Relationships of serum human fractalkine and chitinase-3-like protein 1 levels with early cognitive impairment in elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease
-
摘要:目的
探讨血清人神经趋化蛋白(CX3CL1)、人甲壳质酶蛋白40(YKL-40)水平与老年阿尔茨海默症(AD)患者早期认知功能损害的关系。
方法选取2021年2月—2023年12月新乡医学院第二附属医院收治的110例AD患者作为AD组, 另选取本院同期健康体检者50例作为对照组。比较2组临床资料及血清CX3CL1、YKL-40水平,采用多因素Logistic回归模型分析AD患者认知功能损害的影响因素。根据简易精神状态量表(MMSE)评估结果将110例AD患者分为轻度认知障碍组(n=47)、中度认知障碍组(n=36)、重度认知障碍组(n=27),并采用Spearman相关性分析法分析血清CX3CL1、YKL-40与MMSE评分、Administration认知评估量表第3版(ACE-Ⅲ)评分、蒙特利尔认知评估量表(MoCA)评分的关系。
结果AD组患者80岁以上比率、文化程度为小学及以下比率、吸烟史比率、饮酒史比率、合并糖尿病比率、合并高血压比率、AD家族史比率、独居比率及血清CX3CL1、YKL-40水平高于对照组,从不体育锻炼/体力劳动比率、MMSE评分、ACE-Ⅲ评分及MoCA评分低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。高龄、合并糖尿病、血清CX3CL1、YKL-40是AD患者认知功能损害的独立危险因素(P < 0.05), 大专及以上文化程度为AD患者认知功能损害的保护因素(P < 0.05)。与轻度认知障碍组相比,中度认知障碍组、重度认知障碍组血清CX3CL1、YKL-40水平偏高,与中度认知障碍组相比,重度认知障碍组血清CX3CL1、YKL-40水平偏高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Spearman相关性分析发现,血清CX3CL1、YKL-40与MMSE评分、ACE-Ⅲ评分、MoCA评分均呈负相关(P < 0.05)。
结论血清CX3CL1、YKL-40在老年AD患者体内呈高表达,且与老年AD患者早期认知功能损害关系密切。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the relationships of serum levels of human fractalkine (CX3CL1) and chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) with early cognitive impairment in elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD).
MethodsA total of 110 AD patients in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University from February 2021 to December 2023 were selected as AD group, and 50 healthy individuals with physical examination during the same period were selected as control group. Clinical materials and serum levels of CX3CL1 and YKL-40 were compared between the two groups, and multivariate Logistic regression models were used to analyze the influencing factors of cognitive impairment in AD patients. Based on the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score, the 110 AD patients were divided into mild cognitive impairment group (n=47), moderate cognitive impairment group (n=36), and severe cognitive impairment group (n=27). Spearman correlation analysis was performed to explore the relationships of serum CX3CL1 and YKL-40 with MMSE score, Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination-Ⅲ (ACE-Ⅲ) score, and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) score.
ResultsThe AD group had higher proportions of patients aged over 80 years, with an education level of primary school or below, smoking history, alcohol consumption history, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, AD family history, and living alone as well as higher serum levels of CX3CL1 and YKL-40 compared to the control group; conversely, the AD group had a lower proportion of patients engaging in no physical exercise/labor, and lower MMSE, ACE-Ⅲ, and MoCA scores, with significant between-group differences (P < 0.05). Advanced age, diabetes mellitus, and high serum levels of CX3CL1 and YKL-40 were independent risk factors for cognitive impairment in AD patients (P < 0.05), while an education level of college or above was a protective factor (P < 0.05). Compared with the mild cognitive impairment group, the moderate and severe cognitive impairment groups had higher serum levels of CX3CL1 and YKL-40, and the severe cognitive impairment group had higher serum levels of CX3CL1 and YKL-40 than the moderate group, with significant between-group differences (P < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis revealed that serum CX3CL1 and YKL-40 were negatively correlated with MMSE, ACE-Ⅲ, and MoCA scores (P < 0.05).
ConclusionSerum CX3CL1 and YKL-40 are highly expressed in elderly AD patients, and are closely related to early cognitive impairment in elderly AD patients.
-
难治性癫痫是一种常见的神经系统疾病,治疗以手术切除术最为普遍,但术后仍有部分患者未能有效控制癫痫发作[1-2]。准确预测难治性癫痫的发生与发展对于指导临床治疗至关重要。研究[3]指出,高迁移率族蛋白1(HMGB1)、Toll样受体4(TLR4)可能与难治性癫痫的发病机制及进展存在关联。HMGB1作为一种核蛋白,在感染、组织损伤及炎症等病理条件下,可从细胞核释放至胞外,参与炎症反应及免疫应答。TLR4是与免疫系统紧密关联的受体[4], 其异常活化可诱发神经元损伤及炎症反应。通过监测HMGB1与TLR4的表达水平,临床医生能更精准地评估患者手术适应证及预后。然而,关于HMGB1与TLR4在难治性癫痫患者病灶中的具体表达及其与疾病进展关系的研究尚不充分,且结果间存在差异。本研究探讨HMGB1及TLR4与难治性癫痫患者临床特征的相关性及其预测价值,以期深入理解2种生物标志物的作用机制,并为临床诊疗提供更加精准的指导。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性分析2020年3月—2023年3月收治的84例难治性癫痫患者临床资料,并将其纳入观察组。84例患者中,男56例,女28例; 平均年龄(60.67±4.78)岁; 癫痫发作频率(2.13±0.12)次/周,发作持续时间(5.23±2.12) min; 病程2~19个月,平均(10.24±3.14)个月; 发作类型为全面性强直阵挛31例,非全面性强直阵挛53例。此外,选择同期35例行颅内减压术的高颅内压患者作为对照组。所有标本均在取出后30 min内储存于冰箱内。观察组纳入标准: ①术前均进行头皮视频脑电图与术中皮层脑电图检查,确诊为难治性癫痫者; ②符合国际抗癫痫联盟所制定的难治性癫痫标准[5]者; ③临床资料齐全者; ④首次手术,且无神经系统肿瘤病史和感染系统病史者。对照组纳入标准: ①同期进行颞叶切除、大骨瓣减压的重型颅脑损伤者; ②无神经系统肿瘤史、癫痫病史、感染性疾病者; ③临床资料齐全者。排除并发心血管疾病和恶性肿瘤者。
1.2 方法
观察组术中打开硬脑膜,取得麻醉师配合,减少麻醉药物剂量,采用皮层脑电检测仪器进行脑电监测,脑电图出现异常部位即致病灶脑组织,需手术切除,将病理标本留取足够的前提下,取直径为1 cm白质、灰质的脑组织标本各3份。对照组术中留取灰质、白质非功能区正常脑组织标本各3份,保存于冰箱(-20 ℃)中冷冻待测。
标本包埋后行连续切片,厚度为3 μm, 置于防脱剂预处理后的载玻璃片上,滴加比例为1∶ 20的HMGB1及TLR4单克隆抗体4 ℃过夜。磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)清洗后,滴加生物素,且标记二抗羊抗兔免疫球蛋白G(IgG), 室温孵育20 min, 采用PBS清洗。首先,取出组织后需立即用乙醇、Carnoy固定液或中性福尔马林溶液进行固定。随后,制作7~10 μm的石蜡切片并脱蜡。采用碱性染料如焦油紫或甲苯胺蓝染色25~50 min, 使尼氏体着色。之后,采用乙醇分化并用梯度乙醇脱水。最后,滴入二甲苯使切片透明,中性树胶封固后,即可在显微镜下观察神经元的尼氏体结构。需要注意的是,尼氏体在离体后易溶解,因此需及时固定组织。完成染色的标本应存放在避光处,以防褪色。加辣根过氧化物酶标记链美卵白素工作液,在室温下孵育15 min, DAB显色剂给予显色、冲洗,苏木精复染,常规乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片后在显微镜下观察, PBS液替代一抗染色作为阴性对照。尼氏染色法具体如下: 首先,取出组织后需立即用乙醇、Carnoy固定液或中性福尔马林溶液进行固定。随后,制作7~10 μm的石蜡切片并脱蜡。采用碱性染料如焦油紫或甲苯胺蓝染色25~50 min, 使尼氏体着色。之后,用乙醇分化并用梯度乙醇脱水。最后,二甲苯使切片透明,中性树胶封固后,即可在显微镜下观察神经元的尼氏体结构。完成染色的标本应存放在避光处,以防褪色。蛋白表达标准: 无染色细胞以0分表示; 阳性细胞占比不足25%以1分表示; 阳性细胞占比为25%~50%以2分表示; 阳性细胞占比>50%~75%以3分表示; 阳性细胞占比>75%~100%以4分表示。染色强度以细胞染色深度进行评分,无染色以0分表示; 浅棕色以1分表示; 深棕色以2分表示。采用半定量积分法,将2项指标评分乘积作为最终得分, 0分为阴性(-); 1~4分为低表达(+); 5~8分为高表达(++)。
1.3 统计学处理
采用SPSS 21.0统计学软件处理数据,计数资料以[n(%)]表示,行χ2检验,经Spearman法分析TLR4表达与HMGB1表达的相关性; 计量资料采用(x±s)表示,行t检验, TLR4蛋白、HMGB1蛋白预测效能均采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线进行分析,以α=0.05为检验水准, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 2组HMGB1、TLR4表达情况比较
观察组HMGB1、TLR4阳性颗粒表达较多,且多集中在胞膜上; 对照组阳性颗粒表达少。观察组HMGB1、TLR4阳性表达水平高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 2组HMGB1、TLR4表达情况比较[n(%)]组别 n HMGB1表达情况 TLR4表达情况 阳性 阴性 阳性 阴性 观察组 84 73(86.90)* 11(13.10) 71(84.52)* 13(15.48) 对照组 35 15(42.86) 20(57.14) 8(22.86) 27(77.14) HMGB1: 高迁移率族蛋白B1; TLR4: Toll样受体4。与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。 2.2 Spearman相关性分析
病灶组织中, TLR4与HMGB1表达呈正相关,提示两者存在协同作用,见表 2。
表 2 TLR4与HMGB1在难治性癫痫患者病灶组织中表达的相关性例 HMGB1表达情况 n TLR4表达情况 - + ++ n 84 13 38 33 - 11 9 2 0 + 40 2 25 13 ++ 33 2 11 20 2.3 2组HMGB1、TLR4蛋白水平比较
蛋白印迹法结果表明,观察组HMGB1、TLR4蛋白条带的光密度值与内参β-actin条带光密度值高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 2组HMGB1、TLR4蛋白相对含量比较(x±s)组别 n TLR4/β-actin HMGB1/β-actin 观察组 84 0.35±0.12* 1.35±0.30* 对照组 35 0.21±0.01 0.92±0.19 与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。 2.4 临床因素与病灶组织中TLR4表达的关系
TLR4表达强度与年龄、性别无关,与癫痫发作频率、发作持续时间、病程、癫痫发作类型有关(P < 0.05), 见表 4。
表 4 临床因素与病灶组织中TLR4表达的关系分析[n(%)]临床因素 分类 TLR4表达 χ2 P 阳性(n=71) 阴性(n=13) 性别 男 49(69.01) 7(53.85) 1.138 0.286 女 22(30.99) 6(40.15) 癫痫病程 ≤10年 20(28.17) 10(76.92) 11.376 < 0.001 >10年 51(71.83) 3(23.08) 年龄 < 60岁 38(53.52) 7(53.85) 0.001 0.983 ≥60岁 33(46.48) 6(46.15) 癫痫发作频率 ≤1次/周 39(54.93) 12(92.31) 6.436 0.011 >1次/周 32(45.07) 1(7.69) 癫痫发作持续时间 ≤5 min 34(47.89) 11(84.62) 5.959 0.015 >5 min 37(52.11) 2(15.38) 癫痫发作类型 全面性强直阵挛发作 30(42.25) 1(7.69) 5.637 0.018 非全面性强直阵挛发作 41(57.75) 12(92.31) 2.5 临床因素与病灶组织中HMGB1表达关系的分析
HMGB1表达强度与年龄、性别、癫痫发作类型无关,与癫痫发作频率、发作持续时间、病程有关(P < 0.05), 见表 5。
表 5 临床各因素与病灶组织中HMGB1表达的关系分析[n(%)]临床因素 分类 HMGB1表达 χ2 P 阳性(n=73) 阴性(n=11) 性别 男 47(64.38) 9(81.82) 1.308 0.253 女 26(35.62) 2(18.18) 癫痫病程 ≤10年 20(27.40) 10(90.91) 16.795 < 0.001 >10年 53(72.60) 1(9.09) 年龄 < 60岁 41(56.16) 4(36.36) 1.507 0.220 ≥60岁 32(43.84) 7(63.64) 癫痫发作频率 ≤1次/周 40(54.79) 11(100.00) 8.190 0.004 >1次/周 33(45.21) 0 癫痫发作持续时间 ≤5 min 35(47.95) 10(90.91) 7.095 0.008 >5 min 38(52.05) 1(9.09) 癫痫发作类型 全面性强直阵挛发作 29(39.73) 2(18.18) 1.906 0.167 非全面性强直阵挛发作 44(60.27) 9(81.82) 2.6 ROC曲线分析
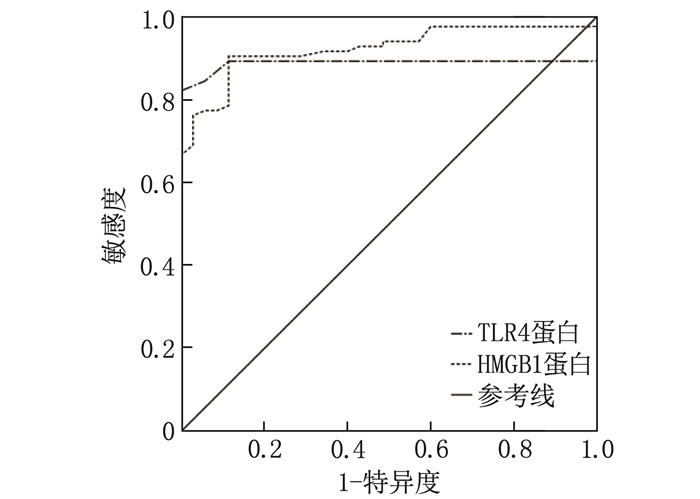
ROC曲线分析结果显示, TLR4蛋白、HMGB1蛋白预测难治性癫痫的曲线下面积分别为0.888、0.923, 见表 6、图 1。
表 6 TLR4、HMGB1预测难治性癫痫患者的效能分析变量 曲线下面积 SE P 95%CI Cut-off 约登指数 敏感度/% 特异度/% TLR4蛋白 0.888 0.034 < 0.001 0.822~0.954 0.25 0.821 82.1 100.0 HMGB1蛋白 0.923 0.025 < 0.001 0.875~0.971 1.13 0.791 90.5 88.6 3. 讨论
癫痫是一种神经系统疾病,具体症状包括短暂意识丧失、肢体抽搐及口唇咀嚼动作等。难治性癫痫是指经药物治疗后仍无法得到有效控制的癫痫发作[6], 发作频率高,持续时间长,对患者日常生活及工作能力造成显著影响。致病灶切除术作为一种手术治疗手段[7-8], 旨在通过切除或消除引发癫痫发作的特定致病灶达到控制癫痫发作的目的。此手术方法通常适用于那些药物治疗无效的患者。切除致病灶可有效减少或消除异常神经元活动,从而实现对癫痫发作的控制。评估致病灶切除术的远期疗效至关重要。鉴于难治性癫痫的复杂性,在选择手术治疗方案时,必须全面考量患者的个体差异、手术潜在风险及预期预后效果。了解远期效果可以帮助医生和患者更好地决策是否进行手术,以及对手术后的预后进行预测和管理。
HMGB1是一种核蛋白[9], 在损伤及炎症反应中发挥关键作用。该蛋白能从细胞核释放至细胞外,参与炎症反应及免疫应答过程。癫痫发作时, HMGB1的表达水平上升,可见其与神经元的损伤及炎症反应紧密相关。TLR4则是与免疫系统紧密关联的受体[10],其过度活化可加剧神经元的损伤与炎症反应。在难治性癫痫患者中, TLR4的表达水平亦显著增加。本研究发现,观察组HMGB1与TLR4的阳性表达较对照组更显著,表明难治性癫痫患者中的2种蛋白的表达水平较高。HMGB1作为促炎细胞因子,在炎症反应中扮演重要角色。难治性癫痫患者可能经历更为复杂且持久的神经炎症反应,从而导致HMGB1表达水平上升。相比之下,高颅内压患者多为颅内损伤或脑出血等急性疾病所致,其病理生理过程并不以持久的神经炎症反应为主要特征。难治性癫痫患者可能伴有免疫系统的异常活化,进而促使TLR4表达增加,而高颅内压患者的病理生理改变主要源于颅内压力增高,并非直接关联于免疫系统的异常激活。本研究还观察到观察组HMGB1与TLR4的阳性颗粒多集中于胞膜上,提示2种蛋白可能与胞膜相关的信号通路存在关联,并可能参与免疫炎症反应及神经元损伤的过程。
HMGB1和TLR4的高表达通常与细胞损伤、炎症反应和免疫系统异常激活相关[11-12], 通过评价其相对含量,可以反映炎症状态的程度和激活程度。本研究显示,观察组HMGB1和TLR4蛋白条带、β-actin蛋白条带光密度值高于对照组,说明难治性癫痫患者的细胞可能受到了损伤或炎症刺激,导致HMGB1和TLR4释放和表达增高,同时β-actin表达亦有所增加。可能原因是HMGB1作为一种促炎分子,可以在神经系统损伤或炎症过程中释放。难治性癫痫可能伴随着慢性炎症反应的增强,导致HMGB1的释放和表达增加。β-actin是一个结构蛋白[13], 在细胞骨架的形成和维持中起到重要作用。难治性癫痫患者可能存在细胞代谢异常,导致β-actin表达水平改变。
TLR4作为免疫系统中的重要受体,参与病原体识别与免疫调节,其表达强度受多种因素的影响。本研究中,癫痫发作频率、发作持续时间、病程和发作类型与TLR4的表达强度存在显著相关性。具体机制分析如下: ①免疫激活。癫痫发作触发神经元剧烈活动与异常放电,可能诱发免疫系统响应。免疫细胞及因子的释放入脑组织,进而促进TLR4表达上调。此免疫激活过程与癫痫的发作频率、持续时间及病程密切相关。②炎症反应。癫痫发作与神经炎症反应密切相关。免疫细胞激活释放的细胞因子与趋化因子等炎性介质,能调节TLR4表达。不同癫痫发作类型可能伴随特异性炎症过程,从而对TLR4表达产生差异化影响。③神经元损伤与修复。癫痫发作可致神经元损伤乃至细胞死亡[14], 激活神经元修复机制。TLR4在神经系统具有修复与再生潜力[15],参与调控神经元生长与修复。因此,癫痫的发作频率、持续时间和病程可能会影响神经元的损伤和修复过程,从而影响TLR4的表达,但确切的机制仍然需要进一步的研究深入探讨TLR4表达与癫痫的关系。
HMGB1的表达强度受到多种因素的影响。本研究显示, HMGB1表达强度与年龄、性别无关,但与癫痫发作频率、发作持续时间和病程有关。具体原因为: ①炎症反应。癫痫发作时,大脑神经元活动异常,并且产生炎症反应。HMGB1在炎症过程中起到促炎作用,可以激活免疫细胞,增强炎性细胞因子的释放,进而导致炎症反应的加剧。②神经元损伤。癫痫发作会导致神经元的损伤和细胞死亡。HMGB1能够通过与其他细胞外分子结合,促进炎症细胞的迁移和活化,导致细胞死亡进程的加剧。③免疫调节。HMGB1在免疫调节中起重要作用,可以影响免疫细胞的活化、迁移和细胞因子的产生。在癫痫中,免疫系统的异常活化与疾病的发展相关。HMGB1可能通过调节免疫反应进一步影响癫痫的发作频率、持续时间和病程。
本研究结果显示, TLR4蛋白和HMGB1蛋白在预测难治性癫痫方面具有较高的准确度,表明TLR4蛋白和HMGB1蛋白在难治性癫痫的发生、发展过程中扮演重要角色,主要原因可能为TLR4蛋白和HMGB1蛋白的曲线下面积值表明其在预测疾病发生、发展时具有很高的准确性,具体机制需要进一步研究来验证和阐明。本研究创新点与创新价值在于揭示了HMGB1和TLR4在难治性癫痫中的重要角色,为理解难治性癫痫患者提供了新视角,为疾病的诊疗提供了一定参考依据,以更准确地判断病情,制订更有效的治疗方案。
综上所述, HMGB1、TLR4在难治性癫痫患者致痫病灶组织中呈高表达,且两者表达强度呈正相关,能够在一定程度上预测疾病发生、发展。本研究选取的样本量有限,后续应扩大样本量进行更深入的研究。
-
表 1 对照组与AD组的临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
临床资料 分类 AD组(n=110) 对照组(n=50) t P 性别 男 69(62.73) 27(54.00) 1.091 0.296 女 41(37.27) 23(46.00) 年龄 65~80岁 35(31.82) 31(62.00) 12.921 <0.001 >80岁 75(68.18) 19(38.00) 文化程度 小学及以下 57(51.82) 12(24.00) 15.301 <0.001 中学/中专 41(37.27) 22(44.00) 大专及以上 12(10.91) 16(32.00) 婚姻状况 已婚 66(60.00) 34(68.00) 0.939 0.333 丧偶/离婚/单身 44(40.00) 16(32.00) 吸烟史 43(39.09) 8(16.00) 8.440 0.004 饮酒史 34(30.91) 8(16.00) 3.947 0.047 合并糖尿病 54(49.09) 10(20.00) 12.121 <0.001 合并高血压 35(31.82) 8(16.00) 4.377 0.036 合并高脂血症 21(19.09) 7(14.00) 0.617 0.432 AD家族史 有 18(16.36) 2(4.00) 4.804 0.028 无 92(83.64) 48(96.00) 体育锻炼/体力劳动 从不 13(11.82) 17(34.00) 11.138 0.004 偶尔 19(17.27) 7(14.00) 经常 78(70.91) 26(52.00) 独居 是 30(27.27) 6(12.00) 4.598 0.032 否 80(72.73) 44(88.00) MMSE评分/分 20.32±5.10 29.05±6.67 9.085 <0.001 ACE-Ⅲ评分/分 55.74±13.85 90.83±16.92 13.835 <0.001 MoCA评分/分 12.57±4.31 27.88±6.84 17.172 <0.001 血清CX3CL1/(pg/mL) 132.95±31.35 97.64±26.58 6.912 <0.001 血清YKL-40/(ng/mL) 365.21±92.43 162.90±55.30 14.340 <0.001 AD: 阿尔茨海默症; MMSE: 简易精神状态量表; ACE-Ⅲ: Administration认知评估量表第3版;
MoCA: 蒙特利尔认知评估量表; CX3CL1: 人神经趋化蛋白; YKL-40: 人甲壳质酶蛋白40。表 1 对照组与AD组的临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
临床资料 分类 AD组(n=110) 对照组(n=50) t P 性别 男 69(62.73) 27(54.00) 1.091 0.296 女 41(37.27) 23(46.00) 年龄 65~80岁 35(31.82) 31(62.00) 12.921 <0.001 >80岁 75(68.18) 19(38.00) 文化程度 小学及以下 57(51.82) 12(24.00) 15.301 <0.001 中学/中专 41(37.27) 22(44.00) 大专及以上 12(10.91) 16(32.00) 婚姻状况 已婚 66(60.00) 34(68.00) 0.939 0.333 丧偶/离婚/单身 44(40.00) 16(32.00) 吸烟史 43(39.09) 8(16.00) 8.440 0.004 饮酒史 34(30.91) 8(16.00) 3.947 0.047 合并糖尿病 54(49.09) 10(20.00) 12.121 <0.001 合并高血压 35(31.82) 8(16.00) 4.377 0.036 合并高脂血症 21(19.09) 7(14.00) 0.617 0.432 AD家族史 有 18(16.36) 2(4.00) 4.804 0.028 无 92(83.64) 48(96.00) 体育锻炼/体力劳动 从不 13(11.82) 17(34.00) 11.138 0.004 偶尔 19(17.27) 7(14.00) 经常 78(70.91) 26(52.00) 独居 是 30(27.27) 6(12.00) 4.598 0.032 否 80(72.73) 44(88.00) MMSE评分/分 20.32±5.10 29.05±6.67 9.085 <0.001 ACE-Ⅲ评分/分 55.74±13.85 90.83±16.92 13.835 <0.001 MoCA评分/分 12.57±4.31 27.88±6.84 17.172 <0.001 血清CX3CL1/(pg/mL) 132.95±31.35 97.64±26.58 6.912 <0.001 血清YKL-40/(ng/mL) 365.21±92.43 162.90±55.30 14.340 <0.001 AD: 阿尔茨海默症; MMSE: 简易精神状态量表; ACE-Ⅲ: Administration认知评估量表第3版;
MoCA: 蒙特利尔认知评估量表; CX3CL1: 人神经趋化蛋白; YKL-40: 人甲壳质酶蛋白40。表 2 导致AD患者认知功能损害的多因素Logistic回归分析
因素 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI 常数项 -0.392 0.285 1.892 0.042 — — 年龄 1.003 0.567 3.129 <0.001 2.726 1.664~3.526 文化程度 -0.556 0.395 1.981 0.025 0.573 0.231~0.768 合并糖尿病 0.472 0.315 2.245 0.002 1.603 1.227~2.373 血清CX3CL1 1.124 0.620 3.287 <0.001 2.361 1.042~3.677 血清YKL-40 0.735 0.462 2.531 <0.001 3.567 1.546~4.885 表 2 导致AD患者认知功能损害的多因素Logistic回归分析
因素 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI 常数项 -0.392 0.285 1.892 0.042 — — 年龄 1.003 0.567 3.129 <0.001 2.726 1.664~3.526 文化程度 -0.556 0.395 1.981 0.025 0.573 0.231~0.768 合并糖尿病 0.472 0.315 2.245 0.002 1.603 1.227~2.373 血清CX3CL1 1.124 0.620 3.287 <0.001 2.361 1.042~3.677 血清YKL-40 0.735 0.462 2.531 <0.001 3.567 1.546~4.885 表 3 不同认知障碍程度AD患者血清CX3CL1、YKL-40水平比较(x±s)
组别 n CX3CL1/(pg/mL) YKL-40/(ng/mL) 轻度认知障碍组 47 89.52±22.84 318.42±87.14 中度认知障碍组 36 112.64±30.55* 373.07±100.36* 重度认知障碍组 27 173.46±46.81*# 436.19±109.07*# 与轻度认知障碍组相比, * P<0.05;
与中度认知障碍组相比, #P<0.05。表 3 不同认知障碍程度AD患者血清CX3CL1、YKL-40水平比较(x±s)
组别 n CX3CL1/(pg/mL) YKL-40/(ng/mL) 轻度认知障碍组 47 89.52±22.84 318.42±87.14 中度认知障碍组 36 112.64±30.55* 373.07±100.36* 重度认知障碍组 27 173.46±46.81*# 436.19±109.07*# 与轻度认知障碍组相比, * P<0.05;
与中度认知障碍组相比, #P<0.05。表 4 血清CX3CL1、YKL-40与MMSE评分、ACE-Ⅲ评分、MoCA评分的相关性
指标 血清CX3CL1 血清YKL-40 r P r P MMSE评分 -0.656 <0.05 -0.528 <0.05 ACE-Ⅲ评分 -0.511 <0.05 -0.430 <0.05 MoCA评分 -0.511 <0.05 -0.427 <0.05 表 4 血清CX3CL1、YKL-40与MMSE评分、ACE-Ⅲ评分、MoCA评分的相关性
指标 血清CX3CL1 血清YKL-40 r P r P MMSE评分 -0.656 <0.05 -0.528 <0.05 ACE-Ⅲ评分 -0.511 <0.05 -0.430 <0.05 MoCA评分 -0.511 <0.05 -0.427 <0.05 -
[1] ZHANG X X, TIAN Y, WANG Z T, et al. The epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease modifiable risk factors and prevention[J]. J Prev Alzheimers Dis, 2021, 8(3): 313-321.
[2] BEATA B K, WOJCIECH J, JOHANNES K, et al. Alzheimer's disease-biochemical and psychological background for diagnosis and treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(2): 1059. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021059
[3] WANG Y Y, YANG L, ZHANG J, et al. The effect of cognitive intervention on cognitive function in older adults with Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neuropsychol Rev, 2022, 32(2): 247-273. doi: 10.1007/s11065-021-09486-4
[4] 陈凡, 王娜, 何夏萍. 炎性免疫参与阿尔茨海默病发病机制的研究进展[J]. 神经疾病与精神卫生, 2022, 22(6): 452-456. [5] GUPTA M, PALIWAL V K, BABU G N. Serum fractalkine and 3-nitrotyrosine levels correlate with disease severity in Parkinson's disease: a pilot study[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2022, 37(1): 209-217. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00801-9
[6] CAMACHO-HERNÁNDEZ N P, PEÑA-ORTEGA F. Fractalkine/CX3CR1-dependent modulation of synaptic and network plasticity in health and disease[J]. Neural Plast, 2023, 2023: 4637073.
[7] 中国微循环学会神经变性病专委会, 中华医学会神经病学分会神经心理与行为神经病学学组, 中华医学会神经病学分会神经康复学组. 阿尔茨海默病康复管理中国专家共识(2019)[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2020, 39(1): 9-19. [8] KACZMAREK B, ILKOWSKA Z, KROPINSKA S, et al. Applying ACE-Ⅲ, M-ACE and MMSE to diagnostic screening assessment of cognitive functions within the Polish population[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(19): 12257. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912257
[9] YU R C, MUKADAM N, KAPUR N, et al. Validation of the Taiwanese version of ACE-Ⅲ (T-ACE-Ⅲ) to detect dementia in a memory clinic[J]. Arch Clin Neuropsychol, 2022, 37(3): 692-703. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acab089
[10] JIA X F, WANG Z H, HUANG F F, et al. A comparison of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) for mild cognitive impairment screening in Chinese middle-aged and older population: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2021, 21(1): 485. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03495-6
[11] 田金洲, 解恒革, 王鲁宁, 等. 中国阿尔茨海默病痴呆诊疗指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2021, 40(3): 269-283. [12] ROSTAGNO A A. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 24(1): 107.
[13] OGBODO J O, AGBO C P, NJOKU U O, et al. Alzheimer's disease: pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions[J]. Curr Aging Sci, 2022, 15(1): 2-25.
[14] CAI Y L, LIU J L, WANG B, et al. Microglia in the neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and related therapeutic targets[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 856376.
[15] CASAGRANDE S S, LEE C, STOECKEL L E, et al. Cognitive function among older adults with diabetes and prediabetes, NHANES 2011-2014[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2021, 178: 108939.
[16] 刘雨莹, 张娇珍, 王宝爱, 等. 阿尔茨海默病患者血清GFAP、BDNF及Hcy水平与认知功能的相关性[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2023, 31(5): 282-285. [17] TWAROWSKI B, HERBET M. Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease-pathomechanism, diagnosis and treatment: a review[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(7): 6518.
[18] BIVONA G, IEMMOLO M, PICCOLI T, et al. High cerebrospinal fluid CX3CL1 levels in Alzheimer's disease patients but not in non-alzheimer's disease dementia[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(19): 5498.
[19] ZHOU F T, SUN Y Y, XIE X H, et al. Blood and CSF chemokines in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2023, 15(1): 107.
[20] BLANCO-PALMERO V A, RUBIO-FERNÁNDEZ M, ANTEQUERA D, et al. Increased YKL-40 but not C-reactive protein levels in patients with Alzheimer's disease[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(9): 1094.
[21] CONNOLLY K, LEHOUX M, O'ROURKE R, et al. Potential role of chitinase-3-like protein 1(CHI3L1/YKL-40) in neurodegeneration and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2023, 19(1): 9-24.




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号