Impact of controlled hypotension by cerebral oxygen saturation monitoring on brain protection and cognitive function in anesthesia patients
-
摘要:目的
分析脑氧饱和度(rSO2)监测控制性降压(CH)对麻醉患者脑保护和认知功能的影响。
方法选取行rSO2监测CH麻醉患者200例为研究对象。根据行rSO2监测CH患者术后是否发生围术期神经认知障碍(PND)分为正常组(n=137)和PND组(n=63), 收集患者治疗前临床资料。采用单因素分析确定行rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的影响因素。采用多因素二元Logistic回归分析法筛选行rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的独立危险因素。基于筛选出的独立危险因素构建预测模型,并绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估其预测价值。
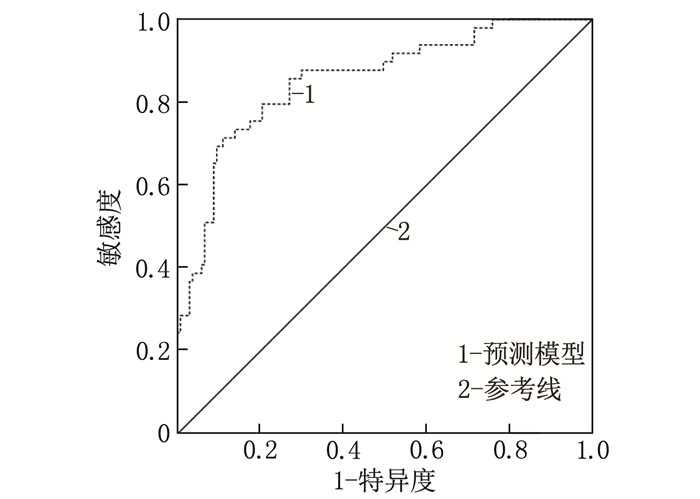
结果年龄、术中出血量、行血管外科手术、术中20 min rSO2监测值、术中20 min中心静脉压(CVP)和合并高血压、脑卒中以及手术时间是行rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的影响因素(P < 0.05)。患者年龄>55岁、术中20 min CVP高、术中20 min rSO2监测值低及行血管外科手术是行rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的独立危险因素(P < 0.05)。ROC曲线分析结果显示,预测模型曲线下面积(AUC)为0.855。
结论临床可通过控制术中CVP以减少失血量,并依据rSO2监测结果及时调整治疗方案,从而降低行rSO2监测CH患者(年龄>55岁,行血管外科手术)术后并发PND的风险。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the impact of controlled hypotension (CH) by cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2) monitoring on brain protection and cognitive function in anesthetized patients.
MethodsA total of 200 patients undergoing rSO2-monitored CH were enrolled. Patients were divided into normal group (n=137) and postoperative neurocognitive disorder (PND) group (n=63) based on whether they developed PND after surgery. Preoperative clinical data were collected. Univariate analysis was performed to identify factors influencing the occurrence of PND in rSO2-monitored CH patients. Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis was used to screen for independent risk factors. A predictive model was constructed based on the identified independent risk factors, and its predictive value was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
ResultsAge, intraoperative blood loss, vascular surgery, 20-minute rSO2 monitoring values, 20-minute central venous pressure (CVP), history of hypertension, stroke and operative time were identified as factors affecting the occurrence of PND in rSO2-monitored CH patients (P < 0.05). Independent risk factors for PND included age >55 years, high CVP during 20 minutes of surgery, low rSO2 monitoring values during 20 minutes and undergoing vascular surgery (P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that the area under the curve (AUC) for the predictive model was 0.855.
ConclusionClinically, the risk of PND in rSO2-monitored CH patients (age >55 years, undergoing vascular surgery) can be reduced by controlling intraoperative CVP to minimize blood loss and by timely adjustment of treatment plans based on rSO2 monitoring results.
-
-
表 1 患者麻醉前、术后的MMSE、MoCA评分比较(n=200)(x ± s)
分 指标 麻醉前 术后第1天 术后1周 MMSE评分 28.48±0.90 23.43±1.69* 26.64±2.31*# MoCA评分 23.32±3.92 17.25±3.55* 20.44±4.23*# 与麻醉前比较, * P < 0.05; 与术后第1天比较, #P < 0.05。 表 1 患者麻醉前、术后的MMSE、MoCA评分比较(n=200)(x ± s)
分 指标 麻醉前 术后第1天 术后1周 MMSE评分 28.48±0.90 23.43±1.69* 26.64±2.31*# MoCA评分 23.32±3.92 17.25±3.55* 20.44±4.23*# 与麻醉前比较, * P < 0.05; 与术后第1天比较, #P < 0.05。 表 2 rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的单因素分析(x ± s)[n(%)]
因素 正常组(n=137) PND组(n=63) χ2/t P 年龄/岁 52.42±17.20 63.48±17.08 4.233 < 0.001 术中出血量/mL 865.64±417.83 1 007.79±425.62 2.222 0.027 血管外科手术 13(9.49) 13(20.63) 4.740 0.030 T2rSO2值/% 67.37±6.21 64.06±6.35 3.477 < 0.001 T2CVP/cmH2O 6.62±0.51 6.94±0.63 3.819 < 0.001 合并高血压 74(54.01) 44(69.84) 4.469 0.035 合并脑卒中 13(9.49) 13(20.63) 4.740 0.030 手术时间/min 181.52±59.34 201.54±58.22 2.229 0.027 表 2 rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的单因素分析(x ± s)[n(%)]
因素 正常组(n=137) PND组(n=63) χ2/t P 年龄/岁 52.42±17.20 63.48±17.08 4.233 < 0.001 术中出血量/mL 865.64±417.83 1 007.79±425.62 2.222 0.027 血管外科手术 13(9.49) 13(20.63) 4.740 0.030 T2rSO2值/% 67.37±6.21 64.06±6.35 3.477 < 0.001 T2CVP/cmH2O 6.62±0.51 6.94±0.63 3.819 < 0.001 合并高血压 74(54.01) 44(69.84) 4.469 0.035 合并脑卒中 13(9.49) 13(20.63) 4.740 0.030 手术时间/min 181.52±59.34 201.54±58.22 2.229 0.027 表 3 rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的多因素分析
因素 β 标准误差 Wald OR 95%CI P 下限 上限 年龄 2.306 0.535 18.552 10.032 3.513 28.646 < 0.001 T2rSO2值 -0.08 0.035 5.281 0.923 0.863 0.988 0.022 T2CVP 1.286 0.418 9.490 3.620 1.597 8.206 0.002 血管外科 1.165 0.557 4.380 3.205 1.077 9.541 0.036 常量 -9.172 3.695 6.160 0 — — 0.013 表 3 rSO2监测CH患者术后并发PND的多因素分析
因素 β 标准误差 Wald OR 95%CI P 下限 上限 年龄 2.306 0.535 18.552 10.032 3.513 28.646 < 0.001 T2rSO2值 -0.08 0.035 5.281 0.923 0.863 0.988 0.022 T2CVP 1.286 0.418 9.490 3.620 1.597 8.206 0.002 血管外科 1.165 0.557 4.380 3.205 1.077 9.541 0.036 常量 -9.172 3.695 6.160 0 — — 0.013 -
[1] BOGOLEPOVA A N. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction[J]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova, 2022, 122(8): 7-11. doi: 10.17116/jnevro20221220817
[2] BORCHERS F, SPIES C D, FEINKOHL I, et al. Methodology of measuring postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a systematic review[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2021, 126(6): 1119-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.01.035
[3] ZHAO S, CHEN F, WANG D W, et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are involved in the progression of postoperative cognitive dysfunction: from mechanism to treatment[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2021, 44(4): 1815-1831. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01387-z
[4] 彭慧萍, 毛一群. 鼻内镜术中控制性降压对老年患者局部脑氧饱和度的影响及与术后认知功能变化的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023, 43(4): 861-864. [5] PAN Y X, WANG J C, LU X Y, et al. Intention to control low central venous pressure reduced blood loss during laparoscopic hepatectomy: a double-blind randomized clinical trial[J]. Surgery, 2020, 167(6): 933-941. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2020.02.004
[6] 汪学清, 孟涛, 吴海波, 等. 创伤性颅脑损伤患者血压变异性对脑灌注压和预后的影响[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2021, 38(S1): 28-29. [7] 包萌萌, 吴安石. 围术期脑电及脑氧饱和度监测的研究进展[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2022, 42(3): 379-384. [8] 张蔚, 王文祥, 赵伟红, 等. 老年脊柱手术患者血清中H-FABP、B-FABP含量变化与术后认知功能改变的相关性[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2019, 35(4): 380-383. [9] 周美艳, 王凯, 宦乡, 等. 目标导向液体疗法对老年肺癌患者术后早期认知功能的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(6): 1221-1223. [10] 夏安琪, 李军, 岳玲, 等. 蒙特利尔认知评估量表在中国社区老人中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报: 医学版, 2021, 41(12): 1661-1667. [11] 典慧娟, 范艳竹, 王琳琳, 等. 体位及头高位对重型颅脑损伤病人颅内压和脑灌注压的影响[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(14): 2520-2523. [12] 董慧慧, 耿智隆, 张银花, 等. 颈动脉校正血流时间和心率对老年患者蛛网膜下腔阻滞后低血压的预测价值[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2022, 38(6): 608-612. [13] 郎志斌, 彭帮田, 邱林, 等. CPB下心脏手术患儿术后中枢神经系统并发症发生的危险因素: 近红外光谱法测定rSO2C[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2021, 41(3): 287-290. [14] 闫龙剑, 李春伟, 王冠男, 等. 脑氧饱和度监测下控制性降压对老年高血压患者术后谵妄的影响[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2020, 36(9): 857-860. [15] BHUSHAN S, LI Y, HUANG X, et al. Progress of research in postoperative cognitive dysfunction in cardiac surgery patients: a review article[J]. Int J Surg, 2021, 95: 106163. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.106163
[16] 郑蒙蒙, 邱丽丽, 邱晓东. 心肺转流期间老年患者局部脑氧饱和度与术后认知功能障碍的相关性[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2022, 38(5): 462-466. [17] TU M Y, ZHANG Q, LIU X S. Influence of narcotrend-assisted anesthesia In-depth monitor on cognitive impairment of elderly patients under general anesthesia[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2022, 2022: 2866188.
[18] 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会心脏重症分会. 心脏及大血管术后谵妄的防治中国专家共识[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103(45): 3635-3644. [19] 刘宇, 张洪伟, 杨鹏, 等. 体外循环下心血管手术相关无症状性脑梗死研究进展[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2021, 28(6): 735-739.




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号