Regulating effect and mechanism of SLC1A5-TM4SF1 complex on cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells
-
摘要:目的
探讨氨基酸转运载体溶质载体家族1成员5(SLC1A5)-四跨膜蛋白超家族成员1(TM4SF1)复合物对食管鳞状细胞癌(ESCC)细胞顺铂耐药的调控作用及分子机制。
方法通过慢病毒载体构建SLC1A5稳定过表达的Eca109细胞, 通过细胞活力试验检测SLC1A5对细胞顺铂敏感性的影响。采用蛋白质免疫印迹法(WB)检测SLC1A5在Eca109细胞及顺铂耐药Eca109细胞(Eca109-R)中的表达。在Eca109-R细胞中通过慢病毒载体敲低SLC1A5表达,检测敲低SLC1A5表达后细胞对顺铂的敏感性。采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)检测SLC1A5敲低对Eca109-R细胞中DNA损伤修复关键基因表达的影响。在SLC1A5敲低的Eca109-R细胞中,通过细胞活力试验检测过表达RAD50后细胞对顺铂的敏感性。在Eca109细胞中,利用慢病毒载体分别或共同过表达SLC1A5、TM4SF1, 通过细胞活力试验检测SLC1A5-TM4SF1复合物对RAD50表达及细胞顺铂耐药的影响。
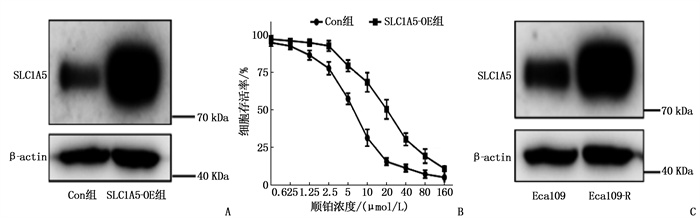
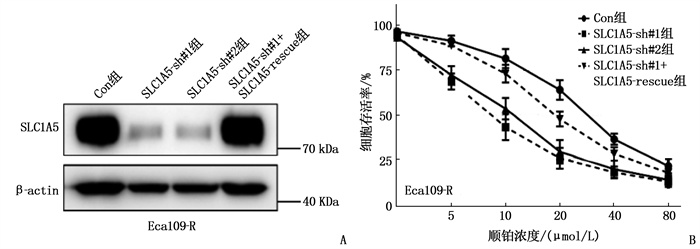
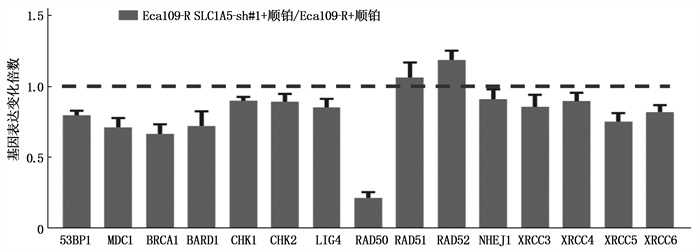
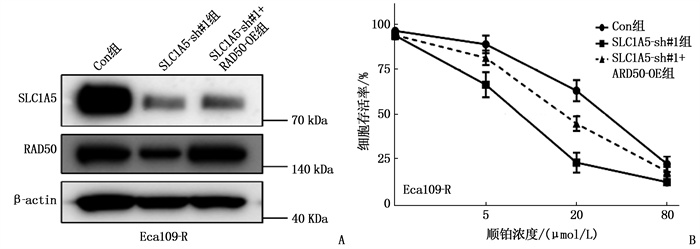
结果与对照细胞相比,过表达SLC1A5的Eca109细胞对顺铂的耐药性增强,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Eca109-R细胞的SLC1A5蛋白表达升高,且与对照细胞相比,敲低SLC1A5表达的细胞对顺铂更敏感,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。顺铂处理条件下, RAD50基因表达水平在敲低SLC1A5后显著下调(P < 0.05)。敲低SLC1A5会抑制RAD50蛋白表达,且与对照细胞相比,在SLC1A5敲低细胞中过表达RAD50可以大幅度恢复细胞对顺铂的耐药,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。SLC1A5与TM4SF1同时过表达可进一步上调RAD50表达,且与对照细胞相比,细胞对顺铂的耐药性增强,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论SLC1A5-TM4SF1复合物通过上调RAD50表达,促进ESCC细胞对顺铂的耐药。
-
关键词:
- 氨基酸转运载体溶质载体家族1成员5 /
- 四跨膜蛋白超家族成员1 /
- RAD50双链断裂修复蛋白 /
- 食管鳞状细胞癌 /
- 耐药 /
- 膜蛋白复合物
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the regulatory effect and molecular mechanism of solute carrier family 1 member 5 (SLC1A5) -tetraspanin superfamily member 1 (TM4SF1) complex on cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells.
MethodsSLC1A5-overexpressing Eca109 cells were constructed using lentiviral vectors, and the effect of SLC1A5 on cisplatin sensitivity was assessed through cell viability assays. Western blotting (WB) was employed to detect SLC1A5 expression in Eca109 cells and cisplatin-resistant Eca109 cells (Eca109-R). SLC1A5 expression was knocked down in Eca109-R cells using lentiviral vectors, and cisplatin sensitivity was examined thereafter. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was utilized to analyze the influence of SLC1A5 knockdown on the expression of key genes involved in DNA damage repair in Eca109-R cells. In SLC1A5-knockdown Eca109-R cells, cell viability assays were performed to evaluate the sensitivity to cisplatin after RAD50 overexpression. Additionally, Eca109 cells were separately or co-overexpressed with SLC1A5 and TM4SF1 using lentiviral vectors, and the effect of the SLC1A5-TM4SF1complex on RAD50 expression and cisplatin resistance was examined through cell viability assays.
ResultsCompared with control cells, Eca109 cells overexpressing SLC1A5 exhibited enhanced cisplatin resistance (P < 0.05). Eca109-R cells showed increased SLC1A5 protein expression, and knockdown of SLC1A5 cells were more sensitivity to cisplatin (P < 0.05). RAD50 gene expression was significantly downregulated upon SLC1A5 knockdown under cisplatin treatment (P < 0.05). Knockdown of SLC1A5 inhibited RAD50 protein expression, and overexpression of RAD50 in SLC1A5-knockdown cells significantly restored cisplatin resistance (P < 0.05). Co-overexpression of SLC1A5 and TM4SF1 can further up-regulate the expression of RAD50, and the drug resistance of the cells to cisplatin was enhanced compared with the control cells(P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe SLC1A5-TM4SF1 complex promotes cisplatin resistance in ESCC cells by upregulating RAD50 expression.
-
特发性膜性肾病(IMN)属于一类由抗体介导的自身免疫性疾病[1], 目前病因不明。近年来随着M型磷脂酶A2受体(PLA2R)、Ⅰ型血小板反应蛋白7A域(THSD7A)等IMN相关生物标志物被发现,越来越多的学者认为B淋巴细胞(简称B细胞)在IMN发病机制中占据重要地位[2-3]。大部分前B细胞与成熟B细胞的细胞膜表面存在一类跨膜磷酸蛋白,即B细胞分化抗原CD20[4]。以利妥昔单抗(RTX)为代表的人/鼠嵌合型单抗对CD20+ B细胞具有靶向作用,最早被用于淋巴瘤的治疗[5]。随着研究的进展, RTX逐渐被应用于免疫相关性疾病的治疗[6-8]。RTX结合CD20, 可通过抗体依赖性细胞介导的细胞毒性反应、补体依赖性细胞毒性反应以及直接诱导细胞凋亡等方式消耗CD20+ B细胞,继而抑制机体过度活跃的免疫应答,有效缓解IMN患者的蛋白尿症状,降低IMN复发风险[9]。既往研究[10-12]认为,基于足细胞损伤的其他疾病如微小病变性肾病、局灶节段性肾小球肾炎、狼疮性肾炎等大多与T淋巴细胞(简称T细胞)的增殖分化相关,然而患者使用RTX亦能达到临床缓解。另有研究[13]显示,使用RTX治疗的IMN患者在治疗早期B细胞尚未完全耗竭或治疗晚期B细胞数量开始恢复时,病情仍然能够得到持续的临床缓解。由此提示,IMN的发病机制以及RTX的治疗效应并非仅局限于B细胞。一项关于RTX治疗自身免疫性疾病患者的研究[14]结果表明, RTX可以纠正T细胞各亚群数量及比例的失衡,而这是RTX发挥作用的另一重要机制。本文综述RTX对IMN患者T细胞亚群的影响及其临床意义,以期为多靶点治疗IMN提供理论依据。
1. IMN与T细胞亚群
根据表面分化抗原CD分子的不同,T细胞亚群主要分为CD4+辅助性T细胞(Th细胞)、CD8+细胞毒性T细胞(Ts细胞)、CD3+CD4-CD8-双阴性T细胞(DNT细胞)。CD4+ T细胞在体液免疫和细胞免疫中起重要作用,与机体免疫系统的活跃程度有关,而CD8+ T细胞在自身免疫性疾病中可抑制致病性CD4+ T细胞,并具有杀伤靶细胞的功能[15]。CD4+ T细胞按照功能特征可进一步分为Th1、Th2、Th17、Treg细胞等。Th1细胞的功能以分泌干扰素(IFN)-γ介导细胞免疫为主,Th2细胞的功能以分泌白细胞介素(IL)-4、IL-10、IL-13为主,能够活化B细胞,同时诱导免疫球蛋白产生,介导体液免疫[16]。Th17细胞对于核转录因子RORγt具备特异性表达能力,并可通过分泌IL-17、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α、IL-6、IL-23等细胞因子影响炎症反应、组织损伤过程[17]。Treg细胞除了可有效抑制自身免疫性疾病的发生,还可能参与诱导移植耐受以及肿瘤免疫调节,在维持机体内环境稳定方面发挥着关键作用[18]。
早在1982年就有研究[19]发现,特发性肾小球肾炎患者存在T细胞亚群数量和功能异常。此后,相关研究[20]指出, IMN患者外周血CD4+和CD8+ T细胞亚群失衡,与健康对照者相比,IMN患者CD4+/CD8+比值显著升高,且CD4+ T细胞呈升高趋势, CD8+ T细胞呈降低趋势,随着肾病的临床缓解, CD4+/CD8+比值逐渐下降。研究[18]结果表明,与健康对照者相比,IMN患者存在Th2细胞分泌的IL-4、IL-10上调,而Th1细胞分泌的IFN-γ下调现象,使得Th1/Th2细胞比值发生变化,由此推测IMN的发病机制与Th2细胞主导的炎性活动存在关联。近年来研究[7-8]报道,儿童肾病综合征、过敏性紫癜性肾炎、系统性红斑狼疮性肾炎等肾脏病患者存在Th17/Treg免疫失衡。另有研究[21]发现,IMN患者外周血Treg细胞水平较正常对照组显著降低, Th17相关因子IL-17、IL-23及RORγt mRNA表达升高,Treg细胞相关因子IL-10及Foxp3 mRNA表达下降,且Th17/Treg细胞失衡越明显,病情严重程度越高,提示Th17/Treg细胞与临床预后密切相关。由此可见,IMN患者体内存在多种免疫细胞数量及比例失衡。
2. RTX与T细胞亚群
B细胞耗竭是治疗T细胞介导的自身免疫性疾病(如类风湿性关节炎、系统性硬化症、1型糖尿病等)的有效方案,而B细胞作为强大的抗原提呈细胞,可为T细胞提供共刺激信号,并产生调节T细胞分化的细胞因子。一方面, RTX耗竭B细胞可以直接减少IMN患者中自身抗体的产生[22]; 另一方面, RTX切断了B细胞依赖性T细胞的激活渠道,阻断过激的免疫反应造成的炎症损伤[23]。值得注意的是, RTX可直接与足细胞表面的酸性鞘磷脂酶样磷酸二酯酶3b(SMPDL-3b)结合,调节酸性鞘磷脂酶(ASMase)活性,阻止肌动蛋白细胞骨架破坏和足细胞凋亡,保护肾小球足细胞[24]。
2.1 RTX纠正CD4+/CD8+失衡
SENTÍS A等[25]将37例肾病综合征患者分为RTX治疗组19例与保守治疗组18例,随访发现RTX治疗组CD4+ T细胞百分比下降,CD8+ T细胞百分比上升。然而林力等[26]研究结果提示,RTX治疗后,局灶节段性肾小球硬化、微小病变性肾病患者CD3+、CD3+CD4+、CD3+CD8+ T细胞及CD56+CD16+自然杀伤(NK)细胞计数与治疗前无显著差异。因此, RTX用于IMN患者是否存在纠正CD4+/CD8+失衡的作用仍需开展大量实验加以探索。
2.2 RTX纠正Th1/Th2细胞失衡
既往研究[8-9]发现,在原发免疫性血小板减少症、免疫性溶血性贫血等Th1细胞占优势的自身免疫性疾病中, RTX治疗可通过下调血清IL-2、IFN-γ水平,上调IL-4、IL-10等细胞因子水平,有效平衡Th1/Th2细胞。BHATIA D等[27]检测18例激素依赖性肾病综合征(SDNS)患者RTX治疗前、治疗1个月、治疗1年后或首次复发时的外周血,发现RTX治疗降低了Th2细胞的绝对数量,对Th1细胞则无明显改变,进而使Th1/Th2比值升高,但该研究样本量较少,且未对不同类型SDNS患者进行分组分析。随后有研究[25]指出, IMN属于Th2细胞占优势的自身免疫性疾病, RTX治疗后IL-4、IL-13等细胞因子水平较治疗前下降,进一步证实RTX对不同功能Th细胞紊乱的纠正作用,然而其机制目前尚未阐明,既往研究[28]认为这主要与RTX对IL-13+ Th2的调控相关。陶书超[29]认为RTX可能通过对B细胞增殖产生抑制作用,使自身抗体减少,抗原提呈作用减弱,并上调抑制性T细胞,进而使Th1/Th2细胞平衡状态得以恢复,改善患者免疫功能。另有研究[30]认为,IMN患者存在B细胞过度活跃情况,其中一类B细胞亚群即Breg细胞可通过直接或间接方式抑制效应性CD4+ T细胞,当RTX消耗B细胞后, B细胞活化因子也被消耗,Breg细胞活性降低,从而抑制Th0细胞向Th2细胞转化,进而减少Th2细胞数量。
2.3 RTX纠正Th17/Treg细胞失衡
ROCCATELLO D等[31]发现,膜性肾病患者使用RTX治疗时,在B细胞耗竭的第12个月,Treg细胞水平会升高至基线的10倍。ROSENZWAJG M等[32]将25例原发性膜性肾病患者分为RTX治疗组16例和保守治疗组9例,发现RTX治疗组Treg细胞水平较保守治疗组显著升高,Th17/Treg细胞比值下降。RTX治疗消耗了B细胞相关细胞因子如IL-6、TGF-β, 从而抑制Th17细胞分化和增殖,另外肥大细胞具有与CD20分子相似结构的FcεRI表型, RTX可与其结合从而抑制肥大细胞依赖的Th17细胞扩增[33]。相关研究[34]证实,在B细胞缺乏的小鼠中, Treg细胞的功能和数量得到提升,这可能是因为RTX抑制B细胞分泌IL-35、IFN-γ等因子,而这些因子可抑制Treg细胞增殖并促进其凋亡。此外, RTX还可以抑制B细胞和T细胞之间的CD40-CD40L共刺激相互作用,使Treg细胞无法分化为炎症表型,进一步增加Treg细胞的含量。因此,B细胞功能越弱, Treg细胞活性越强。
值得关注的是,小剂量IL-2疗法是目前治疗自身免疫性疾病的研究热点,其机制主要是通过IL-2/IL-2R信号通路上调Treg细胞水平。相关研究[35]验证了IL-2、IL-2R缺陷引起外周Treg/Th17细胞数量与功能失衡是系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)发病的主要机制,并提出小剂量IL-2可以在体内同时扩增CD4+和CD8+ Treg细胞,抑制SLE的免疫反应。然而,目前尚无法明确小剂量IL-2治疗IMN患者的效果,仍需开展大量实验预测其可行性。
2.4 RTX直接作用于CD20+ T细胞
既往认为CD20分子只在B细胞表面表达并对B细胞分化与增殖加以调节,但新的实验结果显示免疫系统中还存在一类CD3+CD20+ T细胞,在生物学特征方面,其与传统CD3+ T细胞存在类似但又具独特性的表现。相关研究[36]使用RTX对原代Sjogren氏综合征(SS)进行治疗发现,RTX除了能清除B细胞外,还能使CD3+CD4-CD8- T细胞与CD3+CD4+ T细胞之比大幅降低,进一步分析发现,这2类细胞皆表达CD20分子,提示SS患者机体内分布着对IL-17具有分泌能力的炎症性CD3+CD20+ T细胞,而RTX能够将其清除,在缓解SS疾病方面具有良性作用。因此, RTX在消耗B细胞的同时直接靶向CD20+ T细胞的作用机制或许也值得深入探究。然而LEANDRO M J等[37]强调,仅3.2%的外周CD3+ T细胞可表达低水平的CD20,所以RTX对T细胞的间接作用似乎更可信。
3. T细胞亚群监测的临床意义
虽然RTX在治疗IMN方面已取得令人满意的成效,但其也存在着临床见效慢、完全缓解率相对偏低的不足[38], 仍有小部分患者对RTX没有较好的临床反应性,出现用药后不缓解或者近期复发甚至病情加重。2002年REMUZZI G等[39]报道了RTX治疗8例保守治疗6个月无效的IMN患者的效果,随访1年发现1例患者用药后出现近期复发。FERNANDEZ-FRESNEDO G等[11]纳入8例局灶节段性肾小球硬化患者作为观察对象,有3例患者部分缓解,且其中1例的临床缓解期很短。对RTX无临床反应的患者使用RTX后,不仅疗效不佳,还要承受药物的多种不良反应,因此使用RTX前较为准确地预估治疗效果显得尤为重要。
3.1 CD4+ T细胞的临床意义
REMUZZI G等[39]报道CD4+ T细胞计数可作为IMN患者对RTX反应性的预测指标,但该研究结论后续并未得到进一步证实。在其他免疫相关性疾病中, CD4+ T细胞作为预测指标频繁出现[40]。大多数类风湿性关节炎患者接受RTX干预后,T细胞(主要是CD4+ T细胞)数量显著减少,且CD4+ T细胞消耗越多,临床反应越好。MÉLET J等[41]认为, CD4+ T细胞下调可在一定程度上反映病情改善。LAVIELLE M等[42]纳入52例在院使用RTX治疗的类风湿性关节炎患者作为研究对象,比较治疗前和治疗后3、6个月的淋巴细胞表型变化及临床反应性,发现CD4+ T细胞耗竭提示类风湿性关节炎患者对RTX有反应性。然而由于目前尚缺乏相关研究, RTX治疗后的CD4+ T细胞消耗能否作为IMN患者临床反应性的预测指标尚不可知。
3.2 Treg细胞评估RTX临床反应性
2011年SHIGERU I等[43]研究发现, SLE患者使用RTX治疗后,有临床反应性者Treg细胞较无反应者增加。ROCCATELLO D等[31]发现, RTX治疗膜性肾病临床缓解组患者的Treg细胞经过12个月会上调至基线值的10倍,且PLA2R-Ab阳性患者的Treg细胞水平显著低于阴性患者。ROSENZWAJG M等[32]发现,对RTX有临床反应的重症IMN患者基线时Treg细胞增加幅度相较于无临床反应的患者更明显,而保守治疗组及健康对照组Treg细胞未出现明显变化。尽管目前临床尚不明确Treg细胞通过何种机制影响患者对RTX的反应性,但通过Treg细胞对早期IMN患者进行RTX疗效评估可能具有一定价值,这也有助于临床医生为RTX临床疗效不佳的患者尽早更换治疗方案。
4. 小结
IMN发病机制复杂, T细胞、B细胞、NK细胞等诸多免疫细胞均可产生多种免疫反应,既是潜在的致病关键点,也是潜在的治疗靶点。RTX通过消耗B细胞,调节了T细胞的数量及功能,纠正了T细胞各亚群比例失衡,可促进IMN患者蛋白尿症状的缓解。未来,研究者还应开展更多的实验研究进一步探寻RTX治疗IMN患者临床反应性的预测指标。
-
表 1 qRT-PCR相关引物序列
基因 方向 序列 53BP1 正向 5′-GCCTGATCAATGGACCCTACTGGAAGTCAGG-3′ 反向 5′-CCGCTCGAGTTAGTGAGAAACATAATCGTGT-3′ MDC1 正向 5′-TGCTCTTCACAGGAGTGGTG-3′ 反向 5′-GGGCACACAGGAACTTGACT-3′ BRCA1 正向 5′-CTGAAGACTGCTCAGGGCTATC-3′ 反向 5′-AGGGTAGCTGTTAGAAGGCTGG-3′ BARD1 正向 5′-AGCGTAGGGATGGACCTCTT-3′ 反向 5′-CCATTGAGAATCCCAAGCAT-3′ CHK1 正向 5′-ATATGAAGCGTGCCGTAGACT-3′ 反向 5′-TGCCTATGTCTGGCTCTATTCTG-3′ CHK2 正向 5′-AAGAAGTTGTTGGTAGTG-3′ 反向 5′-TTCCTCAGACAGAAGATC-3′ LIG4 正向 5′-TGCTGCTGAGTTGCATAATGT-3′ 反向 5′-AGCAGCTAGCATTGGTTTTGA-3′ RAD50 正向 5′-TCCACGATAGGTACTTCGCC-3′ 反向 5′-TGAGGACAACAGAACTTGTGAAC-3′ RAD51 正向 5′-GGTCTGGTGGTCTGTGTTGA-3′ 反向 5′-GGTGAAGGAAAGGCCATGTA-3′ RAD52 正向 5′-CTGGCACTGTCCAAAGCATA-3′ 反向 5′-TAGATCGAGCTCCCTGTGTG-3′ NHEJ1 正向 5′-TGCAGATTCATGACAAAGGG-3′ 反向 5′-ACTACCAGGAGAGTGGGGCT-3′ XRCC3 正向 5′-CGTCTTCCGTGCAGATGTAG-3′ 反向 5′-CATCACTGAGCTGGCCG-3′ XRCC4 正向 5′-TTTCAGCTGAGATGTGCTCC-3′ 反向 5′-AGGAGACAGCGAATGCAAAG-3′ XRCC5 正向 5′-GAAGGCTCGGATGCAGTCTA-3′ 反向 5′-CCTGCTGAAAACTTCCGTGT-3′ XRCC6 正向 5′-TGGTTCATTTGTTTCCCGAT-3′ 反向 5′-AGACCAGGAAGCGAGCACT-3′ GAPDH 正向 5′-GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT-3′ 反向 5′-GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG-3′ 表 1 qRT-PCR相关引物序列
基因 方向 序列 53BP1 正向 5′-GCCTGATCAATGGACCCTACTGGAAGTCAGG-3′ 反向 5′-CCGCTCGAGTTAGTGAGAAACATAATCGTGT-3′ MDC1 正向 5′-TGCTCTTCACAGGAGTGGTG-3′ 反向 5′-GGGCACACAGGAACTTGACT-3′ BRCA1 正向 5′-CTGAAGACTGCTCAGGGCTATC-3′ 反向 5′-AGGGTAGCTGTTAGAAGGCTGG-3′ BARD1 正向 5′-AGCGTAGGGATGGACCTCTT-3′ 反向 5′-CCATTGAGAATCCCAAGCAT-3′ CHK1 正向 5′-ATATGAAGCGTGCCGTAGACT-3′ 反向 5′-TGCCTATGTCTGGCTCTATTCTG-3′ CHK2 正向 5′-AAGAAGTTGTTGGTAGTG-3′ 反向 5′-TTCCTCAGACAGAAGATC-3′ LIG4 正向 5′-TGCTGCTGAGTTGCATAATGT-3′ 反向 5′-AGCAGCTAGCATTGGTTTTGA-3′ RAD50 正向 5′-TCCACGATAGGTACTTCGCC-3′ 反向 5′-TGAGGACAACAGAACTTGTGAAC-3′ RAD51 正向 5′-GGTCTGGTGGTCTGTGTTGA-3′ 反向 5′-GGTGAAGGAAAGGCCATGTA-3′ RAD52 正向 5′-CTGGCACTGTCCAAAGCATA-3′ 反向 5′-TAGATCGAGCTCCCTGTGTG-3′ NHEJ1 正向 5′-TGCAGATTCATGACAAAGGG-3′ 反向 5′-ACTACCAGGAGAGTGGGGCT-3′ XRCC3 正向 5′-CGTCTTCCGTGCAGATGTAG-3′ 反向 5′-CATCACTGAGCTGGCCG-3′ XRCC4 正向 5′-TTTCAGCTGAGATGTGCTCC-3′ 反向 5′-AGGAGACAGCGAATGCAAAG-3′ XRCC5 正向 5′-GAAGGCTCGGATGCAGTCTA-3′ 反向 5′-CCTGCTGAAAACTTCCGTGT-3′ XRCC6 正向 5′-TGGTTCATTTGTTTCCCGAT-3′ 反向 5′-AGACCAGGAAGCGAGCACT-3′ GAPDH 正向 5′-GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT-3′ 反向 5′-GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG-3′ -
[1] ZHOU M G, WANG H D, ZENG X Y, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10204): 1145-1158. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1
[2] ZOU F W, YANG S Z, LI W Y, et al. circRNA_001275 upregulates Wnt7a expression by competitively sponging miR-370-3p to promote cisplatin resistance in esophageal cancer[J]. Int J Oncol, 2020, 57(1): 151-160.
[3] HASSANEIN M, HOEKSEMA M D, SHIOTA M, et al. SLC1A5 mediates glutamine transport required for lung cancer cell growth and survival[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(3): 560-570. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2334
[4] LU J, CHEN M, TAO Z H, et al. Effects of targeting SLC1A5 on inhibiting gastric cancer growth and tumor development in vitro and in vivo[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(44): 76458-76467. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19479
[5] 胡效林, 郝鑫, 李文倩, 等. SLC1A5协同TM4SF1通过mTOR信号通路调控食管鳞癌细胞迁移[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2023, 27(14): 33-39, 45. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20230772 [6] MA H R, WU Z Z, PENG J J, et al. Inhibition of SLC1A5 sensitizes colorectal cancer to cetuximab[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018, 142(12): 2578-2588. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31274
[7] WU Y Y, LAW Y Y, HUANG Y W, et al. Glutamine metabolism controls amphiregulin-facilitated chemoresistance to cisplatin in human chondrosarcoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(16): 5174-5186. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.86116
[8] ZHANG Y, DONG P, LIU N, et al. TRIM6 reduces ferroptosis and chemosensitivity by targeting SLC1A5 in lung cancer[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2023, 2023: 9808100.
[9] HOU S C, HAO X, LI J J, et al. TM4SF1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis by interacting with integrin α6[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(7): 609. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05067-2
[10] HOU S C, JIN W G, XIAO W M, et al. Integrin α5 promotes migration and cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(12): 2774-2788.
[11] SZAKÁCS G, PATERSON J K, LUDWIG J A, et al. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2006, 5(3): 219-234. doi: 10.1038/nrd1984
[12] CHEN Z K, WANG Y Z, WARDEN C, et al. Cross-talk between ER and HER2 regulates c-MYC-mediated glutamine metabolism in aromatase inhibitor resistant breast cancer cells[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2015, 149: 118-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.02.004
[13] ALFARSI L H, ANSARI R E, CRAZE M L, et al. SLC1A5 co-expression with TALDO1 associates with endocrine therapy failure in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 189(2): 317-331. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06298-1
[14] WANG C F, WU J M, WANG Z J, et al. Glutamine addiction activates polyglutamine-based nanocarriers delivering therapeutic siRNAs to orthotopic lung tumor mediated by glutamine transporter SLC1A5[J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 183: 77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.035
[15] ROTTENBERG S, DISLER C, PEREGO P. The rediscovery of platinum-based cancer therapy[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 37-50. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-00308-y
[16] KÄSHAMMER L, SAATHOFF J H, LAMMENS K, et al. Mechanism of DNA end sensing and processing by the Mre11-Rad50 complex[J]. Mol Cell, 2019, 76(3): 382-394. e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.035
[17] ALTAN B, YOKOBORI T, IDE M, et al. High expression of MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 is associated with poor prognosis and chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. Anticancer Res, 2016, 36(10): 5237-5247. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11094
[18] TAO X A, LU Y, QIU S B, et al. AP1G1 is involved in cetuximab-mediated downregulation of ASCT2-EGFR complex and sensitization of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to ROS-induced apoptosis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 408: 33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.012
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 张超,魏锦曦,雷敏. 特发性膜性肾病患者血清PPM1A水平及意义. 检验医学与临床. 2025(02): 247-250+256 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 胡琳,彭亮,蒲友敏,陈晶晶,彭晓亮. 特发性膜性肾病患者血清APRIL、MCP-1、CD4+/CD8+比值与免疫抑制剂治疗疗效的关系分析. 现代生物医学进展. 2024(14): 2689-2693 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 费睿成. 血清磷脂酶A2受体抗体水平与特发性膜性肾病临床分期的相关性. 慢性病学杂志. 2024(08): 1242-1244 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈忠锋,夏楠楠,魏艳林,焦琳珊,王瑞,何兵. 利妥昔单抗联合环磷酰胺、泼尼松对特发性膜性肾病患者肾功能及血清抗M型磷脂酶A2受体抗体水平的影响. 中国合理用药探索. 2024(08): 104-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 卢艳,王柯,段丽娜. 利妥昔单抗联合糖皮质激素治疗特发性膜性肾病的效果. 中国实用医刊. 2024(20): 83-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 马娜,陈雨,解长飞,黄玲,刘玫梅. 利妥昔单抗联合甲泼尼龙治疗肾病综合征的临床效果. 临床合理用药. 2024(35): 124-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 徐倩,黄翠,万峻宏. 利妥昔单抗治疗对特发性膜性肾病患者临床效果及安全性的影响. 中国医学创新. 2024(33): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈文君,周雪娟. 利妥昔单抗与氯沙坦钾联合治疗膜性肾病的临床效果. 名医. 2024(20): 165-167 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李平方,徐小刚,刘恒,谭小猛,刘佩,李占亭. 糖皮质激素联合利妥昔单抗对特发性膜性肾病患者血脂、Th17/Treg失衡和血清PLA2R抗体、THSD7A抗体的影响. 现代生物医学进展. 2023(24): 4771-4775 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
