Relationships of expression of high mobility group box 1 protein and toll-like receptor 4 in patients with clinical characteristics of refractory epilepsy and their predictive value
-
摘要:目的
探讨高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)、Toll样受体4(TLR4)表达与难治性癫痫患者临床特征相关性以及预测价值。
方法回顾性分析84例难治性癫痫患者临床资料并将其纳入观察组。同期选择35例行颅内减压术的高颅内压患者作为对照组。采用免疫组织化学法检测HMGB1、TLR4表达情况,采用尼氏染色法观察组织形态,同时分析相关实验结果。
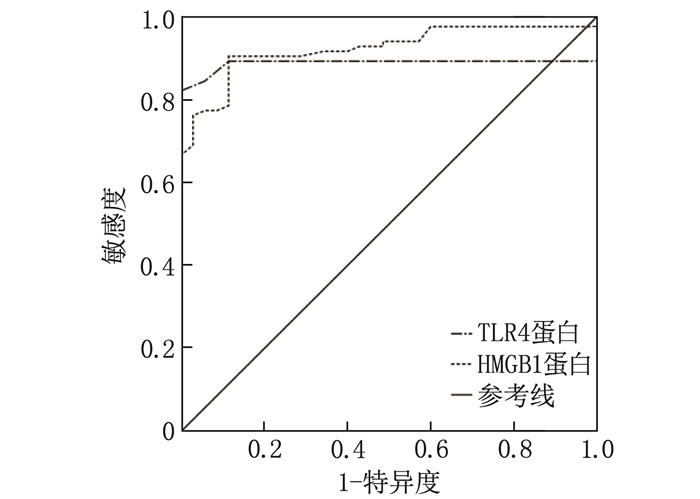
结果观察组HMGB1和TLR4表达高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。观察组HMGB1、TLR4蛋白条带的光密度值与内参β-actin条带光密度值高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。TLR4表达强度与癫痫发作频率、发作持续时间、病程、发作类型有关,而HMGB1表达强度与癫痫发作频率、发作持续时间、病程有关。病灶组织中, TLR4表达与HMGB1的表达呈正相关,提示两者存在协同作用。受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析显示, TLR4蛋白、HMGB1蛋白预测难治性癫痫的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.888、0.923。
结论HMGB1、TLR4在难治性癫痫患者病灶中呈高表达,且两者表达强度呈正相关,能够在一定程度上预测疾病发生、发展情况,为难治性癫痫的诊疗提供了新的生物标志物。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the correlations of the expression of high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with the clinical characteristics of patients with refractory epilepsy, as well as their predictive value.
MethodsA retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 84 patients with refractory epilepsy, and they were included in observation group. During the same period, 35 patients with intracranial hypertension undergoing craniectomy for decompression were selected as control group. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expressions of HMGB1 and TLR4, while Nissl staining was applied to observe tissue morphology. The relevant experimental results were analyzed simultaneously.
ResultsThe expression levels of HMGB1 and TLR4 in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The optical density values of HMGB1 and TLR4 protein bands as well as internal reference β-actin bands in the observation group were significantly higher than those of the control group (P < 0.05). The intensity of TLR4 expression was correlated with seizure frequency, seizure duration, disease duration, and seizure type, while the intensity of HMGB1 expression was correlated with seizure frequency, seizure duration, and disease duration. In the lesion tissues, the expression of TLR4 was positively correlated with the expression of HMGB1, suggesting a synergistic effect between them. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis revealed that the areas under the curve (AUCs) for TLR4 and HMGB1 proteins in predicting refractory epilepsy were 0.888 and 0.923, respectively.
ConclusionHMGB1 and TLR4 are highly expressed in the lesions of patients with refractory epilepsy, and their expression intensities are positively correlated. They can predict the occurrence and development of the disease to a certain extent, providing new biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of refractory epilepsy.
-
-
表 1 2组HMGB1、TLR4表达情况比较[n(%)]
组别 n HMGB1表达情况 TLR4表达情况 阳性 阴性 阳性 阴性 观察组 84 73(86.90)* 11(13.10) 71(84.52)* 13(15.48) 对照组 35 15(42.86) 20(57.14) 8(22.86) 27(77.14) HMGB1: 高迁移率族蛋白B1; TLR4: Toll样受体4。与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。 表 2 TLR4与HMGB1在难治性癫痫患者病灶组织中表达的相关性
例 HMGB1表达情况 n TLR4表达情况 - + ++ n 84 13 38 33 - 11 9 2 0 + 40 2 25 13 ++ 33 2 11 20 表 3 2组HMGB1、TLR4蛋白相对含量比较(x±s)
组别 n TLR4/β-actin HMGB1/β-actin 观察组 84 0.35±0.12* 1.35±0.30* 对照组 35 0.21±0.01 0.92±0.19 与对照组比较, * P < 0.05。 表 4 临床因素与病灶组织中TLR4表达的关系分析[n(%)]
临床因素 分类 TLR4表达 χ2 P 阳性(n=71) 阴性(n=13) 性别 男 49(69.01) 7(53.85) 1.138 0.286 女 22(30.99) 6(40.15) 癫痫病程 ≤10年 20(28.17) 10(76.92) 11.376 < 0.001 >10年 51(71.83) 3(23.08) 年龄 < 60岁 38(53.52) 7(53.85) 0.001 0.983 ≥60岁 33(46.48) 6(46.15) 癫痫发作频率 ≤1次/周 39(54.93) 12(92.31) 6.436 0.011 >1次/周 32(45.07) 1(7.69) 癫痫发作持续时间 ≤5 min 34(47.89) 11(84.62) 5.959 0.015 >5 min 37(52.11) 2(15.38) 癫痫发作类型 全面性强直阵挛发作 30(42.25) 1(7.69) 5.637 0.018 非全面性强直阵挛发作 41(57.75) 12(92.31) 表 5 临床各因素与病灶组织中HMGB1表达的关系分析[n(%)]
临床因素 分类 HMGB1表达 χ2 P 阳性(n=73) 阴性(n=11) 性别 男 47(64.38) 9(81.82) 1.308 0.253 女 26(35.62) 2(18.18) 癫痫病程 ≤10年 20(27.40) 10(90.91) 16.795 < 0.001 >10年 53(72.60) 1(9.09) 年龄 < 60岁 41(56.16) 4(36.36) 1.507 0.220 ≥60岁 32(43.84) 7(63.64) 癫痫发作频率 ≤1次/周 40(54.79) 11(100.00) 8.190 0.004 >1次/周 33(45.21) 0 癫痫发作持续时间 ≤5 min 35(47.95) 10(90.91) 7.095 0.008 >5 min 38(52.05) 1(9.09) 癫痫发作类型 全面性强直阵挛发作 29(39.73) 2(18.18) 1.906 0.167 非全面性强直阵挛发作 44(60.27) 9(81.82) 表 6 TLR4、HMGB1预测难治性癫痫患者的效能分析
变量 曲线下面积 SE P 95%CI Cut-off 约登指数 敏感度/% 特异度/% TLR4蛋白 0.888 0.034 < 0.001 0.822~0.954 0.25 0.821 82.1 100.0 HMGB1蛋白 0.923 0.025 < 0.001 0.875~0.971 1.13 0.791 90.5 88.6 -
[1] FEJA M, MELLER S, DEKING L S, et al. OV329, a novel highly potent γ-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase inactivator, induces pronounced anticonvulsant effects in the pentylenetetrazole seizure threshold test and in amygdala-kindled rats[J]. Epilepsia, 2021, 62(12): 3091-3104. doi: 10.1111/epi.17090
[2] 李承俊, 王丰, 姚培森, 等. 局灶性皮质发育不良相关"难定位" 难治性癫痫的手术疗效及影响因素分析[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2021, 20(8): 793-798. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115354-20201210-00959 [3] 姚娟, 钱忆家, 翁柠, 等. 平肝止痫复方联合卡马西平干预HMGB1/TLR4信号炎症通路的相关作用研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2022, 49(2): 191-198, 后插8. [4] 陈小妮, 谭会会, 殷艳玲, 等. 原发性癫痫患者血清BAFF、HMGB1、TLR4的表达水平及其临床意义[J]. 海南医学, 2023, 34(4): 550-553. [5] 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会癫痫疾病专业委员会. 中国基因性全面性癫痫临床诊治实践指南[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2020, 19(10): 973-976. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115354-20200529-00424 [6] WATSON G D R, AFRA P, BARTOLINI L, et al. A journey into the unknown: an ethnographic examination of drug-resistant epilepsy treatment and management in the United States[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2021, 124: 108319. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.108319
[7] MCALLISTER-WILLIAMS R H, BULMER S, NEWTON K, et al. Assessment for vagus nerve stimulation in patients with difficult-to-treat depression: a model from the Newcastle Regional Affective Disorders Service (RADS)[J]. J Affect Disord, 2021, 280(Pt A): 315-318.
[8] 季涛云, 王若凡, 刘庆祝, 等. 局灶起源的药物难治性癫痫性痉挛的手术预后及相关预后因素分析[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2021, 36(17): 1333-1337. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101070-20200505-00769 [9] 李冬梅, 陈巧彬, 陈琅, 等. FPS-ZM1和mNGF对癫痫幼鼠脑内HMGB1和TRX表达的影响[J]. 福建医科大学学报, 2021, 55(6): 513-516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4194.2021.06.010 [10] 黄亮, 张思磊, 朱作磊, 等. 微小RNA-542-3p和Toll样受体4在癫痫患者血浆中的表达及临床意义[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2022, 30(4): 241-245. [11] 李东秀, 潘彩芬. 血清高迁移率族蛋白B1水平与小儿热性惊厥临床特征及转为癫痫的相关性[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2021, 20(9): 927-931. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2021.09.009 [12] 屈会霞, 袁小锋, 屈昕. 长链非编码RNA核富含丰富的转录本1对癫痫模型海马神经元凋亡的影响和作用机制[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2021, 29(11): 1193-1197, 1212. doi: 10.11852/zgetbjzz2021-0402 [13] 黄凌锋, 廉荣镇, 肖能, 等. 癫痫患儿血清α-突触核蛋白和热休克蛋白70的表达及临床意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2021, 42(13): 1545-1548, 1553. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2021.13.003 [14] 李倩, 顾晶晶. 成年难治性癫痫患者行激光间质热疗术后疗效观察与护理[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2022, 37(11): 1043-1045. [15] 金超, 董琰, 张双, 等. 药物联合方案治疗小儿癫痫临床疗效及其对高迁移率族蛋白-1、Toll样受体4水平影响[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2022, 50(6): 636-638, 641.




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
