Influencing factors of self-management ability of coronary heart disease patients after percutaneous coronary intervention and construction of nomogram model
-
摘要:目的
分析冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入术(PCI)治疗后自我管理能力的影响因素并构建列线图模型。
方法选取行PCI治疗的247例冠心病患者作为研究对象,均接受冠心病自我管理行为量表(CSMS)评估。通过多因素Logistic回归分析筛选出冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的独立影响因素,应用R软件构建列线图模型,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线、校准曲线和Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验评估列线图模型的区分度、校准度和拟合效度。
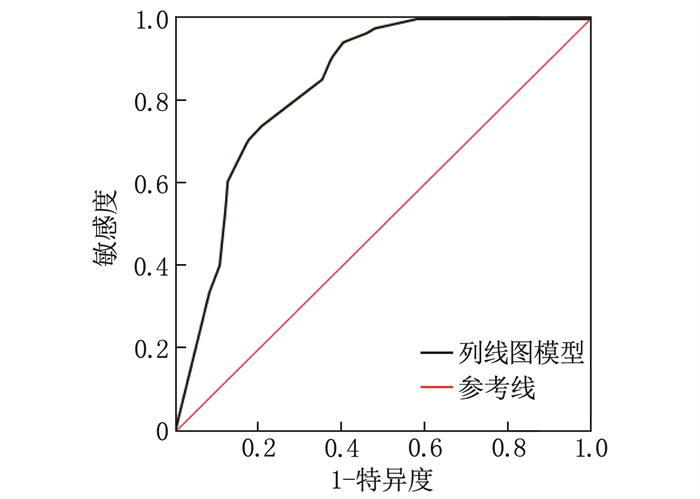
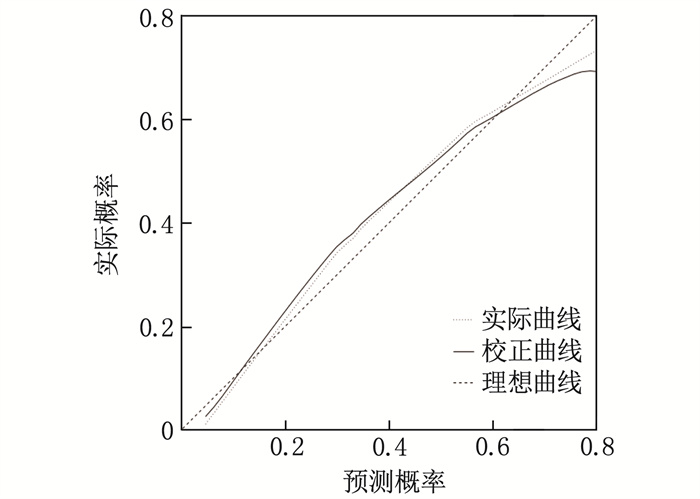
结果247例患者的平均CSMS评分为(86.79±9.22)分,以86.79分为临界值将患者分为低分组89例、高分组158例; 低分组年龄、受教育程度、家庭人均月收入、自我效能与高分组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄、受教育程度、家庭人均月收入、自我效能为冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的独立影响因素(P < 0.05); 基于4个影响因素构建列线图模型发现,年龄>70岁增加86.2分权重,受教育程度为高中以下增加87.4分权重,家庭人均月收入 < 3 500元人民币增加82.3分权重,自我效能较低增加99.6分权重。ROC曲线分析结果显示,列线图模型预测冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的曲线下面积为0.842(95%CI: 0.794~0.890); 校准曲线斜率接近1, 拟合优度检验χ2=10.226、P=0.233。
结论年龄、受教育程度、家庭人均月收入、自我效能为冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的影响因素, 据此构建的列线图模型对自我管理能力具有较高的预测价值。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the influencing factors of self-management ability of coronary heart disease patients after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and construct a nomogram model.
MethodsA total of 247 CHD patients who underwent PCI were selected as the research subjects, and all of them were evaluated by Coronary Heart Disease Self-management Scale (CSMS). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was used to screen out the independent influencing factors of self-management ability of CHD patientsafter PCI, and R software was used to construct a nomogram model. The discrimination, calibration, and goodness-of-fit of the nomogram model were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration curve, and Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test.
ResultsThe average CSMS score of 247 patients was (86.79±9.22), and these patients were divided into low-score group(89 patients) and high-score group (158 patients)based on the critical value of 86.79 points. There were significant differences in age, education level, monthly per capita family income, and self-efficacy between the low-score group and the high-score group (P < 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that age, education level, monthly per capita family income, and self-efficacy were independent influencing factors of self-management ability of CHD patients after PCI (P < 0.05). The nomogram model constructed based on the four influencing factors found that age >70 years increased the weight by 86.2 points, education level below high school increased the weight by 87.4 points, monthly per capita family income < 3 500 yuan increased the weight by 82.3 points, and low self-efficacy increased the weight by 99.6 points. The results of ROC curve analysis showed that the area under the curve of the nomogram model for predicting self-management ability ofCHD patients after PCI was 0.842 (95%CI, 0.794 to 0.890). The slope of the calibration curve was close to 1, and the results of goodness-of-fit test was as follows: χ2=10.226, P=0.233.
ConclusionAge, education level, monthly per capita family income, and self-efficacy are influencing factors of self-management ability of CHD patients after PCI, and the nomogram model constructed based on these factors has high predictive value for self-management ability.
-
冠心病是临床常见的心脑血管疾病之一,尤其多发于老年人,近年来其发病率呈逐年上升趋势[1]。冠心病患者常因冠状动脉狭窄或闭塞引起心脏供血不足,临床表现为胸痛、胸闷等症状,严重者还可并发心肌梗死,严重危害生命健康[2-3]。经皮冠状动脉介入术(PCI)是治疗冠心病的主要手段之一,具有手术创伤小、治疗效果好等特点,但部分患者治疗后仍会出现胸痛、胸闷等症状,甚至引发不良心脑血管事件,给患者及家属带来负担[4-5]。相关研究[6]指出,患者具备较好的自我管理能力是保障PCI治疗效果的关键因素。本研究探讨冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的影响因素并构建列线图预测模型,以期为冠心病患者PCI治疗后康复方案的制订提供参考依据。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2021年10月—2023年2月于淮安市第二人民医院接受PCI治疗的247例冠心病患者作为研究对象。纳入标准: ①符合《稳定性冠心病诊断与治疗指南》[7]中冠心病诊断标准,且具有PCI治疗指征[8]者; ②年龄≥60岁者; ③临床资料完整者。排除标准: ①非首次PCI治疗者; ②伴有恶性肿瘤疾病者; ③合并肝、肾、肺等重要脏器功能损伤者; ④伴有免疫系统疾病者; ⑤合并严重精神疾病者。本研究经淮安市第二人民医院医学伦理委员会审核批准。
1.2 研究方法
收集所有患者的年龄、性别、体质量指数(BMI)、糖尿病史、高血压史、受教育程度、病程、家庭人均月收入、婚姻状况、自我效能等临床资料。自我效能采用慢性病自我效能量表(SECD6)[9]进行评估,包括症状管理和疾病共性管理2个维度,共6个问题,每个问题分值为1~10分, 1分表示毫无信心, 10分表示完全有信心, 6个问题的均分即SECD6评分,评分≥7分表示自我效能高, < 7分表示自我效能低。
采用冠心病自我管理行为量表(CSMS)评估患者PCI治疗后的自我管理能力,该量表包括疾病知识、情绪认知、不良嗜好、治疗依从性、一般生活、症状、急救7个维度共27个条目,每个条目1~5分,总分为27~135分,分值越高表示自我管理能力越好。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 20.0统计学软件分析数据。计量资料以(x±s)表示, 2组间比较行t检验; 计数资料以[n(%)]表示, 2组间比较行χ2检验。将单因素分析中差异有统计学意义的因素纳入多因素Logistic回归分析,筛选冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的独立影响因素。将筛选出的影响因素导入R3.6.3软件与rms程序包,构建预测冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的列线图模型。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线、校准曲线和Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验评估列线图模型的区分度、校准度和拟合效度。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 临床资料比较
247例冠心病患者PCI治疗后的平均CSMS评分为(86.79±9.22)分,以86.79分为临界值,将患者分为低分组(CSMS评分 < 86.79分)89例和高分组(CSMS评分≥86.79分)158例。2组患者性别、BMI、糖尿病史、高血压史、病程、婚姻状况比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 2组患者年龄、受教育程度、家庭人均月收入、自我效能比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 高分组与低分组患者临床资料比较[n(%)]指标 分类 n 低分组(n=89) 高分组(n=158) χ2 P 年龄 ≤70岁 145 27(30.34) 118(74.68) 16.844 < 0.001 >70岁 102 62(69.66) 40(25.32) 性别 男 118 46(51.69) 72(45.57) 0.853 0.356 女 129 43(48.31) 86(54.43) 体质量指数 < 22 kg/m2 118 41(46.07) 77(48.73) 0.162 0.687 ≥22 kg/m2 129 48(53.93) 81(51.27) 糖尿病史 有 58 22(24.72) 36(22.78) 0.119 0.731 无 189 67(75.28) 122(77.22) 高血压史 有 83 31(34.83) 52(32.91) 0.094 0.759 无 164 58(65.17) 106(67.09) 受教育程度 高中以下 92 61(68.54) 31(19.62) 58.288 < 0.001 高中及以上 155 28(31.46) 127(80.38) 病程 < 2年 96 40(44.94) 56(35.44) 2.163 0.141 ≥2年 151 49(55.06) 102(64.56) 家庭人均月收入 < 3 500元人民币 139 72(80.90) 67(42.41) 34.284 < 0.001 ≥3 500元人民币 108 17(19.10) 91(57.59) 自我效能 低 128 70(78.65) 58(36.71) 40.115 < 0.001 高 119 19(21.35) 100(63.29) 婚姻状况 有配偶 186 70(78.65) 116(73.42) 0.839 0.360 无配偶 61 19(21.35) 42(26.58) 2.2 冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
以冠心病患者PCI治疗后CSMS评分为因变量(低分=1, 高分=0), 以年龄(≤70岁=0, >70岁=1)、受教育程度(高中以下=1, 高中及以上=0)、家庭人均月收入(< 3 500元人民币=1, ≥3 500元人民币=0)、自我效能(低=1, 高=0)为自变量,纳入多因素Logistic回归分析。分析结果显示,年龄、受教育程度、家庭人均月收入、自我效能均为冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的独立影响因素(P < 0.05), 公式为Z=1.096×年龄+1.111×受教育程度+1.042×家庭人均月收入+1.272×自我效能-3.013, 见表 2。
表 2 冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析指标 β SE Wald P OR 95%CI 年龄 1.096 0.379 8.343 0.004 2.992 1.422~6.295 受教育程度 1.111 0.381 8.515 0.004 3.037 1.440~6.404 家庭人均月收入 1.042 0.369 7.986 0.005 2.834 1.376~5.837 自我效能 1.272 0.354 12.941 < 0.001 3.568 1.784~7.137 常量 -3.013 0.411 53.712 < 0.001 0.049 — 2.3 列线图模型的构建
将冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的独立影响因素引入R软件,构建预测冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的列线图模型。结果显示,年龄>70岁增加86.2分权重,受教育程度为高中以下增加87.4分权重,家庭人均月收入 < 3 500元人民币增加82.3分权重,自我效能较低增加99.6分权重。见图 1。
2.4 列线图模型的验证
ROC曲线分析结果显示,列线图模型预测冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的曲线下面积为0.842(95%CI: 0.794~0.890), 说明该列线图模型具有良好的区分度,见图 2。
校准曲线、Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验结果显示,校准曲线斜率接近1, 拟合优度检验χ2=10.226、P=0.233, 说明该列线图模型具有良好的校准度、拟合效度,见图 3。
3. 讨论
冠心病是由冠状动脉粥样硬化引起的心血管疾病,常见症状为心肌缺氧、缺血等,严重威胁患者的生命健康[10-11]。PCI是一种在血管病变部位置入支架的治疗方法,可疏通狭窄、闭塞的血管,促进缺血心肌再灌注[12]。然而,由于老年冠心病患者对PCI了解有限,且缺乏自我护理、心脏康复相关知识,加之体质较弱,免疫力下降,术后康复效果受到影响,心绞痛、再次PCI等不良预后事件的发生风险增加[13-15]。因此,提升冠心病患者的自我管理能力对优化PCI治疗效果及改善预后具有重要意义。本研究基于多因素Logistic回归分析、R3.6.3软件及rms程序包等分析冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的影响因素并构建列线图预测模型,以期为术后康复措施的制订提供参考依据。
本研究结果显示, 247例冠心病患者PCI治疗后的平均CSMS评分为(86.79±9.22)分,年龄>70岁、受教育程度为高中以下、家庭人均月收入 < 3 500元人民币、自我效能低为冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力低的独立危险因素(P < 0.05)。老年患者通常对冠心病及手术知识掌握不足,疾病警惕性与重视度较低,易忽视自我照护和用药管理的重要性,且入院前大多伴有基础疾病,体质较弱,导致自我管理能力较低[16-17]。教育背景差异亦显著影响患者术后自我管理能力,受教育程度高的患者常通过多种渠道主动猎取医疗知识,有效应对康复过程中的问题,且具备良好的医患沟通能力,有利于病情管理; 受教育程度较低的患者对疾病的重视程度及知识储备不足,导致自我管理能力低下,影响术后康复效果。因此,对于老年患者、受教育程度较低的患者,护理人员应加强疾病知识宣教,强化其自我管理意识,预防不良预后事件的发生。经济条件不佳(家庭人均月收入 < 3 500元人民币)的患者,常因治疗费用负担重而减少必要的医疗服务,或采取不恰当的应对措施(如擅自停药、选用低价药品),严重影响治疗效果及术后健康状况[18-20]。对于此类患者,医护人员应积极普及医保政策,定期电话随访,确保按时按量用药和补充营养,以维持良好的身体状况。此外,年龄、家庭收入、受教育程度均能直接影响患者的自我效能感,进而影响自我管理能力。
本研究基于多因素Logistic回归分析筛选出的影响因素,构建预测冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的列线图模型。ROC曲线、校准曲线验证结果显示,该列线图模型预测冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力的曲线下面积为0.842(95%CI: 0.794~0.890), 校准曲线斜率接近1, 拟合优度检验χ2=10.226、P=0.233, 提示该列线图模型对冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力具有较好的预测能力。
综上所述,基于年龄、受教育程度、家庭人均月收入、自我效能这4个影响因素构建的列线图模型,对冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力具有较高的预测价值。护理人员可根据预测结果采取个体化干预措施,以改善冠心病患者的预后。然而,本研究纳入样本量较少,收集的影响因素亦不够全面,因此未来需要进一步扩大样本量深入研究,以增强该列线图模型的可靠性和普适性。
-
表 1 高分组与低分组患者临床资料比较[n(%)]
指标 分类 n 低分组(n=89) 高分组(n=158) χ2 P 年龄 ≤70岁 145 27(30.34) 118(74.68) 16.844 < 0.001 >70岁 102 62(69.66) 40(25.32) 性别 男 118 46(51.69) 72(45.57) 0.853 0.356 女 129 43(48.31) 86(54.43) 体质量指数 < 22 kg/m2 118 41(46.07) 77(48.73) 0.162 0.687 ≥22 kg/m2 129 48(53.93) 81(51.27) 糖尿病史 有 58 22(24.72) 36(22.78) 0.119 0.731 无 189 67(75.28) 122(77.22) 高血压史 有 83 31(34.83) 52(32.91) 0.094 0.759 无 164 58(65.17) 106(67.09) 受教育程度 高中以下 92 61(68.54) 31(19.62) 58.288 < 0.001 高中及以上 155 28(31.46) 127(80.38) 病程 < 2年 96 40(44.94) 56(35.44) 2.163 0.141 ≥2年 151 49(55.06) 102(64.56) 家庭人均月收入 < 3 500元人民币 139 72(80.90) 67(42.41) 34.284 < 0.001 ≥3 500元人民币 108 17(19.10) 91(57.59) 自我效能 低 128 70(78.65) 58(36.71) 40.115 < 0.001 高 119 19(21.35) 100(63.29) 婚姻状况 有配偶 186 70(78.65) 116(73.42) 0.839 0.360 无配偶 61 19(21.35) 42(26.58) 表 2 冠心病患者PCI治疗后自我管理能力影响因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
指标 β SE Wald P OR 95%CI 年龄 1.096 0.379 8.343 0.004 2.992 1.422~6.295 受教育程度 1.111 0.381 8.515 0.004 3.037 1.440~6.404 家庭人均月收入 1.042 0.369 7.986 0.005 2.834 1.376~5.837 自我效能 1.272 0.354 12.941 < 0.001 3.568 1.784~7.137 常量 -3.013 0.411 53.712 < 0.001 0.049 — -
[1] 董莞, 张兵. CT冠脉成像、超声心动图对冠心病患者左心室功能、冠脉斑块稳定性的评估价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(6): 93-95. [2] 任何, 汪洁, 张东伟, 等. 血清FKN、COMP、LTBP-2表达水平与冠心病严重程度的关系[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(10): 1694-1696. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202110023.htm [3] ZHAO D H, FAN Q, NING J X, et al. Myocardial bridge-related coronary heart disease: independent influencing factors and their predicting value[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2019, 7(15): 1986-1995. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i15.1986
[4] 黄彩妹, 陆柳雪, 邓惠英, 等. 老年冠心病PCI治疗患者认知加工与应对方式对其创伤后成长水平影响研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2022, 51(21): 3681-3688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQYX202221017.htm [5] 王玎羽, 谢翔, 赵东英, 等. PLT/TBIL对冠心病患者PCI术后临床结局的预测价值[J]. 重庆医学, 2022, 51(14): 2432-2436, 2440. [6] 尹琳, 胥清华, 杜丹. 基于行为改变理论的干预模式对PCI术后患者自我管理行为和健康素养的影响[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2020, 26(2): 256-260. [7] 中华医学会心血管病学分会介入心脏病学组, 中华医学会心血管病学分会动脉粥样硬化与冠心病学组, 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会血栓防治专业委员会, 等. 稳定性冠心病诊断与治疗指南[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2018, 46(9): 680-694. [8] 中华医学会心血管病学分会介入心脏病学组, 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会血栓防治专业委员会, 中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 中国经皮冠状动脉介入治疗指南(2016)[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2016, 44(5): 382-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJXB201612016.htm [9] FREUND T, GENSICHEN J, GOETZ K, et al. Evaluating self-efficacy for managing chronic disease: psychometric properties of the six-item Self-Efficacy Scale in Germany[J]. J Eval Clin Pract, 2013, 19(1): 39-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2011.01764.x
[10] WU X L, VON BIRGELEN C, ZHANG S, et al. Simultaneous evaluation of plaque stability and ischemic potential of coronary lesions in a fluid-structure interaction analysis[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2019, 35(9): 1563-1572. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01611-y
[11] 付琳, 王敏, 李瑾. 冠心病病人载脂蛋白B/载脂蛋白A1、胱抑素C、血清胆红素水平变化及其与冠状动脉病变严重程度的相关性[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 20(7): 1287-1292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202207027.htm [12] DAWSON L P, COLE J A, LANCEFIELD T F, et al. Incidence and risk factors for stroke following percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Int J Stroke, 2020, 15(8): 909-922. doi: 10.1177/1747493020912607
[13] 段雯洁, 李小琼, 姜艳艳, 等. 跨理论模型下协同护理用于PCI老年冠心病患者自我管理能力及健康行为的影响[J]. 中国医药导报, 2022, 19(35): 172-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202235035.htm [14] 樊明媛, 李雪萍, 芮思艳, 等. 冠心病PCI支架植入术后1年再入院的中医证素分布规律及相关危险因素分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 20(15): 2783-2787. [15] 郭丽敏, 郭莹洁, 史宁, 等. 冠心病患者PCI术后自我管理现状的研究进展[J]. 河北医药, 2022, 44(10): 1561-1565. [16] 袁雨涵, 高春红, 汤一帆, 等. 冠心病管理APP对老年冠心病病人PCI术后自我管理与生活质量的效果[J]. 实用老年医学, 2022, 36(1): 100-103. [17] 王飞宇, 张玉莲. 情景模拟健康教育对冠心病PCI术后患者手术认知水平及自我管理能力的影响[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2019, 19(2): 192-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXFZ201902030.htm [18] 高倩, 李晓敏, 孙王乐贤, 等. 自我调节疲劳对冠心病患者自我管理行为的影响[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2019, 27(1): 38-42. [19] 柳志敏, 王巧, 郝娟. 老年冠心病行PCI术后患者自我管理能力影响因素分析及护理对策[J]. 齐鲁护理杂志, 2020, 26(19): 5-8. [20] 陈晨, 彭德荣, 杨芬红, 等. 上海市某社区冠心病患者自我管理与自我效能的相关性及其影响因素[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2020, 19(11): 1020-1024.




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
