Risk factor and nomogram prediction model construction for postoperative inflammatory complications in gastric cancer patients
-
摘要:目的
探讨胃癌根治性切除术后炎性并发症的危险因素, 并构建风险预测列线图模型。
方法回顾性分析402例接受胃癌根治性切除术治疗的原发性胃癌患者的临床资料,患者术前均接受营养风险筛查2002(NRS2002)评分、患者主观整体评估(PG-SGA)分级、第3腰椎骨骼肌质量指数(L3-SMI)评估及血清学指标检测。采用单因素分析筛选胃癌术后炎性并发症的影响因素,并采用多因素Logistic回归分析确定胃癌术后炎性并发症的独立危险因素。基于多因素Logistic回归分析结果构建预测胃癌根治性切除术后炎性并发症的列线图模型,并通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线、校准曲线评价模型的预测效能。
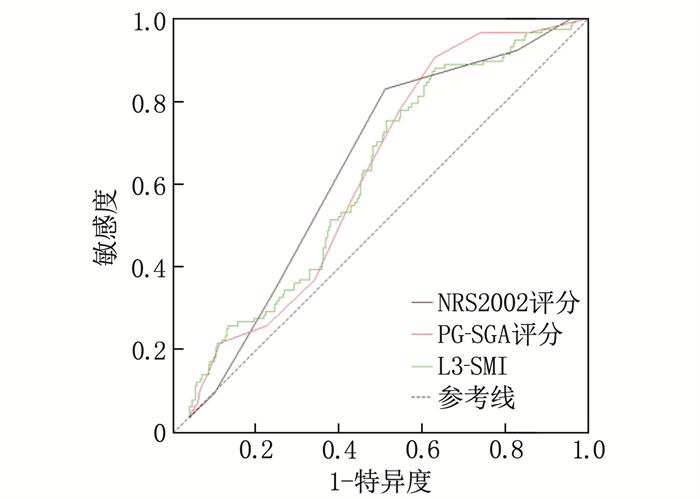
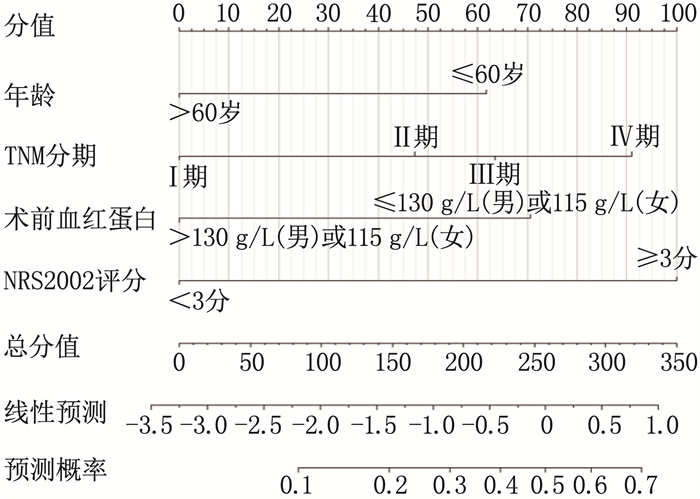
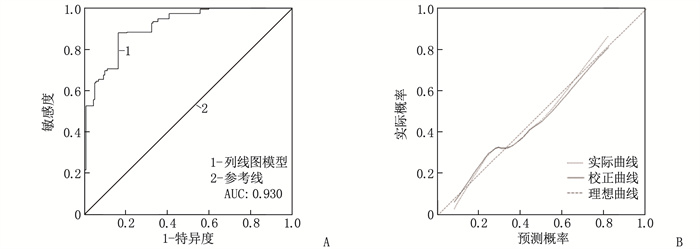
结果单因素分析结果显示,年龄、TNM分期、体质量指数、术前血红蛋白、术前白蛋白、术前球蛋白、NRS2002评分、PG-SGA分级、L3-SMI是胃癌根治性切除术后患者发生炎性并发症的影响因素(P < 0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄≤60岁、术前血红蛋白≤130 g/L(男)或115 g/L(女)、TNM分期为Ⅳ期、NRS2002评分≥3分、L3-SMI≤52.4 cm2/m2(男)或38.5 cm2/m2(女)是胃癌患者术后发生炎性并发症的独立危险因素(P < 0.05)。基于年龄、术前血红蛋白、TNM分期、NRS2002评分构建列线图模型, ROC曲线显示列线图模型的曲线下面积为0.930, 敏感度和特异度分别为93.2%和89.2%, 校准曲线显示列线图预测的炎性并发症发生概率与实际结果具有良好的一致性。
结论年龄≤60岁、术前低血红蛋白、TNM分期为Ⅳ期、NRS2002评分≥3分、低L3-SMI是胃癌患者术后发生炎性并发症的独立危险因素, 基于年龄、术前血红蛋白、TNM分期、NRS2002评分构建的列线图模型能够精准预测胃癌术后炎性并发症。
-
关键词:
- 胃癌 /
- 营养风险筛查2002评分 /
- 患者主观整体评估评分 /
- 第3腰椎骨骼肌质量指数 /
- 炎性并发症
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the risk factors for inflammatory complications after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer and construct a nomogram model for risk prediction.
MethodsThe clinical data of 402 patients with primary gastric cancer who underwent radical gastrectomy were retrospectively analyzed. All patients underwent preoperative Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (NRS2002) score, Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) grading, Lumbar 3 Skeletal Muscle Index (L3-SMI) assessment, and serological index testing. Univariate analysis was used to screen for influencing factors of postoperative inflammatory complications of gastric cancer, and multivariate Logistic regression analysis was conducted to determine independent risk factors. A nomogram model for predicting postoperative inflammatory complications after radical gastrectomy was constructed based on the results of multivariate Logistic regression analysis, and the predictive performance of the model was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and calibration curve.
ResultsUnivariate analysis revealed that age, TNM stage, body mass index, preoperative hemoglobin, preoperative albumin, preoperative globulin, NRS2002 score, PG-SGA grade, and L3-SMI were influencing factors of postoperative inflammatory complications in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy (P < 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that age ≤60 years, preoperative hemoglobin ≤130 g/L(male) or ≤115 g/L(female), TNM staging of Ⅳ stage, NRS2002 score≥3, and L3-SMI ≤52.4 cm2/m2(male) or ≤38.5 cm2/m2(female) were independent risk factors for postoperative inflammatory complications in gastric cancer patients (P < 0.05). A nomogram model was constructed based on age, preoperative hemoglobin, TNM stage, and NRS2002 score. The ROC curve showed that the area under the curve of the nomogram model was 0.930, with sensitivity and specificity of 93.2% and 89.2%, respectively. The calibration curve demonstrated good consistency between the predicted probability of inflammatory complications and the actual outcomes.
ConclusionAge≤60 years, low preoperative hemoglobin, TNM staging of Ⅳ stage, NRS2002 score ≥3, and low L3-SMI are independent risk factors for postoperative inflammatory complications in gastric cancer patients. The nomogram model constructed based on age, preoperative hemoglobin, TNM stage, and NRS2002 score can accurately predict postoperative inflammatory complications after gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
-
中国血液净化病例信息登记系统(CNRDS)数据显示,截至2021年末,中国的血液透析(HD)患者数量约为74.9万例,与2011年相比, 10年间透析患者总人数增加了3.2倍。透析患者常存在液体超载、营养不良、微炎症状态和认知功能障碍等问题,严重影响生活质量和预后。生物电阻抗分析(BIA)是一种无创伤、便携带、易操作和经济的人体成分测量方法,已被广泛应用于透析患者的临床管理中。BIA根据电阻和容抗的测量结果估计身体成分,包括细胞内水分(ICW)、细胞外水分(ECW)、全身水量(TBW)、体细胞质量(BCM)、蛋白质质量、矿物质质量、骨骼肌质量和内脏脂肪面积等身体成分参数[1]。根据BCM可以计算出新指数即体细胞质量指数(BCMI), 公式为BCMI=BCM/身高2。研究[2-3]表明, BCMI与维持性血液透析(MHD)患者营养状态、微炎症状态、认知功能以及预后等密切相关。本文将基于BIA测定的BCMI在MHD患者中的研究进展综述如下。
1. BCMI概述
BIA的基本原理是假设人体是一个均匀的圆柱形导体,电流通过不同的人体组织时显示出不同的导电性,同时也产生不同的抗性。电阻抗的大小取决于电阻和容抗的矢量和[4], 电阻与水化状态有关,而容抗与细胞膜完整性有关[5]。水和电解质含量高的瘦组织电阻低,是较好的导体; 水和电解质含量低的脂肪、骨骼和皮肤电阻高,是较差的导体。BIA通过测量人体各部分电阻抗而分析人体成分,如无脂质量(FFM)、ECW、ICW和BCM等。BCM是没有骨矿物质或ECW的瘦组织的质量,主要是骨骼肌,也包括内脏器官、血液和脑组织[6]。BCM与氧气消耗、二氧化碳产生和能量消耗相关[7], 是身体中代谢最活跃的细胞团的总质量[8]。BCMI可根据BCM计算而得,研究[2]表明, BCMI是识别疾病所致身体成分异常的有力工具。
2. BCMI与营养不良
营养不良是一种摄入与需求不平衡或能量、蛋白质和其他营养物质缺乏或不平衡的营养状态,可引起人体代谢改变、功能受损和体质量下降,从而影响MHD患者的生活质量,增加住院和死亡风险[9]。营养不良在MHD患者中非常普遍,由于应用的筛查工具不同,其确切发病率从18%至75%不等[10]。早期发现营养不良并干预,减轻营养不良状态,有利于MHD患者获得更好的预后。营养不良的筛查工具很多,其中最常用的是主观综合营养评估(SGA)和营养风险评分(NRS), 这2种筛查方法的诊断依据主要是体质量减轻(6个月内体质量减轻超过10%),然而透析人群因液体平衡紊乱而体质量变化不够明显,使用上述筛查工具有一定局限性[9]。体质量指数(BMI)是目前公认的一种营养评估指标[11], 但MHD患者长时间处于过度水合状态,造成BMI虚假性偏高,因此透析患者ECW增加可能会掩盖内脏或躯体蛋白质质量的减少[12],从而高估营养状态。TALLURI A等[13]研究发现,BMI正常或偏高的MHD患者BCMI有很大变异性,这意味着依据BMI值归类为营养状态良好的MHD患者可能存在较低的BCMI值,即实际处于营养不良状态。由此可见,BCMI可以更准确地评估透析患者的营养状态。VALENTE A等[10]研究表明, BCMI是诊断蛋白能量消耗(PEW)的重要参数,建议将BCMI纳入诊断PEW的参数组合中。一项队列研究[14]纳入1 882例MHD患者并根据BCMI四分位数分为4组,校正混杂因素后,最低四分位数组患者PEW发病风险较其余组高,且发现BCMI≤8.56 kg/m2对PEW发病具有预测价值。另一项纳入2 527例MHD患者的队列研究[15]以BCMI平均值6.4 kg/m2将受试者分为2组,随访24个月发现BCMI < 6.4 kg/m2组(n=1 366)MHD患者的营养状况较差,表现出较低的瘦组织指数(LTI)、白蛋白和BMI水平。WU B Y等[16]研究发现,LTI和BCMI是与MHD患者病死率相关性最高的营养状况指标。但透析患者每次血液透析都会发生体液波动,且瘦组织质量(LTM)对人体水合状态的变化较敏感[15], 因此LTM受透析患者水合状态变化的影响较大。LTI具有与LTM同样的劣势,相较而言,BCM不受透析患者水合状态变化的影响[17], 因此BCMI是比LTI更准确的营养状况评价指标。不同的研究显示不同的临界值,可能与受试者群体不同及分组方法不同等有关,也可能与设备类型不同有关,未来仍需开展大型的多中心高质量研究,以确定最佳临界值,为MHD患者提供可靠的指导意见。
3. BCMI与微炎症状态
身体受到微生物、内毒素、化学物质和循环免疫复合体的影响,表现为全身循环中肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)和C反应蛋白(CRP)等持续轻度增高且无明显临床症状时,即存在微炎症状态[18]。研究[19-20]表明, MHD患者普遍存在微炎症状态,且微炎症状态与心血管疾病、认知功能障碍、肾性骨病、红细胞生成素抵抗和PEW等密切相关,影响MHD患者的生存质量及预后。白蛋白是对MHD患者病死率最具有预测价值的实验室指标之一。研究[21]表明, MHD患者透析2年后,白蛋白水平每降低1 g/dL, 死亡风险将增加47%。白蛋白常被认为是营养状态的标志物,然而低蛋白血症在纯粹的蛋白质-能量营养不良中并不常见,通常需要其他因素才能使白蛋白浓度显著降低,例如存在炎症反应。在IL-6、TNF-α等促炎细胞因子的控制下, CRP等急性时相反应蛋白合成速率加快、血浆水平升高,导致白蛋白合成减少、血清浓度降低,这一变化与营养状态完全无关[22]。BCM包括体内所有代谢活跃的细胞的质量,不仅对肌肉的枯竭敏感,而且对炎症的存在敏感[15]。RONDANELLI M等[2]研究显示,老年人群的BCMI与白蛋白呈正相关,与CRP呈负相关, BCMI每增加1个单位,平均白蛋白水平提高0.062 g/dL。另一项纳入2 527例HD患者的前瞻性多中心研究[15]也有类似发现,即BCMI < 6.4 kg/m2组患者的血清白蛋白水平较低, CRP水平较高,提示BCMI在MHD患者微炎症状态管理中具有重要意义,此外该组患者表现出更高水平的过度水化,推测可能是炎症状态导致毛细血管通透性增加和ECW扩张。RYMARZ A等[19]纳入142例受试者进行研究,包括MHD患者组(n=48)、未接受透析治疗的慢性肾脏病(CKD)4~5期患者组(n=61)和肾功能正常的健康成人组(n=33), 发现MHD患者组BCM仅与IL-6呈弱负相关,且3组BCM与CRP水平差异均无统计学意义,与上述研究结果不同,但该研究纳入的MHD患者样本量不多,研究证据力度不足。BCMI与MHD患者微炎症状态的关系需要开展更多的样本量大、随访时间长并增加其他炎症指标的多中心队列研究进一步验证。
4. BCMI与认知功能障碍
认知是指人脑接受外界信息,并将其加工转化为内在心理活动,从而获取或应用知识的过程。认知功能包括学习、记忆、复杂注意力、语言、视觉空间、执行功能、知觉运动能力等。认知功能障碍是指上述1种或多种认知功能的损害[23], 损害程度从轻度认知功能障碍至重度痴呆不等[24]。与一般人群相比, MHD患者认知功能障碍患病率明显较高,可达到60%~80%[25]。认知功能障碍可扰乱MHD患者日常生活、工作和情绪,降低服药和治疗依从性,导致病情恶化甚至终止透析[26], 是MHD患者全因死亡的独立预测因子[27]。尤其是认知功能中的执行能力损害,会显著增加MHD患者的住院及死亡风险[28]。研究[29]显示,MHD患者的LTI与认知功能呈显著正相关。WU B Y等[16]发现,LTI与BCMI具有强相关性,故推测BCMI与MHD患者认知功能障碍可能存在一定相关性。OU Q Q等[3]证实了这一猜测,其通过对2 008例MHD患者进行的多中心队列研究发现,低BCMI值是MHD患者发生认知功能障碍的独立危险因素,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线显示BCMI预测认知功能障碍的曲线下面积为0.713, 最佳截断值、敏感性和特异性分别为9.0 kg/m2、71.5%和62.7%。由此推测,BCMI可以用于预测MHD患者认知功能障碍的发生,为临床诊断提供一定依据。但目前BCMI与MHD患者认知功能障碍相关性方面的研究数量较少,仍需更多的研究进一步明确。
5. BCMI与预后
多项研究表明, BCMI与MHD患者临床结局如住院率和病死率具有密切联系。VALENTE A等[10]针对3 696例透析患者进行多中心纵向观察性队列研究发现,含有BCMI < 6.4 kg/m2的参数组合是透析患者全因死亡的独立预测因子(HR=1.48,95%CI: 1.00~2.19,P=0.048)。另一项多中心纵向队列研究[30]也有类似发现,该研究纳入697例患者随访12个月,采用COX模型校正混杂因素后发现,BCMI≤5.2 kg/m2是MHD患者1年病死率的预测因子(HR=1.929,95%CI: 1.012~3.675,P=0.046)。不同研究的临界值不同,可能与患者群体、样本量、随访时间、地域及分组方法不同有关,建议排除混杂因素后开展大型多中心高质量研究,以确定最佳临界值。OLIVEIRA T等[15]的前瞻性多中心队列研究纳入2 527例MHD患者,随访24个月,单变量COX回归分析发现,与G2组(BCMI≥6.4 kg/m2, n=1 161)相比, G1组(BCMI < 6.4 kg/m2, n=1 366)死亡风险显著增加(HR=2.1, 95%CI: 1.714~2.629, P < 0.001), 校正混杂因素后, BCMI仍然是透析患者全因死亡的独立预测因素(HR=1.7, 95%CI: 1.141~2.498, P=0.009), G1组与G2组患者主要死因均为心血管疾病, G1组因感染性疾病和PEW具有更高的全因死亡率。BCMI与营养状态和微炎症状态密切相关,间接提示低BCMI患者可能会因营养不良及处于微炎症状态而预后较差。近期一项单中心队列研究[16]纳入704例MHD患者随访33个月,多因素校正的COX模型分析显示,较高的ECW/BCM(HR=1.49, 95%CI: 1.19~1.85, P < 0.001)、较低的LTI(HR=0.7, 95%CI: 0.57~0.86, P < 0.001)和较低的BCMI(HR=0.7, 95%CI: 0.58~0.85, P < 0.001)与MHD患者更高的死亡风险相关,在完全调整的模型中, BCMI在预测MHD患者全因死亡率方面表现最佳(IDI=0.02, NRI=0.11, P=0.04)。上述研究表明, BCMI在临床上可用作MHD患者发生不良结局的监测工具,及时纠正相关风险因素,有助于提升患者生活质量并改善不良结局。
6. 小结
生物电阻抗设备已越来越多地被用于MHD患者身体成分评估中,作为床边工具,其具有无创伤、便携带、易操作和更经济等优点[10]。BCMI不受MHD患者常见水合状态变化的影响,且对肌肉质量和蛋白质组织变化较敏感[15]。但BCMI亦存在一定局限性: ①在儿童、孕妇或佩戴起搏器的受试者中, BCMI的准确性受限,且BCMI的评估结果还可能受到极端肥胖或进食、剧烈体力活动的影响[31]; ② BIA设备测量值存在一定误差,包括阻抗测量误差、回归误差、参考方法的固有误差、电容量模型误差等[32]; ③ BCMI评估MHD患者容量状态的价值有限,建议结合其他身体成分参数指导MHD患者的容量管理。
综上所述, BCMI具有快速、非侵入性、便携带、易操作和更经济等优点,已被用于评估MHD患者的营养状态、微炎症状态、认知功能以及预测不良结局等方面。目前, BCMI在MHD患者中的最佳临界值仍未确定,在临床应用方面亦有待进一步研究,未来还需继续开展更深入的研究,从而使BCMI在MHD患者中具有良好的应用前景。
-
表 1 胃癌患者术后发生炎性并发症的单因素分析[n(%)]
项目 分类 n 无炎性并发症患者(n=289) 有炎性并发症患者(n=113) χ2 P 性别 男 293 210(72.66) 83(73.45) 0.001 0.972 女 109 79(27.34) 30(26.55) 年龄 ≤60岁 137 82(28.37) 55(48.67) 14.010 <0.001 >60岁 265 207(71.63) 58(51.33) TNM分期 Ⅰ期 63 55(19.03) 8(7.08) 17.669 <0.001 Ⅱ期 113 87(30.10) 26(22.92) Ⅲ期 178 121(41.87) 57(50.44) Ⅳ期 48 26(8.99) 22(19.47) 手术类型 开腹手术 99 73(25.26) 26(22.92) 0.117 0.732 腹腔镜手术 303 216(74.74) 87(77.08) 肿瘤类型 腺癌 331 237(82.01) 94(82.30) 0.018 0.894 其他 71 52(17.99) 19(16.70) BMI <18.5 kg/m2 36 20(6.92) 16(14.16) 14.683 0.001 18.5~<24.0 kg/m2 227 154(53.29) 73(64.60) ≥24.0 kg/m2 139 115(39.79) 24(21.24) 术前血红蛋白 ≤130 g/L(男)或115 g/L(女) 206 120(41.52) 86(76.11) 37.517 <0.001 >130 g/L(男)或115 g/L(女) 196 169(58.48) 27(23.89) 术前白蛋白 ≤35.0 g/L 147 94(32.53) 53(46.90) 6.632 0.010 >35.0 g/L 255 195(67.47) 60(53.10) 术前球蛋白 ≤20 g/L 34 16(5.54) 18(15.93) 10.030 0.002 >20 g/L 368 273(94.46) 95(84.07) 术前前白蛋白 ≤280 mg/L 328 231(79.93) 97(85.84) 1.516 0.218 >280 mg/L 74 58(20.07) 16(14.16) NRS2002评分 <3分 167 147(50.87) 20(17.70) 35.443 <0.001 ≥3分 235 142(49.13) 93(82.30) PG-SGA分级 A级 47 43(14.88) 4(3.54) 10.170 0.006 B级 273 190(65.74) 83(73.45) C级 82 56(19.38) 26(23.01) L3-SMI ≤52.4 cm2/m2(男)或38.5 cm2/m2(女) 314 210(72.66) 104(92.04) 16.713 <0.001 >52.4 cm2/m2(男)或38.5 cm2/m2(女) 88 79(27.34) 9(7.96) 术中失血量 <200 mL 353 253(87.54) 100(88.50) 0.009 0.926 ≥200 mL 49 36(12.46) 13(11.50) 表 2 胃癌患者术后发生炎性并发症的多因素Logistic回归分析
因素 分类 OR(95%CI) P 年龄 ≤60岁 — — >60岁 0.42(0.25~0.72) <0.001 术前血红蛋白 ≤130 g/L(男)或115 g/L(女) — — >130 g/L(男)或115 g/L(女) 0.39(0.22~0.70) 0.002 TNM分期 Ⅰ期 — — Ⅱ期 2.47(0.98~6.22) 0.054 Ⅲ期 1.95(0.81~4.71) 0.135 Ⅳ期 3.70(1.27~10.74) 0.016 NRS2002评分 <3分 — — ≥3分 6.45(2.71~15.32) <0.001 L3-SMI ≤52.4 cm2/m2(男)或38.5 cm2/m2(女) — — >52.4 cm2/m2(男)或38.5 cm2/m2(女) 0.33(0.14~0.79) 0.012 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] LIDORIKI I, SCHIZAS D, MYLONAS K S, et al. Postoperative changes in nutritional and functional status of gastroesophageal cancer patients[J]. J Am Nutr Assoc, 2022, 41(3): 301-309.
[3] ZHOU D, ZHANG Y, GAO X J, et al. Long-term outcome in gastric cancer patients with different body composition score assessed via computed tomography[J]. J Invest Surg, 2021, 34(8): 875-882. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2019.1708997
[4] TOKUNAGA M, KUROKAWA Y, MACHIDA R, et al. Impact of postoperative complications on survival outcomes in patients with gastric cancer: exploratory analysis of a randomized controlled JCOG1001 trial[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2021, 24(1): 214-223. doi: 10.1007/s10120-020-01102-3
[5] BRACALE U, PELTRINI R, LUCA M D, et al. Predictive factors for anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic and open total gastrectomy: a systematic review[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(17): 5022. doi: 10.3390/jcm11175022
[6] ZIZZO M, ZANELLI M, SANGUEDOLCE F, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: an updated systematic review[J]. Medicina, 2022, 58(6): 834. doi: 10.3390/medicina58060834
[7] 刘哲魁, 韩晓帆, 王泽正, 等. 胃癌根治性切除术后感染性并发症的危险因素分析及预测模型的建立: 一项回顾性队列研究[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2024, 31(2): 218-224. [8] PRADO C M, LIEFFERS J R, MCCARGAR L J, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2008, 9(7): 629-635. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70153-0
[9] BALSTAD T R, BYE A, JENSSEN C R, et al. Patient interpretation of the Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) Short Form[J]. Patient Prefer Adherence, 2019, 13: 1391-1400. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S204188
[10] DE SOUSA I M, SILVA F M, DE CARVALHO A L M, et al. Accuracy of isolated nutrition indicators in diagnosing malnutrition and their prognostic value to predict death in patients with gastric and colorectal cancer: a prospective study[J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2022, 46(3): 508-516. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2199
[11] HIRAHARA N, TAJIMA Y, FUJII Y, et al. Prediction of postoperative complications and survival after laparoscopic gastrectomy using preoperative Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in elderly gastric cancer patients[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35(3): 1202-1209. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07487-7
[12] SASAKI M, MIYOSHI N, FUJINO S, et al. The Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index predicts postoperative complications and prognosis in elderly patients with colorectal cancer after curative surgery[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10: 10744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67285-y
[13] 曾藜, 王惠惠, 王晓宇, 等. 四种营养评价方法对腰椎退行性疾病术后并发症的预测价值比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(11): 1349-1355. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0410 [14] 陈雅蕊. 术前体重变化对可切除胃癌患者术后并发症及生存的预测价值[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2023. [15] 陆晟. 老年胃癌患者临床病理特征与外科预后分析[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. [16] KONDRUP J, ALLISON S P, ELIA M, et al. ESPEN guidelines for nutrition screening 2002[J]. Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl, 2003, 22(4): 415-421.
[17] OTTERY F D. Definition of standardized nutritional assessment and interventional pathways in oncology[J]. Nutrition, 1996, 12(1 Suppl): S15-S19.
[18] 孙慧, 徐慧, 陆滢滢, 等. 营养风险筛查工具识别胃癌患者肌减少症的临床价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2023, 27(2): 78-83. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20223111 [19] 钱雪蔚, 朱琴琴, 江晓晖. L3骨骼肌质量指数与控制营养状况评分对胃癌患者术后预后的预测价值[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2023, 31(21): 3985-3991. [20] 肖海燕, 刘婷, 李岱, 等. 胃癌合并肌少症的研究进展[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2022, 31(8): 1121-1128. [21] HUANG D D, CAI H Y, CHEN X Y, et al. Value of Sarcopenia defined by the new EWGSOP2 consensus for the prediction of Postoperative Complications and Long-term Survival after Radical Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: a comparison with four common nutritional screening tools[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(19): 5852-5860. doi: 10.7150/jca.49815
[22] 杜园, 郭超, 张慧芳, 等. 术前PG-SGA评分对胃癌患者术后恢复情况及并发症的预测价值[J]. 山东医药, 2023, 63(19): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2023.19.014 [23] LI Y L, WU H Z, XING C Z, et al. Prognostic evaluation of colorectal cancer using three new comprehensive indexes related to infection, anemia and coagulation derived from peripheral blood[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(13): 3834-3845. doi: 10.7150/jca.42409
[24] JUN J H, YOO J E, LEE J A, et al. Anemia after gastrectomy in long-term survivors of gastric cancer: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Int J Surg, 2016, 28: 162-168. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.02.084
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李梅莹,张斯萍. 基于ORTCC模型联合抗阻训练对维持性血液透析肌少症患者握力、依从性和步速的影响. 河北医药. 2024(24): 3745-3749 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
