Efficacy of Aiyu Capsule combined with FOLFOX4 chemotherapy in treatment of median or advanced rectum cancer and its impacts on cellular immunity and survival
-
摘要:目的
观察在FOLFOX4化疗基础上使用艾愈胶囊对直肠癌中晚期患者的临床疗效,并探讨其对患者细胞免疫功能和生存期的影响。
方法将2018年3月—2019年6月病理类型为腺癌的中晚期直肠癌患者347例纳入本研究,按照单双号将其分为对照组173例与观察组174例,并随访36个月。对照组采用FOLFOX4化疗方案治疗,观察组在对照组基础上口服艾愈胶囊, 2组均连续治疗4个疗程。观察2组患者治疗2、4个疗程后的临床疗效与中医证候积分,比较2组患者治疗前和治疗2、4个疗程后肿瘤标志物、细胞免疫功能,并记录2组患者治疗期间不良反应发生情况以及累积存活率。
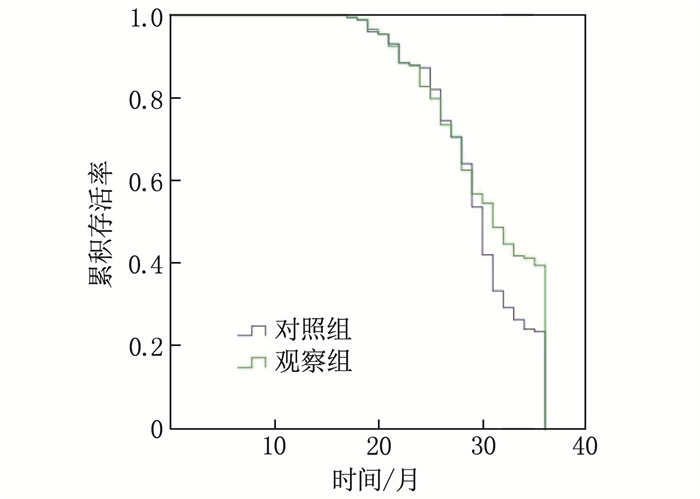
结果治疗2、4个疗程后,观察组完全缓解率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 治疗2个疗程后,观察组疾病控制率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后, 2组主症、次症积分及总积分均降低,且观察组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗2个疗程后, 2组患者癌胚抗原(CEA)、糖原抗原19-9(CA19-9)水平较治疗前降低,且观察组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 治疗4个疗程后, 2组患者CEA、CA19-9水平较治疗前和治疗2个疗程后降低,且观察组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗2个疗程后,观察组CD3+、CD4+ T细胞水平和CD4+/CD8+较治疗前均增高, CD8+ T细胞水平较治疗前降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗4个疗程后,对照组CD4+ T细胞水平和CD4+/CD8+较治疗2个疗程后增高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗4个疗程后,观察组CD3+、CD4+ T细胞水平和CD4+/CD8+较治疗前均增高,CD8+ T细胞水平较治疗前降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗期间,观察组皮炎和肝功能损害发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。K-M生存曲线显示,观察组累积存活率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.011)。
结论艾愈胶囊联合FOLFOX4化疗方案能促进中晚期直肠癌患者免疫功能恢复,缓解化疗不良反应,延长患者生存期,提高临床化疗疗效。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the clinical efficacy of Aiyu Capsule in combination with FOLFOX4 chemotherapy for patients with median or advanced rectum cancer, and to investigate its impacts on cellular immune function and survival.
MethodsA total of 347 patients with adenocarcinoma-type median or advanced rectum cancer were enrolled in this study from March 2018 to June 2019 were selected as study objects. Patients were divided into control group (173 patients) or observation group (174 patients) using an odd-even number system, and both groups were followed up for 36 months. The control group received FOLFOX4 chemotherapy, while the observation group additionally took Aiyu Capsule orally. Both groups underwent four consecutive treatment cycles.Clinical efficacy and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome scores were evaluated after 2 and 4 cycles. Tumor markers, cellular immune function, adverse reaction rates, and cumulative survival rates were compared between the two groups before and after treatment.
ResultsAfter 2 and 4 cycles of treatment, the complete response rate and disease control rate were significantly higher in the observation group compared to the control group (P<0.05). After 2 cycles of treatment, disease control rate in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). Both primary and secondary symptom scores, as well as total scores, decreased in both groups post-treatment, with lower scores in the observation group (P<0.05). Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) levels decreased in both groups after 2 cycles, with significant reduction in the observation group (P<0.05). After 4 courses of treatment, CEA and CA19-9 levels in two groups were lower than before treatment and 2 courses of treatment, and the observation group was lower than the control group (P<0.05). After two treatment cycles, the levels of CD3+, CD4+ T cells, and the CD4+ to CD8+ ratio(CD4+/CD8+) in the observation group were significantly elevated compared to pre-treatment, whereas the CD8+ T cell levels decreased significantly (P<0.05). After four treatment cycles, the control group demonstrated elevation in CD4+ T cell levels and the CD4+/CD8+ compared to the levels after two cycles (P<0.05). After four treatment cycles, the observation group had significant increase in CD3+, CD4+ T cell levels, and the CD4+/CD8+, whereas a significant reduction in CD8+ T cells compared to pretreatment (P<0.05). The incidence of dermatitis and liver function impairment was lower in the observation group (P<0.05). The Kaplan-Meier survival curve demonstrated a higher cumulative survival rate in the observation group (P=0.011).
ConclusionThe combination of Aiyu Capsule and FOLFOX4 chemotherapy promotes immune function recovery, alleviates chemotherapy-related adverse reactions, extends survival outcomes, and enhances clinical efficacy in patients with median or advanced rectum cancer.
-
妊娠期糖尿病是孕产妇较为常见的并发症之一,也是导致不良妊娠结局的重要原因之一[1-2]。因此,在临床实践中有效预测并及时干预妊娠期糖尿病对改善患者预后具有重要意义[3]。研究[4]表明,多种因素与妊娠期糖尿病的发生显著相关,主要包括妊娠期葡萄糖代谢异常、胰岛素抵抗以及胰岛素分泌异常。甲状腺功能减退可能会影响血液中葡萄糖和脂肪酸水平,但目前关于甲状腺功能减退与妊娠期糖尿病的相关性及其预测模型的研究相对较少[5]。研究[6]显示,随着甲状腺功能减退,生长激素水平会升高,而长期高水平的生长激素会导致胰岛素受体敏感性下降。本研究建立个体化预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病风险的Nomogram模型,为临床诊断提供参考。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
本研究采用前瞻性研究设计,选取2021年1—12月在本院诊断并治疗的甲状腺功能减退孕产妇160例作为研究对象。患者年龄为21~31岁,平均(25.66±2.59)岁; 孕周为22~30周,平均(26.54±2.91)周; 孕次为0~3次,平均(1.26±0.32)次; 产次为0~2次,平均为(1.09±0.12)次。其中,合并妊娠期糖尿病患者(观察组)85例,血糖正常患者(对照组)75例。所有患者均签署知情同意书。本研究经伦理委员会论证通过。
纳入标准: ①妊娠期糖尿病诊断标准者, 在孕期24~28周,进行75 g口服葡萄糖耐量试验(OGTT), 其空腹血糖或1 h后血糖或2 h后血糖异常[7]; ②年龄40岁以下者; ③经B超确定怀孕者; ④孕期诊断甲状腺功能减退(甲减),入组时表现为甲状腺功能水平异常降低者。排除标准: ①感染性疾病者; ②肿瘤患者; ③精神疾病者; ④孕前糖尿病者; ⑤经临床评估有心、脑、肾、胎盘等受损者。
1.2 方法
所有患者入组后均进行静脉采血4 mL, 15 000 r/min离心15 min后,取上清液。采用全自动生化仪对患者的空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)进行检测,采用化学发光法对患者的甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体(TPOAb)、血清游离四碘甲腺原氨酸(FT4)、游离三碘甲腺原氨酸(FT3)和促甲状腺激素(TSH)水平进行检测。胰岛素抵抗水平: 通过胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR)、胰岛β细胞功能指数(HOMA-β)进行评估。HOMA-IR=空腹胰岛素含量×空腹血糖含量/22.5。HOMA-β= 20×空腹胰岛素/(空腹血糖含量-3.5)。
记录所有患者的孕次、产次、孕前摄入碘含量、接受教育年限、自然流产史和孕期合并症等情况。
1.3 观察指标
比较2组患者的孕次、产次、接受教育年限、自然流产史、孕前空腹血糖、HbA1c、TPOAb、FT4、FT3以及TSH水平。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 26.0软件进行数据分析,所有计量资料均符合正态分布,采用(x±s)表示,行独立样本t检验,计量资料采用[n(%)]表示,行卡方检验。采用多因素Logistic分析法筛选妊娠期糖尿病发病的影响因素。采用Nomogram模型预测甲状腺功能减退患者发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估Nomogram模型对甲状腺功能减退患者发生妊娠期糖尿病风险的预测价值。P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 妊娠期糖尿病的单因素分析
观察组患者年龄、孕次、产次、孕前体质量指数、孕前TPOAb、孕前HOMA-IR和孕前HOMA-β高于对照组,孕前FT4、孕前FT3、孕前TSH低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 妊娠期糖尿病的单因素分析(x±s)指标 观察组(n=85) 对照组(n=75) t P 年龄/岁 27.38±3.16 22.49±3.72 8.898 < 0.001 孕次/次 2.75±0.82 1.54±0.22 13.081 < 0.001 产次/次 2.06±0.37 1.08±0.27 19.284 < 0.001 孕前体质量指数/(kg/m2) 25.44±1.84 24.03±1.17 5.851 < 0.001 接受教育年限/年 13.65±3.32 13.68±2.81 0.062 0.951 自然流产次数/次 1.21±0.78 1.22±0.67 0.087 0.931 孕前空腹血糖/(mmol/L) 6.08±1.36 6.11±1.09 0.155 0.877 孕前HbA1c/% 6.17±1.02 6.27±1.47 0.494 0.622 孕前TPOAb/(IU/mL) 421.39±22.98 218.94±23.85 54.504 < 0.001 孕前FT4/(ng/dL) 0.34±0.11 0.45±0.02 5.101 < 0.001 孕前FT3/(pg/mL) 1.65±0.12 2.47±0.33 12.456 < 0.001 孕前TSH/(mIU/mL) 0.29±0.01 2.99±1.87 11.184 < 0.001 孕前HOMA-IR 2.24±0.23 1.02±0.77 13.211 < 0.001 孕前HOMA-β 115.66±3.89 69.14±3.11 83.962 < 0.001 HbA1c: 糖化血红蛋白; TPOAb: 甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体; FT4: 游离四碘甲腺原氨酸; FT3: 游离三碘甲腺原氨酸; TSH: 促甲状腺激素; HOMA-IR: 胰岛素抵抗指数; HOMA-β: 胰岛β细胞功能指数。 2.2 妊娠期糖尿病的多因素分析
多因素分析显示,较高的年龄、孕次、产次、孕前体质量指数、孕前TPOAb、孕前HOMA-IR、孕前HOMA-β以及较低的孕前FT4、孕前FT3、孕前TSH是甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素(P < 0.05), 见表 2、表 3。
表 2 赋值表指标 赋值 年龄/岁 实际值 孕次/次 实际值 产次/次 实际值 孕前体质量指数/(kg/m2) 实际值 孕前TPOAb/(IU/mL) 实际值 孕前FT4/(ng/dL) 实际值 孕前FT3/(pg/mL) 实际值 孕前TSH/(mIU/mL) 实际值 孕前HOMA-IR 实际值 孕前HOMA-β 实际值 表 3 妊娠期糖尿病的多因素分析因素 β S. E. Wald P OR 95%CI 年龄 1.018 2.361 1.322 0.001 1.019 1.009~1.926 孕次 1.062 3.269 1.333 0.002 1.632 1.331~2.320 产次 0.369 4.139 1.691 < 0.001 1.089 1.002~2.065 孕前体质量指数 1.302 2.541 1.025 < 0.001 1.002 1.001~1.568 孕前TPOAb 1.022 2.521 1.002 < 0.001 1.259 1.023~1.599 孕前FT4 1.262 3.251 1.332 < 0.001 0.541 0.023~0.947 孕前FT3 1.003 4.110 1.741 < 0.001 0.225 0.200~0.521 孕前TSH 1.047 5.119 1.025 < 0.001 0.210 0.025~0.574 孕前HOMA-IR 1.552 6.521 1.302 < 0.001 1.336 1.098~1.521 孕前HOMA-β 1.669 4.201 1.587 < 0.001 1.417 1.052~1.977 2.3 Nomogram模型预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素
Nomogram模型预测显示,较高的年龄(28~31岁)、孕次(2次以上)、产次(1次以上)、孕前体质量指数(24 kg/m2以上)、孕前TPOAb(>421.33 IU/mL)、孕前HOMA-IR(>2.21)、孕前HOMA-β(>115.66), 较低的孕前FT4(<0.33 ng/dL)、孕前FT3(<1.65 pg/mL)、孕前TSH(<0.26 mIU/mL)均是甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的危险因素。见图 1。
2.4 ROC曲线分析
ROC曲线分析显示, Nomogram模型预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的曲线下面积为0.785, 预测效能较好,见图 2。
3. 讨论
妊娠期糖尿病是临床上较为常见的妊娠期并发症之一,可对孕产妇和新生儿健康构成严重威胁[8]。研究[9]表明,妊娠期糖尿病与多种不良妊娠结局显著相关。产后,特别是在产后3~6年内,超重或肥胖的风险显著增加。不合理的孕期膳食、高龄、不良孕产史、高体质量指数和分娩巨大儿都是导致妊娠期糖尿病发生的危险因素[10]。在该病的进展过程中,随着孕期对葡萄糖需求量的增加,机体的胰岛素抵抗和分泌异常成为引起代谢异常的影响因素[11]。在孕期女性代谢异常发生时,其激素水平也显著波动,并成为其代谢异常的危险因素。内分泌异常主要包括性激素和生长激素水平异常。当甲状腺功能异常时,机体促性腺激素和促性腺激素释放激素的分泌量过高,会对婴幼儿产生严重影响。同时,在长期促性腺激素和促性腺激素释放激素过高的刺激下,机体代谢能力发生显著变化,胰岛素敏感性显著降低,可增加机体糖尿病发生风险[12-13]。在甲状腺功能减退孕妇的健康教育中,临床营养师通常建议加强营养指导,必要时及时检测孕妇甲状腺功能和血糖水平,并在整个孕期适当补充甲状腺素,以有效预防妊娠期糖尿病的发生[14]。
随着年龄增长,机体甲状腺功能和胰岛素分泌功能可能会出现显著退化[15]。随着孕次和产次增加,患者机体受到性激素波动影响也随之升高,而机体性激素波动水平异常是临床上影响患者发生妊娠期胰岛素功能异常和胰岛素分泌异常的重要因素[16]。在性激素过度影响下,机体下丘脑性激素轴的功能发生显著偏差,对糖脂代谢调控功能显著降低,其也是导致机体妊娠期糖尿病发生的重要危险因素[17]。本研究结果显示,在Nomogram模型预测中得出的截断值可作为临床预测甲状腺功能低下孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的重要参考[18]。随着机体甲状腺功能降低,胰岛细胞和多种蛋白质合成细胞的能力以及新陈代谢功能发生显著改变。同时,在炎性反应和多种代谢产物的应激作用下,局部病灶部位的微循环障碍风险逐渐升高,这也是孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病的重要危险因素。但妊娠期糖尿病的发生受遗传因素的影响较大,不同地区、不同人种的遗传基因多态性也是造成其妊娠期糖尿病发生的重要影响因素。本研究仍存在局限性: 研究中模型的验证存在一定单一性,需要结合多种因素进行多中心分析,后续还需开展多中心、大样本研究进一步验证。
综上所述,风险预测Nomogram模型在个体化预测甲状腺功能减退孕妇发生妊娠期糖尿病方面具有一定优势,其可作为临床诊断的参考工具之一。
-
表 1 2组治疗后临床疗效比较[n(%)]
时点 组别 n 完全缓解 部分缓解 病情稳定 疾病进展 疾病控制 治疗2个疗程后 对照组 173 7(4.05) 85(49.13) 72(41.62) 9(5.20) 164(94.80) 观察组 174 28(16.09)* 94(54.02) 52(29.89)* 0* 174(100.00)* 治疗4个疗程后 对照组 173 14(8.09) 89(51.45) 67(38.73) 3(1.73) 170(98.27) 观察组 174 36(20.69)* 99(56.90) 39(22.41)* 0 174(100.00) 与对照组比较, * P<0.05。 表 2 2组治疗前后中医证候积分比较($\overline x $ ±s)
分 时点 组别 n 主症积分 次症积分 总积分 治疗前 对照组 173 16.49±3.07 5.66±1.62 22.15±5.32 观察组 174 16.34±3.16 5.71±1.58 22.05±4.74 治疗2个疗程后 对照组 173 11.37±2.59* 4.97±1.21* 16.34±3.80* 观察组 174 9.46±2.48*△ 4.25±1.07*△ 13.71±3.55*△ 治疗4个疗程后 对照组 173 7.94±2.01*# 2.84±1.16*# 10.78±3.17*# 观察组 174 5.68±1.46*#△ 1.95±0.73*#△ 7.63±2.92*#△ 与治疗前比较, * P<0.05; 与治疗2个疗程后比较, #P<0.05; 与对照组比较, △P<0.05。 表 3 2组治疗前后血清肿瘤标志物水平比较($\overline x $ ±s)
时点 组别 n 癌胚抗原/(ng/mL) 糖类抗原19-9/(U/mL) 治疗前 对照组 173 19.88±5.23 46.78±11.25 观察组 174 19.67±5.33 47.04±11.23 治疗2个疗程后 对照组 173 18.72±5.21* 42.16±10.78* 观察组 174 16.22±4.48*△ 38.44±8.22*△ 治疗4个疗程后 对照组 173 16.73±5.32*# 38.99±9.56*# 观察组 174 14.26±3.88*#△ 34.22±7.35*#△ 与治疗前比较, * P<0.05; 与治疗2个疗程后比较, #P<0.05; 与对照组比较, △P<0.05。 表 4 2组治疗前后细胞免疫功能比较($\overline x $ ±s)
时点 组别 n CD3+/% CD4+/% CD8+/% CD4+/CD8+ 治疗前 对照组 173 54.26±4.32 32.28±3.29 26.88±3.17 1.20±0.22 观察组 174 54.34±4.29 32.31±3.18 26.67±3.27 1.21±0.24 治疗2个疗程后 对照组 173 53.72±4.05 32.75±3.74 25.46±2.78 1.28±0.25 观察组 174 55.49±5.21* 35.64±3.62* 23.16±2.54* 1.54±0.27* 治疗4个疗程后 对照组 173 54.45±5.01 34.55±3.82*# 24.67±2.59* 1.40±0.21*# 观察组 174 56.73±4.48* 36.87±4.01* 23.01±1.57* 1.60±0.25* 与治疗前比较, * P<0.05; 与治疗2个疗程后比较, #P<0.05。 表 5 2组治疗期间不良反应情况比较[n(%)]
组别 n 腹泻 骨髓抑制 皮炎 肝功能损害 肾功能损害 对照组 173 31(17.92) 33(19.08) 33(19.08) 25(14.45) 11(6.36) 观察组 174 25(14.37) 31(17.82) 11(6.32)* 6(3.45)* 6(3.45) 与对照组比较, *P<0.05。 -
[1] D'SOUZA N, DE NEREE TOT BABBERICH M P M, D'HOORE A, et al. Definition of the rectum: an international, expert-based Delphi consensus[J]. Ann Surg, 2019, 270(6): 955-959. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003251
[2] 冯小雪, 燕忠生. 结直肠癌中医证型与客观指标的相关性研究概况[J]. 江苏中医药, 2020, 52(8): 82-86. [3] 郭天安, 谢丽, 赵江, 等. 中国结直肠癌1988—2009年发病率和死亡率趋势分析[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2018, 21(1): 33-40 doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2018.01.007 [4] CHEN L J, NGUYEN T N M, LAETSCH D C, et al. Association of Comedication Quality With Chemotherapy-Related Adverse Drug Reactions and Survival in Older Colorectal Cancer Patients[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2022, 77(5): 1009-1019. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glab198
[5] 徐胜昔, 张利群, 郭翔取, 等. 艾愈胶囊辅助治疗乳腺癌的有效性、安全性及经济性研究[J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析, 2014, 14(9): 780-782, 783. [6] 卢秀花, 杜瑞超, 杨波. 艾愈胶囊用于老年晚期非小细胞肺癌化疗患者的临床观察[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2016, 32(4): 123-125. [7] 邓建辉, 童小燕, 刘秋江. 艾愈胶囊配合针刺治疗胃癌化疗后白细胞减少症临床观察[J]. 中国医学创新, 2015, 12(32): 103-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2015.32.031 [8] 中华人民共和国卫生和计划生育委员会医政医管局, 中华医学会肿瘤学分会. 中国结直肠癌诊疗规范(2017年版)[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志: 电子版, 2018, 10(3): 1-21. [9] 中华中医药学会. 中医肛肠科常见病诊疗指南[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2012: 65-69. [10] URBUTE A, SAND F L, BELMONTE F, et al. Trends in rectal cancer incidence, relative survival, and mortality in Denmark during 1978—2018[J]. Eur J Cancer Prev, 2021, 31(5): 451-458.
[11] 朱伟明, 陈玉超. 陈玉超辨治中晚期大肠癌的中医辨证及方药规律总结[J]. 中医药导报, 2018, 24(4): 36-38. [12] 周义志, 张忠伟, 向立斌, 刘岩, 王硕, 曹美楠. 结直肠癌组织中Rictor蛋白的表达及其与临床病理特征、预后的关系[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(15): 80-83, 88. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20220770 [13] 刘景华, 王海玲, 赵阳, 等. circPRKCI和miR-545在结直肠癌中的表达及相关性研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2024, 22(3): 376-379. [14] 史学伟, 封凯, 黄燕东, 等. 免疫检查点抑制剂在结直肠癌中的应用现状及进展[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2023, 51(7): 781-784. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2023.07.007 [15] DIJKSTRA E A, HOSPERS G A P, KRANENBARG E M, et al. Quality of life and late toxicity after short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer-The RAPIDO trial[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2022, 171: 69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.04.013
[16] 向林果, 谭憬一, 姚远, 等. 结直肠癌组织中MMR蛋白表达、MSI、RAS和BRAF基因突变与临床病理特征的关系[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2024, 21(1): 1-7. [17] BAHADOER R R, DIJKSTRA E A, VAN ETTEN B, et al. Short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy before total mesorectal excision (TME) versus preoperative chemoradiotherapy, TME, and optional adjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer (RAPIDO): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(1): 29-42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30555-6
[18] 季漪, 吴勉华. 山慈菇化学成分及其抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2018, 36(3): 596-598. [19] 杨守研, 刘瑛琦. 苦参的化学成分、药理作用及临床应用研究进展[J]. 中国药物滥用防治杂志, 2024, 30(1): 80-83. [20] 赫军, 马秉智, 田雪峰, 等. 白英化学成分和抗肿瘤药理作用的研究进展[J]. 中国药房, 2014, 25(39): 3713-3718. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2014.39.24 [21] 李静, 何牟, 李玲, 等. 白术挥发油化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2024, 46(3): 881-889. [22] LIU J, YU L, MO N L, et al. Supercritical fluid extract of Angelica sinensis and Zingiber officinale roscoe ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(15): 3816. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153816
[23] ZHOU R R, HE D, XIE J, et al. The synergistic effects of polysaccharides and ginsenosides from American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L. ) ameliorating cyclophosphamide-induced intestinal immune disorders and gut barrier dysfunctions based on microbiome-metabolomics analysis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 665901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665901
[24] 章玲玲, 胡本辉, 刘雅雯, 等. 艾愈胶囊联合放化疗对中晚期宫颈癌患者的临床疗效与造血系统的影响[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志, 2023, 7(12): 16-18. [25] SEFRIOUI D, BEAUSSIRE L, GILLIBERT A, et al. CEA, CA19-9, circulating DNA and circulating tumour cell kinetics in patients treated for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2021, 125: 725-733. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01431-9
[26] PAUL M S, OHASHI P S. The roles of CD8+ T cell subsets in antitumor immunity[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2020, 30(9): 695-704. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.06.003
[27] 王洋, 唐娟, 孙鹏, 等. 山慈菇提取物对人结直肠癌SW480细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2021, 27(11): 1754-1758, 1842. [28] 曹建, 魏润杰, 邓茹芸, 等. 苦参碱及氧化苦参碱抑制肿瘤作用机制研究进展及展望[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(3): 753-760. [29] 梁彪, 高家治, 徐朝辉, 等. 基于网络药理学的淫羊藿增强免疫功能作用机制研究[J]. 世界中医药, 2021, 16(23): 3467-3471, 3477. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2021.23.011 [30] 陈彦旭, 杨华, 徐慧琳, 等. 苦参多糖的提取分离、理化性质及免疫调节活性研究[J]. 国际药学研究杂志, 2018, 45(8): 611-618. [31] 杨锦涛, 程希, 陈红伟, 等. 白术多糖免疫调节作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国兽药杂志, 2018, 52(6): 80-85. [32] DROTT J, FOMICHOV V, STARKHAMMAR H, et al. Oxaliplatin-Induced Neurotoxic Side Effects and Their Impact on Daily Activities: A Longitudinal Study Among Patients With Colorectal Cancer[J]. Cancer Nurs, 2019, 42(6): E40-E48. doi: 10.1097/NCC.0000000000000674
[33] 沈红, 雷舒. 基于加速康复外科理念的护理干预在晚期直肠癌减瘤术联合腹腔灌注化疗患者中的应用效果[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2024, 28(7): 110-114. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20232986 [34] ZHANG E, YIN S, ZHAO S, et al. Protective effects of glycycoumarin on liver diseases[J]. Phytother Res, 2020, 34(6): 1191-1197. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6598
[35] 王雪娇, 刘力, 徐赟, 等. 当归止痒合剂治疗血虚风燥型老年性皮肤瘙痒症的效果[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(32): 115-118, 126. [36] 陈淼, 郭成云. 艾愈胶囊联合化疗治疗直肠癌的应用效果观察[J]. 实用中西医结合临床, 2023, 23(22): 17-20.




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
