后生活质量的影响. 河南医学研究. 2019(16): 3041-3043 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 朱之桦. 椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的近期效果及对患者VAS评分影响分析. 内蒙古医科大学学报. 2019(S1): 18-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
31. 周迎锋,张超,马超,徐海斌. 经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的临床效果. 内蒙古医学杂志. 2019(10): 1206-1207 .  百度学术
百度学术
32. 杨杰,范开,朱守雷,杨建东. 经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性压缩骨折新鲜与陈旧性骨折的对比分析. 临床医药文献电子杂志. 2019(93): 29+45 .  百度学术
百度学术
33. 李军,达朝明. 椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的近期疗效及对VAS评分的影响. 中国全科医学. 2019(S2): 113-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
34. 徐静,李俊霞. 促进康复计划对老年下肢骨折手术预后及生活质量的影响. 河南科技大学学报(医学版). 2018(02): 150-151+156 .  百度学术
百度学术
35. 钟成跃,凤旭东,王灿,周辉. 七氟醚+臂丛神经阻滞在小儿骨折术中的应用及安全性分析. 实用中西医结合临床. 2018(04): 102-103+134 .  百度学术
百度学术
36. 韩金龙. 椎体成形术在老年脊柱骨质疏松中的应用. 世界最新医学信息文摘. 2018(10): 44-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
37. 王自刚,盛文辉. 经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的应用效果观察. 中国当代医药. 2018(19): 95-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
38. 傅磊,梁伟之. 经皮椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的临床效果观察. 基层医学论坛. 2018(31): 4488-4489 .  百度学术
百度学术
39. 王涛,高宗保. 经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的临床效果. 临床医学研究与实践. 2018(35): 58-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
40. 王琳. 椎体成形术后疼痛缓解欠佳的原因及对策. 深圳中西医结合杂志. 2018(22): 182-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号