Diagnostic value of exhaled nitric oxide, alveolar nitric oxide and eosinophils in respiratory diseases among children aged 3 to 6 years
-
摘要:目的
探讨呼出气一氧化氮(FeNO)、肺泡一氧化氮(CaNO)和嗜酸性粒细胞(EOS)在甘肃省兰州市3~6岁儿童呼吸系统疾病鉴别诊断中的应用价值。
方法选取确诊哮喘或过敏性鼻炎或下呼吸道感染的360例3~6岁儿童作为研究对象, 采用斯皮尔曼秩相关系数评估FeNO、CaNO、EOS的相关性,通过随机森林模型、受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线、多因素逻辑回归分析评估FeNO、CaNO和EOS对3种疾病的鉴别诊断价值。
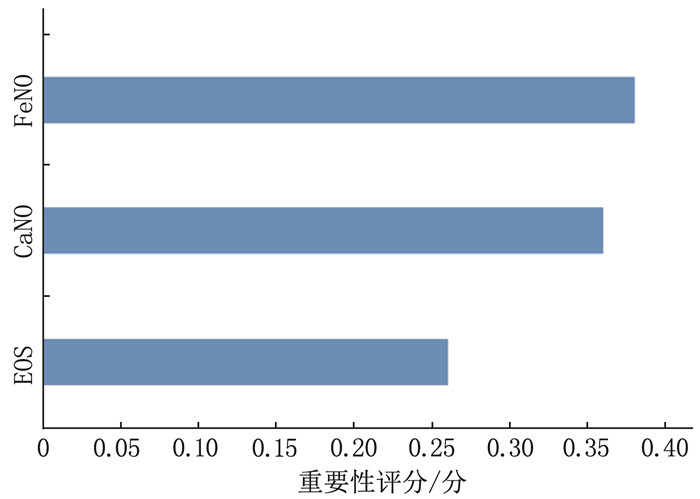
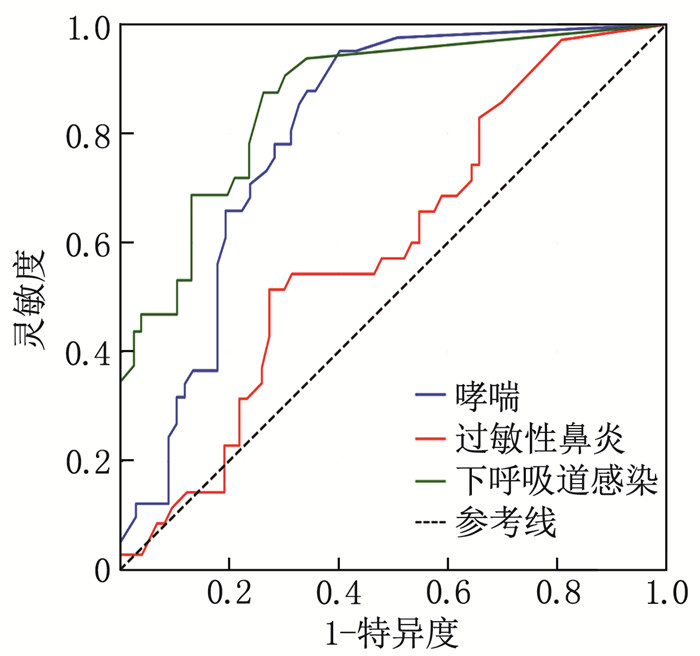
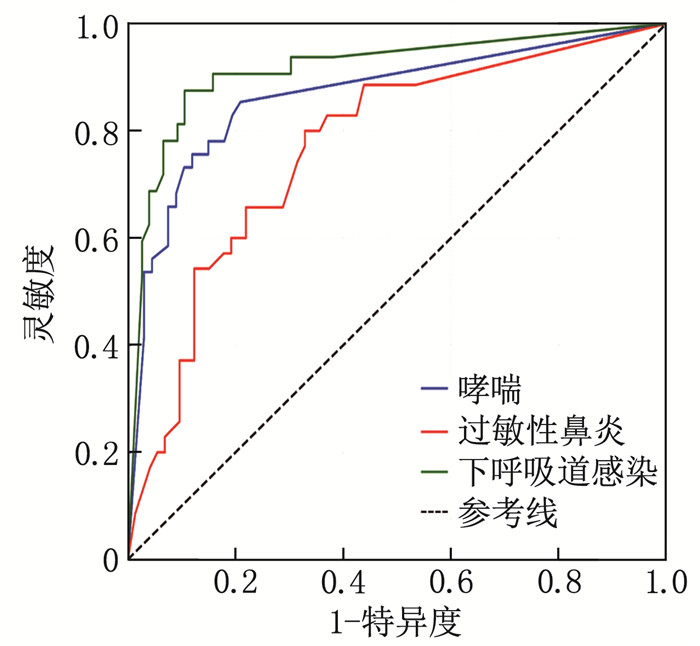
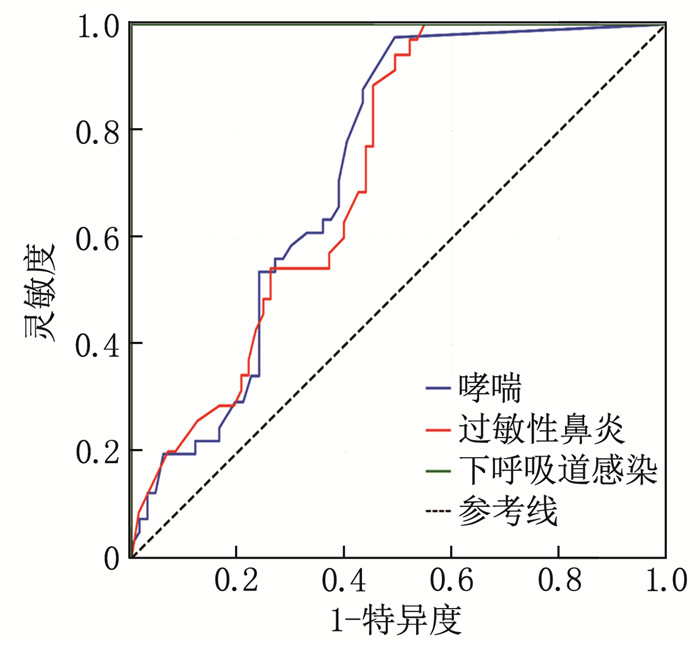
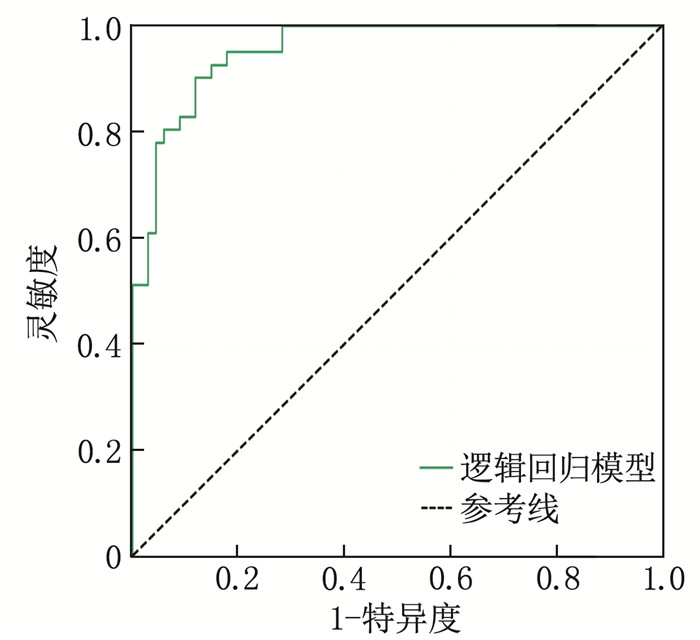
结果哮喘患儿的FeNO、CaNO中位数高于其他疾病患儿,过敏性鼻炎患儿的EOS中位数最低,下呼吸道感染患儿的FeNO、CaNO中位数最低。相关性分析结果显示, FeNO与CaNO呈正相关(r=0.59, P < 0.05), FeNO与EOS呈负相关(r=-0.61, P < 0.05), CaNO与EOS呈负相关(r=-0.63, P < 0.05)。随机森林模型显示, FeNO在疾病分类中的重要性最高。ROC曲线分析结果显示, 3种疾病中, FeNO、CaNO、EOS对下呼吸道感染的诊断效能均最高(曲线下面积分别为0.86、0.91、1.00)。多因素逻辑回归模型诊断哮喘的曲线下面积为0.96, 灵敏度为0.902, 特异度为0.881。
结论FeNO、CaNO和EOS在鉴别诊断兰州地区3~6岁儿童哮喘、过敏性鼻炎、下呼吸道感染方面展现出较好的潜力,且基于三者构建的多因素逻辑回归模型可有效提升对哮喘的诊断准确性。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the application value of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), alveolar nitric oxide (CaNO), and eosinophils (EOS) in the differential diagnosis of respiratory diseases in children aged 3 to 6 years in Lanzhou, Gansu Province.
MethodsA total of 360 children aged 3 to 6 years with confirmed asthma, allergic rhinitis, or lower respiratory tract infection were selected as research subjects. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was used to evaluate the correlation between FeNO, CaNO and EOS. The diagnostic value of FeNO, CaNO, and EOS for the differential diagnosis of the three diseases was assessed through random forest models, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and multivariate Logistic regression analysis.
ResultsThe median valuesof FeNO and CaNO were higher in asthmatic children than in those with other diseases. The median value of EOS was the lowest in children with allergic rhinitis, and the median values of FeNO and CaNO were the lowest in children with lower respiratory tract infection. Correlation analysis showed a positive correlation between FeNO and CaNO (r=0.59, P < 0.05), a negative correlation between FeNO and EOS (r=-0.61, P < 0.05), and a negative correlation between CaNO and EOS (r=-0.63, P < 0.05). The random forest model indicated that FeNO had the highest importance in disease classification. ROC curve analysis revealed that FeNO, CaNO, and EOS had the highest diagnostic efficiency for lower respiratory tract infection among the three diseases (with areas under the curve of 0.86, 0.91, and 1.00, respectively). The area under the curve of the multivariate Logistic regression model for diagnosing asthma was 0.96, with a sensitivity of 0.902 and a specificity of 0.881.
ConclusionFeNO, CaNO and EOS demonstrate good potential in the differential diagnosis of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and lower respiratory tract infection in children aged 3 to 6 years in Lanzhou. Furthermore, the multivariate Logistic regression model based on these three factors can effectively improve the diagnostic accuracy of asthma.
-
髋部骨折是骨科常见的一种骨折类型,主要包括粗隆间骨折和股骨颈骨折,多发于老年群体,严重影响患者的生活质量[1-2]。目前临床中多采用非手术保守方案或外科手术方案对髋部骨折患者进行治疗,但非手术保守治疗的周期较长,患者需长期卧床,易增大并发症发生风险,不利于患者骨折部位的康复[3]。随着外科手术水平的不断提升,内固定术和人工髋关节置换术逐渐成为临床治疗老年髋部骨折患者的主要方案,但目前临床对于如何选择最佳手术治疗方案仍存在一定争议[4]。本研究探讨了人工髋关节置换术与内固定对老年髋部骨折患者术后功能康复的影响,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2016年1月—2018年6月本院收治的80例老年髋部骨折患者,按照随机双盲法分为2组,各40例。对照组中,男26例,女14例; 年龄60~78岁,平均(65.37±3.24)岁; 左髋17例,右髋23例。观察组中,男24例,女16例; 年龄60~79岁,平均(66.02±3.27)岁; 左髋19例,右髋21例。2组患者一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性。纳入标准: 经X线片检查确诊为髋部骨折; 患者均签署知情同意书。排除标准: 合并严重脏器功能障碍者; 精神异常、不具认知能力者; 对手术不耐受者。
1.2 方法
对照组行内固定治疗: ①股骨近端髓内钉固定术治疗(17例)。患者取仰卧位,使用骨科牵引床对患肢进行适当内旋,进行复位,并在C臂透视下确诊复位情况,于大粗隆定点向近端做切口,长约4 cm, 钝性切开部分臂中肌纤维,将导诊置入大粗隆顶点前外侧位置,并在C臂透视引导下插入主钉,而后使用体位瞄准器在股骨颈部位置入导针,待股骨外侧皮质完成钻孔后,打入螺旋刀片,并将主钉的尾帽置入,进行内固定,冲洗伤口,留置引流管,逐层缝合伤口。②动力髋螺钉内固定术(23例)。指导患者取仰卧位,将患侧髋粗隆部抬高,在C臂肌透视下先给予患肢外展30 °、内旋15 °的持续牵引,待透视可见满意复位后,于股骨近端外侧做一切口,沿着135 °导向器插入导针,使用扩孔器进行扩孔,并根据患者具体骨折情况选择适宜的动力髋螺钉,将其置入股骨颈骨质中,并将选择的配对动力髋螺钉钢板于股骨干实施固定,固定完成后,在C臂透视下观察骨折部位是否得到满意复位,若复位较好,可冲洗伤口,放置负压引流管,缝合伤口。
观察组行人工髋关节置换术: 患者取仰卧位,于髋关节后外侧做切口,长13~16 cm, 逐层分离肌群后,将髋关节囊切开,对骨折部位周边筋膜组织进行保护,进行大小转子复位,复位完成使用钢丝固定,并于小转子上方1.0 cm处进行股骨颈截骨取出,常规护理髋臼,放置臼杯,以小粗隆为中心向前方倾斜15 °后,使用髓腔锉进行扩髓处理,并测量股骨头长度,选择合适的股骨柄对股骨头假体实施置换,完成髋关节复位后,需对置换关节情况进行评价,在达到标准后,清洗伤口,置入负压引流管,缝合伤口。术后对2组患者进行6个月的跟踪随访。
1.3 观察指标
① 手术指标及首次负重时间: 记录2组患者术中出血量、手术时间、术后引流量及术后首次负重时间。②髋关节功能: 采用髋关节Harris评分量表评价患者术前、术后3个月及术后6个月髋关节功能恢复情况,分别从疼痛(0~44分)、日常活动(0~14分)、步态(0~11分)、步行距离(0~11分)、畸形(0~4分)、辅助行走(0~11分)及活动范围(0~5分)7个方面进行评价,总分100分,评分越高表示髋关节功能恢复越好。③并发症: 包括伤口感染、假体脱位、异位骨化、骨折、下肢深静脉血栓。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 24.0软件进行数据处理,计量资料以(x±s)表示,采用t检验,计数资料用[n(%)]表示,采用χ2检验, P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 手术指标及术后首次负重时间
对照组术中出血量低于观察组,术后首次负重时间晚于观察组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 2组手术时间及术后引流量比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 2组患者手术指标及术后首次负重时间对比(x±s)组别 术中出血量/mL 手术时间/min 术后引流量/mL 术后首次负重时间/d 对照组(n=40) 323.57±42.25 92.57±18.76 107.65±21.54 38.64±5.47 观察组(n=40) 472.65±58.16* 87.52±17.21 110.62±21.61 25.54±4.87* 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.2 髋关节功能
观察组术后3个月、6个月Harris评分均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 2组患者术前、术后3个月、6个月Harris评分对比(x±s)分 组别 术前 术后3个月 术后6个月 对照组(n=40) 45.62±4.57 70.25±6.01 81.24±8.74 观察组(n=40) 45.59±4.48 84.63±8.62* 91.68±6.52* 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.3 并发症
观察组的并发症发生率低于观察组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 2组患者并发症发生情况对比[n(%)]组别 伤口感染 假体脱位 异位骨化 下肢深静脉血栓 骨折 合计 对照组(n=40) 4(10.00) 0 2(5.00) 2(5.00) 6(15.00) 14(35.00) 观察组(n=40) 1(2.50) 2(5.00) 1(2.50) 0 2(5.00) 6(15.00)* 与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。 3. 讨论
髋部骨折是老年群体较为常见的一种骨折,占人体全身骨折的3%~4%, 严重影响患者的日常生活质量。目前临床针对髋部骨折的治疗方案较多,包括传统的保守治疗、内固定术及人工髋关节置换术等,其中保守治疗周期较长,患者需长期卧床,会导致患者机体各项生理机能衰退,易诱发褥疮、肺炎及泌尿系统感染等并发症,不仅影响患者骨折的康复,严重时还可危及老年患者生命安全[5-6]。外科手术是目前临床治疗老年髋部骨折的首选方法,而近年来随着置换术技术及内固定物的不断发展与完善,内固定术及人工髋关节置换术成为治疗髋部骨折的主要手术方式,外科手术治疗老年髋部骨折的目的在于减小创伤,缩短卧床时间,降低并发症发生率,促进髋关节功能改善[7-9]。
本研究结果显示,对照组术中出血量及术后3个月、6个月Harris评分显著低于观察组,术后首次负重时间晚于观察组,并发症发生率高于观察组。由此说明,人工髋关节置换术与内固定相比,更利于老年髋部骨折患者术后髋关节功能恢复,可缩短术后负重时间,利于改善患者预后。究其原因,动力髋螺钉内固定治疗是临床常用的手术方式,主要通过在轴向压力和垂直剪力共同作用,以达到固定骨折的效果,而股骨近端髓内钉固定术治疗是在动力髋螺钉内固定基础上改进而来,主要适用于各种股骨粗隆间骨折的治疗,尤其对骨折疏松患者治疗效果较佳,但内固定手术治疗创伤性较大[10-11]。70岁以上老年患者股骨颈解剖学特点较为特殊,在行内固定术治疗后,仍存在股骨头缺血性坏死的风险,且老年患者均存在不同程度的骨质疏松,在固定后易发生固定失败,增大再次骨折的风险,不利于患者术后髋关节功能恢复,推迟术后负重时间[12-13]。与内固定治疗相比,人工髋关节置换术创伤较小,不会离断髋关节肌肉,能够最大程度减少手术对骨骼肌、韧带及关节囊的损伤,更利于提高骨折内固定的效果,避免愈合畸形、延迟骨折愈合及股骨头坏死等不良现象,还可有效促进患者术后髋关节功能恢复,使患者尽快下床活动,利于降低肌肉萎缩及下肢静脉血栓等并发症的发生率,缩短患者术后负重时间,改善患者预后[14-15]。与内固定治疗相比,人工髋关节置换术更利于降低老年髋部骨折患者术后的并发症发生率,并促进术后髋关节功能恢复,可作为临床治疗老年髋部骨折的首选方案。
综上所述,与内固定治疗相比,人工髋关节置换术更利于促进老年髋部骨折患者术后髋关节功能恢复,可缩短术后首次负重时间,降低术后并发症发生率,安全性更高。
-
表 1 哮喘、过敏性鼻炎和下呼吸道感染疾病患儿的FeNO、CaNO、EOS的描述性统计分析
指标 统计结果 下呼吸道感染(n=120) 哮喘(n=120) 过敏性鼻炎(n=120) FeNO/(×10-9mol/L) 平均值 14.05 26.60 21.37 标准差 4.55 4.63 5.06 最小值 2.20 13.90 10.87 25%值 10.97 24.14 17.21 中位数 13.92 26.63 21.93 75%值 17.14 28.91 24.31 最大值 24.67 39.32 40.26 CaNO/(×10-9mol/L) 平均值 4.38 9.40 6.74 标准差 1.46 1.57 1.42 最小值 0.44 5.37 3.46 25%值 3.56 8.23 5.74 中位数 4.17 9.39 6.74 75%值 5.41 10.57 7.75 最大值 8.06 12.60 10.37 EOS/% 平均值 11.75 2.75 2.17 标准差 1.50 1.37 1.29 最小值 7.65 0.34 0.47 25%值 10.81 1.72 1.21 中位数 11.80 2.83 2.00 75%值 12.62 3.70 3.00 最大值 15.47 6.42 6.24 -
[1] 洪建国. 我国儿童哮喘流行病学和诊治状况[J]. 中华医学信息导报, 2020, 35(2): 22-22. [2] WISE S K, DAMASK C, ROLAND L T, et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: Allergic rhinitis-2023[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2023, 13(4): 293-859.
[3] ZHU H Y, HAO C L, YU X M, et al. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) integrating airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) examination promotes etiologic diagnosis and treatment for children with chronic cough[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2021, 27: e928502.
[4] CELIS-PRECIADO C A, LACHAPELLE P, COUILLARD S. Exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO): bridging a knowledge gap in asthma diagnosis and treatment[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2023, 53(8): 791-793. doi: 10.1111/cea.14374
[5] BARAÑSKI K, ZEJDA J E. Screening accuracy of FeNO measurement for childhood asthma in a community setting[J]. Children, 2022, 9(6): 858. doi: 10.3390/children9060858
[6] SCHNEIDER A, FADERL B, SCHWARZBACH J, et al. Prognostic value of bronchial provocation and FENO measurement for asthma diagnosis: results of a delayed type of diagnostic study[J]. Respir Med, 2014, 108(1): 34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2013.11.008
[7] 李芮, 董晓艳, 蒋鲲, 等. 口鼻呼出气一氧化氮检测在儿童支气管哮喘控制评估及过敏性鼻炎诊断中的应用[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2022, 24(1): 90-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDKZ202201013.htm [8] SCHNEIDER A, BRUNN B, HAPFELMEIER A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of FeNO in asthma and predictive value for inhaled corticosteroid responsiveness: a prospective, multicentre study[J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2022, 50: 101533. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101533
[9] MUNTEAN I A, BOCSAN I C, VESA S, et al. Could FeNO predict asthma in patients with house dust mites allergic rhinitis[J]. Medicina, 2020, 56(5): 235. doi: 10.3390/medicina56050235
[10] NAKWAN N, THIDARAT RUKLERD T, PERKLEANG T, et al. The levels and correlations of FeNO, blood eosinophils and lung function in well-controlled asthma[J]. Adv Respir Med, 2022, 90(3): 183-192. doi: 10.5603/ARM.a2022.0015
[11] 高永伟. 呼出气一氧化氮检测在小儿支气管哮喘早期诊断及病情评估中的应用[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2020, 24(3): 90-93. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.202003026 [12] LIPWORTH B, KUO C R, CHAN R. 2020 Updated Asthma Guidelines: clinical utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (Feno) in asthma management[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 146(6): 1281-1282. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.03.006
[13] WANG J, WANG W T, LIN H, et al. Role of pulmonary function and FeNO detection in early screening of patients with ACO[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(2): 830-837.
[14] 任莉, 杨俊. 呼出气一氧化氮在儿童哮喘管理中的临床价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(5): 96-99. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20214064 -
期刊类型引用(24)
1. 林冰冰. 老年髋部骨折人工股骨头置换术后出院准备度评估及影响因素、护理对策分析. 中外医学研究. 2024(30): 92-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丁玉辉,胡振忠,李东超. 人工髋关节置换手术在老年髋部骨折患者治疗中的应用效果. 医药前沿. 2024(14): 51-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王金英,钟明强,郭玲,赵勇. 超声引导下髂筋膜神经阻滞联合喉罩全身麻醉在AD老年患者髋部骨折手术中的临床应用. 吉林医学. 2023(01): 92-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈敏,曾志,刘建,项惠灿. 血栓弹力图和凝血四项在髋部骨折术后凝血功能中的相关性. 数理医药学杂志. 2023(01): 16-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐冬利,王晓娜. 无痛康复治疗技术在人工髋关节置换术后的应用效果研究. 临床医学工程. 2023(09): 1249-1250 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田涛,陆定松,杨志奎,李鹏. 内固定术与人工关节置换术治疗老年髋部骨折的临床效果比较. 临床医学研究与实践. 2022(03): 74-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郭树胜,常连胜. 内固定手术与人工髋关节置换术治疗老年髋部骨折的疗效及术中出血量对比. 数理医药学杂志. 2022(03): 332-334 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 肖虹. 家居音乐康复操对老年髋部骨折出院患者髋关节功能、生活质量及自护能力的影响. 中国医药指南. 2022(10): 92-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 黄敏. 人工髋关节置换术与股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定术治疗老年不稳定型髋部骨折的效果比较. 中国民康医学. 2022(05): 141-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 毛团员,易倩,婷游辉. 人工髋关节置换术与内固定治疗髋部骨折对患者髋关节功能评分的影响. 透析与人工器官. 2022(01): 26-28+32 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 朱鑫,熊小云,李鹏,章晓富,陈高飞. 基于信息化沟通的长期强化家庭康复训练在老年髋部骨折术后的应用观察. 中国疗养医学. 2022(06): 607-610 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘海龙,刘广,王志刚,龚箭. 内固定术与人工髋关节置换术治疗老年髋部骨折患者的临床效果. 中国医药指南. 2022(17): 104-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 郝光明. 人工关节置换术对老年髋部骨折患者髋关节功能康复的影响. 反射疗法与康复医学. 2022(06): 61-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 方雄明,陈国勋,刘旭良,李伯庭,王兆杰. 人工关节置换术对髋部骨折患者髋部功能与骨密度的影响. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志. 2022(21): 62-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 彭送兰,李延谦,朱丽青. 长期强化家庭康复训练法对老年髋部骨折患者术后功能恢复情况的影响. 智慧健康. 2022(23): 185-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 刘韶华,李琨,朱丽. 以问题为中心的质量改进护理模式及护理标识在髋关节置换术患者中的应用. 齐鲁护理杂志. 2021(02): 106-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 谢勇. 髋关节骨折患者人工髋关节置换治疗的效果及对患者血清白细胞介素-6 C反应蛋白肿瘤坏死因子-α水平的影响. 实用医技杂志. 2021(07): 936-938 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 侯光军. 高龄转子间骨折内固定术与人工关节置换术治疗效果对比. 黑龙江中医药. 2021(04): 139-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 李国. 人工髋关节置换术治疗老年髋部骨折的临床价值分析. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志. 2021(19): 51-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 李国. 老年髋部骨折分别应用人工髋关节置换术与内固定术治疗的临床疗效观察. 黑龙江医药. 2021(06): 1440-1442 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 李光明. 股骨近端髓内钉螺旋刀片内固定与人工关节置换术在老年股骨粗隆间骨折中的临床对比分析. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志. 2021(03): 15-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 代巍,代颖,芦英,王雪力,王岩峰. 塞来昔布在全髋关节置换手术超前镇痛中的应用价值分析. 实用药物与临床. 2020(01): 30-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 彭美荣,梁皑琨. 老年髋部骨折病人术后耐受力及髋关节功能恢复影响因素的调查分析. 全科护理. 2020(10): 1270-1273 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 韩春芝,范捷,刘淑杰,周蓓,苏洋,臧波,丁丽. 超声引导下髂筋膜阻滞用于老年髋部骨折手术的临床价值. 医学影像学杂志. 2020(12): 2356-2358 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
