Effect and mechanism of remimazolam on retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
-
摘要:目的
探讨瑞马唑仑(Rem)对大鼠视网膜缺血再灌注损伤(RIRI)的作用及其对高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)/晚期糖基化终末产物受体(RAGE)/核转录因子-κB(NF-κB)信号通路的调控机制。
方法将大鼠随机分为假手术组(Sham组)、模型组(Model组)、低剂量Rem组(Rem-L组)、中剂量Rem组(Rem-M组)、高剂量Rem组(Rem-H组)和高剂量Rem加HMGB1激活剂地塞米松(DEX)组(Rem-H+DEX组), 每组15只。除Sham组外,其他各组大鼠均通过升高眼压法构建RIRI模型。采用苏木素-伊红(HE)染色法观察各组大鼠视网膜组织结构变化; 采用TUNEL法检测视网膜组织细胞凋亡情况; 采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠血清白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)表达水平; 使用试剂盒检测氧化应激指标[超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)、丙二醛(MDA)]水平; 采用蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)检测视网膜组织中缺氧相关因子[缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)、血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)]及HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路相关蛋白表达水平。
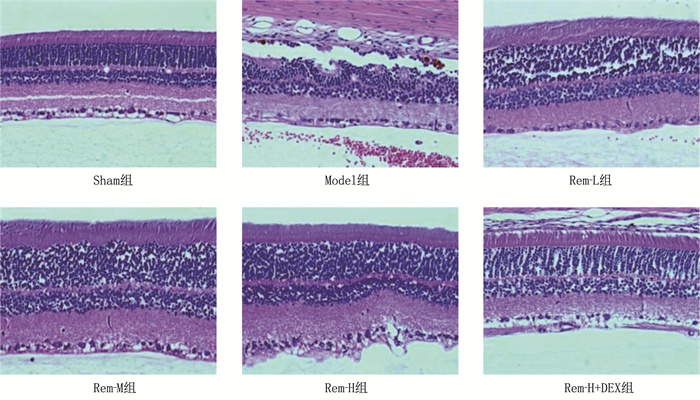
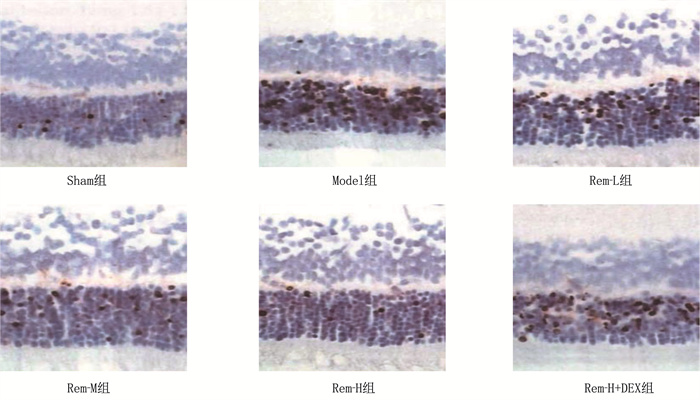
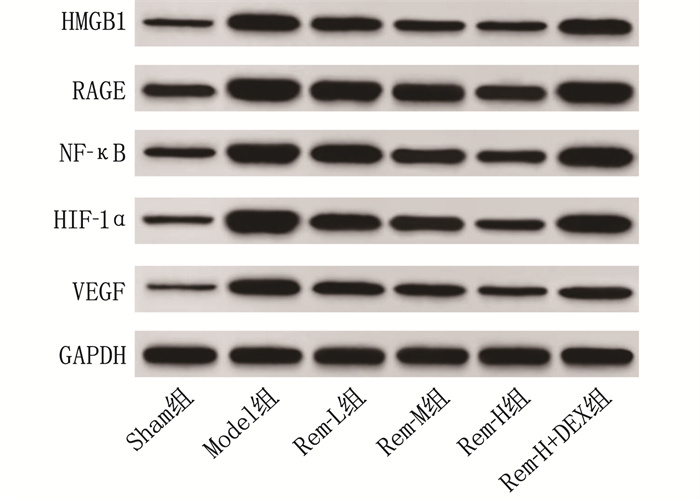
结果相较于Sham组, Model组大鼠视网膜高度水肿,神经节细胞数量显著减少,细胞呈现空泡样变化且排列紊乱,细胞间隙增宽; 随着Rem注射剂量的增加, RIRI大鼠视网膜水肿程度逐渐减轻,神经节细胞数量增多,排列更加有序。相较于Sham组, Model组大鼠视网膜细胞凋亡率和血清IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平及视网膜组织中MDA、HMGB1、RAGE、NF-κB、HIF-1α、VEGF表达水平均升高,而SOD、GSH-PX表达水平降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 相较于Model组, Rem-L组、Rem-M组和Rem-H组大鼠视网膜细胞凋亡率和血清IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平及视网膜组织中MDA、HMGB1、RAGE、NF-κB、HIF-1α、VEGF表达水平呈剂量依赖性降低,而SOD、GSH-PX表达水平呈剂量依赖性升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05); 相较于Rem-H组, Rem-H+DEX组上述指标变化趋势逆转。
结论Rem能够抑制大鼠RIRI的发生,其作用机制可能与调控HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路有关。
-
关键词:
- 视网膜缺血再灌注损伤 /
- 瑞马唑仑 /
- 高迁移率族蛋白B1 /
- 晚期糖基化终末产物受体 /
- 核转录因子-κB /
- 信号通路
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of remimazolam (Rem) on retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury (RIRI) in rats and its regulatory mechanism on the high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)/receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway.
MethodsRats were randomly divided into Sham group, Model group, Rem-L group (low-dose Rem), Rem-M group (medium-dose Rem), Rem-H group (high-dose Rem), and high-dose Rem plus HMGB1 activator dexamethasone (DEX) group (Rem-H+DEX group), with 15 rats in each group. Except for the Sham group, RIRI model was established in the other groups by increasing intraocular pressure. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was used to observe the changes in retinal tissue structure in each group. The TUNEL method was used to detect retinal tissue apoptosis. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed to detect the expression levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the serum of rats in each group. Kits were used to detect the levels of oxidative stress indicators, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), and malondialdehyde (MDA). Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of hypoxia-related factors [hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)] and HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway-related proteins in retinal tissue.
ResultsCompared with the Sham group, the Model group showed severe retinal edema, a significant decrease in the number of ganglion cells, vacuolar changes in cells with disordered arrangement, and widened cell gaps. With increasing doses of Rem, the degree of retinal edema gradually decreased, the number of ganglion cells increased, and their arrangement became more orderly in RIRI rats. Compared with the Sham group, the Model group exhibited increased retinal cell apoptosis rate, serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α and increased expression levels of MDA, HMGB1, RAGE, NF-κB, HIF-1α and VEGF in retinal tissue, while the expression levels of SOD and GSH-PX decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the Model group, the Rem-L, Rem-M, and Rem-H groups showed dose-dependent decreases in retinal cell apoptosis rate, serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, and expression levels of MDA, HMGB1, RAGE, NF-κB, HIF-1α and VEGF in retinal tissue, with dose-dependent increases in the expression levels of SOD and GSH-PX (P < 0.05). Compared with the Rem-H group, the Rem-H+DEX group showed reversed trends in the above indicators.
ConclusionsRem can inhibit the occurrence of RIRI in rats, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of the HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway.
-
炎症性肠病(IBD)是一类以肠道慢性、非特异性炎症为主要特征的疾病,主要包括溃疡性结肠炎(UC)及克罗恩病(CD)。IBD临床症状主要有腹痛、腹泻及便血,严重影响患者生活质量。在未来,中国IBD患病率最高可能达到0.1%, 2025年的患病人数将超过150万,几乎与西方国家发病率持平[1]。IBD发生、发展与免疫异常调节、遗传易感性、肠道菌群紊乱、肠道持续感染、慢性肠黏膜屏障损伤、饮食等因素有关。在目前所有有关IBD的治疗方法中,粪菌移植(FMT)具有重要的作用,在临床上已广泛应用于治疗IBD、难治性艰难梭状芽孢杆菌感染、腹泻型及便秘型肠易激综合征、胰岛素抵抗的糖尿病、肥胖症等,并取得了一定的疗效[2]。2013年,美国首次将FMT方案列入临床治疗复发性艰难梭状芽孢杆菌感染(rCDI)的指南[3]。张发明等[4]率先在中国针对严重CD合并肠瘘感染患者开展了FMT治疗。最新的研究结果显示FMT存在以下问题: ①质量和安全性难以控制; ② FMT过程复杂; ③粪便菌群不能长期保存; ④供体筛选流程复杂。因此,建立适合IBD患者最佳的肠道微环境,维持肠道微生态,就显得尤为重要。肠道益生菌L. reuteri可在肠道内持续定植[5],通过改变肠道内微环境来预防和阻止炎症性肠病的发生; L. reuteri还可以调节肠道内一类特殊的免疫细胞—双阳性上皮内T细胞(DPIELs), DPIELs是由CD4+ T细胞分化而来,与肠道免疫稳态有关,可增强免疫系统耐受性,调节过于活跃的免疫反应,减轻IBD患者的肠道炎症反应[6]。
1. 肠道微生态参与IBD发病机制
1.1 肠道微生态的建立和细菌分布特点
人的肠道是不同微生物的共同“栖息地”,这些微生物包括细菌、病毒、真菌等,数量约100兆,比人体细胞总数10倍还要多[7-8]。目前研究[9-10]普遍认为,人类肠道内微生物的定植是婴儿在分娩过程中从产道、皮肤、粪便以及出生后母乳喂养中开始形成的。据估计,人体肠道内的细菌数量超过1 000种,其中大多数为专性厌氧菌,包括厚壁菌、拟杆菌、变形菌和放线菌[11]。厚壁菌属(革兰阳性菌)和拟杆菌属(革兰阴性菌)是所有哺乳动物的主要门类,超过肠道内菌群的90%[12]。细菌的总数和组成在人体胃肠道内不同部位有所不同,如胃和小肠的上段的细菌分布就较少。值得注意的是,肠道内细菌组成的变化可通过不同的信号通路影响肠道内的稳态。肠道内细菌主要负责对碳水化合物产生的短链脂肪酸(SCFAs)进行降解,促进维生素K、维生素B12、叶酸以及氨基酸的合成,并调节脂肪代谢,有助于维持肠道屏障功能的完整性[13]。肠道中的细菌可通过抑制病原菌的定植和产生抗菌化合物来保护肠道上皮免受病原体的侵害,保护肠黏膜屏障,从而维持内环境稳定[14]。
1.2 肠道微生态紊乱与IBD发生、发展的关系
IBD发病的影响因素包括肠道微生物群及其代谢物的紊乱、宿主的遗传易感性、宿主的先天和后天性免疫[15-16]等。肠道微生态与IBD的关系有: ①动物实验[17]证实,肠道菌群在IBD的发病机制有重要的作用,因为在无菌动物模型中不能诱发结肠炎; ② IBD患者粪便和肠道黏膜中微生物群的生物多样性减少,并有异常成分[16]; ③肠道微生物群的代谢物紊乱(如丁酸盐代谢异常)涉及到IBD的发病[18]; ④一些益生菌产品可以有效地减轻肠道症状,预防溃疡性结肠炎的复发[19]; ⑤一些抗生素可能引起并维持IBD的缓解[20]; ⑥许多环境因素如西方化的饮食、现代的生活方式或滥用抗生素等,会对肠道菌群的组成产生重要影响,导致IBD的发病率显著增高[21]。
国外研究[22]使用16S rRNA为基础的单链构象多态性检测(SSCP)、16S rRNA基因的末端限制性片段分析技术(T-RFLP)、变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)、定量实时聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)和高通量测序等技术,其结果证实,与健康个体相比, IBD患者的微生物群多态性明显较少,肠道常发生微生态失衡,即有害菌超过有益菌,以脆弱拟杆菌和肠杆菌数量增加为主,尤其是大肠埃希菌。Walker等[23]研究发现,在IBD患者的炎性与非炎性反应区,厚壁菌数量下降,而拟杆菌数量上升,细菌分布也存在着显著差异。因此,肠道微生态改变与IBD发生和病情发展密切相关,尽管目前还无确切证据说明哪种特定的病原体导致IBD发生,然而在IBD患者中使用益生菌确实获得了一定的疗效。
2. FMT在IBD治疗中的应用
FMT本质是重建肠道菌群平衡,修复由抗生素导致的菌群紊乱,其最强的适应证是难治性艰难梭菌感染。对于IBD, FMT能改善IBD患者紊乱的肠道微生态,补充IBD患者减少的肠道共生菌,调节肠屏障功能和通透性,并参与肠黏膜的免疫调节。
FMT首次被报道是在1958年, Eiseman等[24]报道了4例对抗生素治疗无反应的伪膜性结肠炎患者资料,所有患者在粪便保留灌肠后完全痊愈。在过去的几十年中, FMT已经被申请用于难治性梭状芽胞杆菌感染的治疗,并被认为是治疗IBD的一个潜在方法。1989年Bennet等[25]在Lancet上发表了FMT在IBD中最早应用的个案报道, Bennet自身患UC 7年,期间不能耐受柳氮磺胺吡啶类和激素,他尝试使用大量粪液保留灌肠, 3个月后肠镜检查显示急性炎症消退, 6个月后症状基本消失。首例个案报道虽然带来了阳性的结果,但IBD是活动期和缓解期交替的,半年的随访并不能证实FMT的长期有效性。2003年, 一项回顾性分析[26]表明, 6例难治性UC患者采用连续5 d粪液保留灌肠,此后1~13年随访中,患者病情基本缓解,表明FMT治疗的长期有效性。Anderson等[27]系统性地回顾分析了FMT在IBD患者中应用的文献报道,共包含41例IBD患者(27例UC、12例CD、2例非定型),随访期从2周到13年,结果发现FMT可以使63.0%的IBD患者达到临床缓解,而76.0%的患者可以停止服用IBD相关的药物,并且消化系统症状减少。国内一项研究[28]回顾总结了12份报告,发现FMT治疗成人的总体成功率为77.8%。通过衡量症状的消失或溃疡性结肠炎的活动指数的减少(UCAI), FMT改善UC的成功率约为90.0%。对于难治性IBD, 与传统疗法如抗感染、类固醇、免疫抑制和生物制剂等相比, FMT可能是一种较为理想的治疗方案。
3. L. reuteri与IBD
3.1 L. reuteri的特性与功效
L. reuteri属于乳杆菌属,为革兰阳性菌,属兼性厌氧菌,形态学表现为轻微不规则、圆形末端的弯曲杆菌,属专性特异型发酵菌种,能发酵糖产生二氧化碳(CO2)、乳酸、乙酸等,与广泛存在于脊椎动物和哺乳动物肠道内的乳酸杆菌具有良好的生物相容性,对人体无毒害,不会导致疾病发生[29-30]。L. reuteri在人的肠胃中天然存在,是少量适应定植在人肠胃的乳酸杆菌之一,其可以定植在胃酸和胆盐的环境中,承受胃酸汁液和胆汁酸,而到达小肠上部,则可黏附在小肠壁。L. reuteri作为重要的益生菌之一,具有如下功能: ①调整肠道菌群平衡,抑制腹泻。L. reuteri在生长代谢过程中能够产生有机酸、过氧化氢、细菌素等多种拮抗物质,可以有效地抑制体内有害菌的生长和繁殖,抑制由抗生素等引起的腹泻。②黏附在宿主消化道内并定植和存活下来形成生物屏障,一方面可以抑制病原菌在消化道黏膜上的黏附,并通过与病原菌竞争营养物质而抑制病原菌的生长; 另一方面可以防止毒素等有害物质的吸收并中和有毒产物。③产生独特的抑菌素,抑制有害菌。L. reuteri能通过代谢甘油产生一种特殊的抑菌物质罗伊氏素(reuterin), 主要成分是3-羟基丙醛(3-HPA)的单体、水合物及环化二聚体, 3-HPA是一种低分子量的非蛋白、中性、可溶性的细菌素。Axelsson L T等[31]研究表明, L. reuteri有很宽的抑菌谱带,较低浓度即可抑制多种有害病原菌的生长,如大肠埃希氏杆菌、鼠伤寒杆菌、白假丝酵母菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、黄曲霉菌、空肠弯曲杆菌及产芽孢梭菌等病菌。④刺激免疫系统,提高免疫功能,抑制有害菌,维护胃肠道平衡。L. reuteri产生酸性环境,从而抑制有害微生物的生长和繁殖,可有效避免沙门氏杆菌的感染,并帮助维持肠道菌群的正常化。Liu等[32]研究发现,多种人源L. reuteri(包括DSM17938、ATCC PTA4659、ATCC PTA 5289、ATCC PTA6475等)均可通过单核巨噬细胞系统来刺激免疫调节反应,进而不同程度地减轻人类肠道炎症程度。⑤抗过敏。过敏反应是人类常见自身免疫性疾病, L. reuteri有预防肠道过敏反应以及调节肠道的免疫功能作用[33]。
3.2 L. reuteri在IBD中的定植
IBD是一种慢性胃肠道疾病,病因尚不十分清楚,其中环境因素特别是肠道微生物引起的复杂免疫反应是导致其发病的一个重要诱因。L. reuteri与IBD关系的研究是近些年的研究热点,但目前相关的研究报道并不多。Ott S J等[34]研究显示, IBD患者肠道微生物多样性较正常人明显减少,原因是类杆菌、真杆菌和乳酸杆菌明显缺失,这会直接导致肠道黏膜的炎症反应,包括腹泻和肠黏膜的出血。Schreiber O等[5]研究显示,在大鼠模型中,葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的溃疡性结肠炎会引起乳酸杆菌的定植增加,这可能与肠黏膜功能受打击有关。通过连续给予4株乳酸杆菌,其中包括L. reuteri R2lc菌株,结果发现L. reuteri R2lc菌株在大鼠结肠黏液中定植,可预防溃疡性结肠炎发生,并显著减轻肠黏膜炎症反应。Petrella C[35]研究也显示, L. reuteri的2个不同菌株ATCC PTA 4659(人类的起源)和R2lc(啮齿类动物的起源)在大鼠溃疡性结肠炎模型中均有减少。上述研究都强调了L. reuteri的抗感染潜力,连续补充益生菌几乎完全阻止了DSS诱导的大鼠溃疡性结肠炎的发生[5], 考虑与益生菌肠道内持续定植有关。
3.3 L. reuteri在IBD肠道免疫调节中的作用
肠道免疫调节是由数以万亿计的微生物及许多模式受体基因产物相互作用而保证的,目的是维持肠道内环境的稳定,其中这些受体就包括C型凝集素受体(CLRs)[36]、特定的细胞间黏附分子3(SIGNR3)[37]。肠内稳态环境是受肠道免疫信号通路严格调控的,这种免疫机制可减轻IBD患者的肠道炎症反应,保护肠黏膜屏障功能,当调节机制破坏时,将不可避免地导致IBD的发生。IBD患者肠道炎症正是由于肠道免疫系统过度活跃引起的[38]。
肠道细胞免疫调节主要是受淋巴细胞免疫调节影响。研究[39]报道小鼠肠道内分布不同上皮内T淋巴细胞亚群。在αβT淋巴细胞亚群中,双阴性T细胞和CD8αα+ T细胞在大肠中分布比例较高, CD8αα+ T细胞在小肠中较高,而双阳性上皮内T细胞在小肠远端较高; 在γδT淋巴细胞亚群中, CD8αα+ T细胞在小肠中分布较高,双阴性T细胞在大肠中较高。肠道免疫细胞DPIELs为鼠和人类共有,研究L. reuteri对明确DPIELs特殊调节机制及IBD患者治疗提供了新方向。
2017年,来自华盛顿大学医学院的一项研究[6]显示, L. reuteri是一种可以调节DPIELs的肠道微生物; 研究人员将大鼠随机分为大量DPIELs组与不含DPIELs组,将携带DPIELs组肠道菌群移植给另一组小鼠,结果显示该组小鼠也含有相当数量的DPIELs, 再经过4种抗生素处理后,小鼠体内DPIELs又消失了,表明肠道菌群在参与肠道免疫调节过程中发挥重要的作用。在对新霉素有抗药性的肠道内革兰阳性菌中,在大鼠体内经过逐个的细菌移植,研究[19]发现只有L. reuteri能决定CD4+ T细胞是否能分化为DPIELs, 其他的5类拟杆菌目细菌均无此作用,表明L. reuteri有抑制有害菌的作用。菌群的紊乱可加重肠道的炎症反应,诱发IBD。
IBD与肠道的免疫和微生物菌群密切相关,色氨酸(Trp)是一种炎症抑制因子,是肠道菌群的调节剂。研究[40]发现,在小鼠结肠炎模型中,通过添加Trp可降低苏氨酸、蛋氨酸及脯氨酸谱来调节血清氨基酸谱,影响肠道免疫功能,同时可抑制白介素-22在结肠中表达,改变肠道微生物群。
关于L. reuteri是如何让T细胞分化为DPIELs的问题, Colonna研究[6]显示L. reuteri可通过代谢Trp而产生吲哚-3-乳酸,并激活CD4+ T细胞中的芳香烃受体,从而引起转录因子Thpok表达的减少,使CD4+ T细胞进一步分化为DPIELs,这与Reis等[41]发现的Thpok下调引导的分化机制是一致的。同时,该研究将大鼠分为3组,分别以高水平Trp(0.48%)、标准水平Trp(0.24%)和低水平Trp(0.11%)饮食喂养4周,对于移植了缺陷型L. reuteri菌株的无菌小鼠而言,即使补充高水平的Trp也不能升高小鼠DPIELs的水平;而对于普通L. reuteri水平正常的小鼠而言,标准Trp水平喂养的DPIELs是低水平的2倍,高水平的则达到3倍; 表明这些大量存在于健康人肠道的有益菌若想发挥特殊的免疫调节机制,需要人体必需氨基酸之一的Trp的参与。目前尚不清楚在正常机体中诱导免疫细胞的发育是否与L. reuteri产生的Trp有关,但在炎症性肠病患者中发现与Trp代谢相关基因缺陷[6]。
3.4 L. reuteri在IBD中应用潜力
目前通过FMT植入益生菌可以重建或调整肠道微生物菌群、维持内环境稳态,减少炎症因子的释放以及参与肠黏膜免疫调节,发挥治疗IBD的功效。L. reuteri作为肠道益生菌,不但能抑制有害菌生长,减轻肠道炎症反应,而且可以上调小肠中DPIELs的水平,参与肠道微生态及免疫机制调节[5-6, 33]。
4. 展望
本综述对L. reuteri在IBD中粪菌移植中的作用做了总结,分析国内外大量基础和临床研究结果,认为L. reuteri具有建立或调整肠道微生物菌群、预防或治疗因肠道感染引起的腹泻、调节肠道免疫功能的功效,但还需要在生物化学、分子生物学、遗传特性及基因调控等方面展开更深入的研究。
-
表 1 各组大鼠血清炎症因子表达水平比较(x±s)
pg/mL 组别 n IL-1β IL-6 TNF-α Sham组 15 21.36±1.76 86.68±5.62 136.69±8.06 Model组 15 39.55±3.48* 144.02±8.59* 209.46±11.39* Rem-L组 15 33.03±3.01# 130.64±7.36# 186.78±9.27# Rem-M组 15 24.69±2.58#△ 115.01±6.13#△ 162.16±8.87#△ Rem-H组 15 19.14±1.93#△▲ 99.35±5.87#△▲ 145.22±8.33#△▲ Rem-H+DEX组 15 34.06±3.20▽ 139.62±8.22▽ 189.81±10.03▽ IL-1β: 白细胞介素-1β; IL-6: 白细胞介素-6; TNF-α: 肿瘤坏死因子-α。与Sham组比较, * P < 0.05; 与Model组比较, #P < 0.05;与Rem-L组比较, △P < 0.05; 与Rem-M组比较, ▲P < 0.05; 与Rem-H组比较, ▽P < 0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠视网膜细胞凋亡率比较(x±s)
组别 n 细胞凋亡率/% Sham组 5 5.72±0.69 Model组 5 36.55±3.46* Rem-L组 5 24.66±2.32# Rem-M组 5 12.03±2.18#△ Rem-H组 5 8.70±1.10#△▲ Rem-H+DEX组 5 25.37±2.43▽ 与Sham组比较,* P < 0.05; 与Model组比较,#P < 0.05; 与Rem组比较,AP < 0.05; 与Rem-M组比较,▲P < 0.05; 与Rem-H组比较, ▽ P < 0.05。 表 3 各组大鼠视网膜组织中氧化应激相关指标表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n SOD/(U/mg) GSH-PX/(U/mg) MDA/(nmol/mg) Sham组 5 236.29±12.79 185.33±11.94 1.30±0.13 Model组 5 136.59±7.61* 81.39±5.95* 4.63±0.45* Rem-L组 5 159.62±8.20# 113.26±6.55# 3.24±0.29# Rem-M组 5 180.35±9.38#△ 145.87±7.32#△ 2.56±0.22#△ Rem-H组 5 204.57±11.84#△▲ 169.73±9.53#△▲ 1.57±0.13#△▲ Rem-H+DEX组 5 149.82±7.95▽ 106.25±6.21▽ 3.57±0.33▽ SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶; GSH-PX: 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶; MDA: 丙二醛。与Sham组比较, * P < 0.05; 与Model组比较, #P < 0.05;与Rem-L组比较, △P < 0.05; 与Rem-M组比较, ▲P < 0.05; 与Rem-H组比较, ▽P < 0.05。 表 4 各组大鼠视网膜组织中缺氧相关因子及HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路相关蛋白表达水平比较(x±s)
组别 n HMGB1 RAGE NF-κB HIF-1α VEGF Sham组 5 0.33±0.02 0.80±0.07 0.59±0.04 0.38±0.05 0.22±0.03 Model组 5 1.13±0.09* 1.62±0.14* 1.38±0.11* 1.59±0.13* 0.98±0.07* Rem-L组 5 0.80±0.07# 1.41±0.12# 1.22±0.09# 1.10±0.12# 0.81±0.06# Rem-M组 5 0.62±0.05#△ 1.20±0.11#△ 1.07±0.08#△ 0.99±0.10#△ 0.65±0.05#△ Rem-H组 5 0.45±0.03#△▲ 0.95±0.08#△▲ 0.78±0.06#△▲ 0.65±0.08#△▲ 0.41±0.03#△▲ Rem-H+DEX组 5 1.05±0.08▽ 1.53±0.12▽ 1.36±0.10▽ 1.19±0.12▽ 0.79±0.06▽ HMGB1: 高迁移率族蛋白B1; RAGE: 晚期糖基化终末产物受体; NF-κB: 核转录因子-κB; HIF-1α: 缺氧诱导因子-1α; VEGF: 血管内皮生长因子。与Sham组比较, * P < 0.05; 与Model组比较, #P < 0.05; 与Rem-L组比较, △P < 0.05; 与Rem-M组比较, ▲P < 0.05; 与Rem-H组比较, ▽P < 0.05。 -
[1] 潘奕吉, 杨家翼, 邢怡桥, 等. S100A4过表达对视网膜缺血再灌注损伤小鼠视网膜毛细血管细胞和神经节细胞的影响[J]. 中华眼底病杂志, 2024, 40(4): 296-302. [2] 夏江南, 沈蕾, 李晶晶. KLF7对TLR4/NLRP3炎症小体激活的抑制作用及其对视网膜缺血-再灌注损伤大鼠细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 眼科新进展, 2022, 42(9): 699-703. [3] 王玉丽, 林娟, 李新, 等. 丹红化瘀口服液对视网膜缺血再灌注损伤大鼠视网膜中央静脉阻塞症的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(6): 1621-1627. [4] 张娟, 罗会林, 吴志林, 等. 瑞马唑仑对全身麻醉下胸腔镜肺手术后急慢性疼痛和创伤后应激障碍的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21(21): 2350-2353. [5] 姚艳粉, 李丕宝, 孙玮, 等. 瑞马唑仑复合右美托咪定镇静对老年创伤性颅脑损伤患者疗效相关指标的影响[J]. 立体定向和功能性神经外科杂志, 2022, 35(4): 235-240. [6] SHI M, CHEN J, LIU T X, et al. Protective effects of remimazolam on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting of NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2022, 16: 413-423. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S344240
[7] 时卫刚, 李萱, 高深, 等. 瑞马唑仑通过调节AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α信号通路对脑缺血再灌注大鼠神经损伤的影响[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2023, 29(6): 573-576, 579. [8] TAVERNA S, TONACCI A, FERRARO M, et al. High mobility group box 1: biological functions and relevance in oxidative stress related chronic diseases[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(5): 849.
[9] GAO J, ZHANG Z, YAN J Y, et al. Inflammation and coagulation abnormalities viatheactivation of the HMGB1-RAGE/NF-κB and F2/Rhopathways in lung injury induced by acute hypoxia[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2023, 52(2): 67.
[10] 潘敏丽, 黄国定, 卢宏全, 等. 依托咪酯对缺氧复氧诱导心肌细胞损伤及HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB通路的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2022, 39(2): 282-289. [11] ZHAO Y Z, ZHANG X N, YIN Y, et al. N-acetylserotonin alleviates retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB pathway in rats[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2024, 17(2): 228-238.
[12] 任越磊, 姜艳. 甘草甜素抑制HMGB1/RAGE信号通路对细菌性脑膜炎大鼠神经损伤的影响[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2023, 18(10): 1122-1126. [13] 于雯, 陈肖君, 肖正霞, 等. 槲皮素腹腔注射对大鼠视网膜缺血再灌注损伤的影响及其机制[J]. 山东医药, 2023, 63(29): 31-35. [14] MUSAYEVA A, UNKRIG J C, ZHUTDIEVA M B, et al. Betulinic acid protects from ischemia-reperfusion injury in the mouse retina[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2440.
[15] LIU X L, LIN S P, ZHONG Y Y, et al. Remimazolam protects against LPS-induced endotoxicity improving survival of endotoxemia mice[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 739603.
[16] 王德勇, 涂英兵, 袁娟, 等. 基于PERK/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路研究瑞马唑仑对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠铁死亡的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2023, 23(1): 4427-4433. [17] 郭小丽, 杨昌明, 王婵, 等. 基于Sirt1/FoxO1通路探讨瑞马唑仑减轻脓毒症小鼠脑损伤的机制研究[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2023, 31(1): 82-90. [18] 王东亚, 乔丹, 陈炜佳, 等. 瑞马唑仑对颅脑损伤大鼠脑组织损伤及TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB通路的影响[J]. 河北医学, 2024, 30(2): 177-182. [19] 赵健衡, 王丽, 蒋燕, 等. 丙泊酚调节SIRT1/HMGB1/NF-κB信号通路对缺血缺氧性脑损伤新生大鼠神经元损伤的影响[J]. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2023, 31(4): 708-714. [20] HUANG S Q, WEN Y, SUN H Y, et al. Abdominal paracentesis drainage attenuates intestinal inflammation in rats with severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the HMGB1-mediated TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(9): 815-834.
[21] 颜培夏, 王媛媛. HMGB1、cTnⅠ、CK-MB及NT-proBNP对脓毒症心肌损伤的诊断价值[J]. 重庆医学, 2023, 52(5): 737-741. [22] WANG J X, XIN Y Y, CHU T T, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates perioperative neurocognitive disorders by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation and HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 150: 113006.
[23] 刘艳文, 刘水清, 林少伟, 等. 毛蕊花糖苷调节HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路对动脉粥样硬化大鼠内皮功能障碍的影响[J]. 天津医药, 2023, 51(12): 1339-1343. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 魏静,白焕焕,徐红波,张海钢. 罗伊氏乳杆菌对脓毒症小鼠肠道保护机制的初步研究. 临床医学研究与实践. 2024(16): 45-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谭学蓉,张莉,徐兰,李鲜,王嘉英,邹永蓉. 罗伊氏乳杆菌治疗早产儿喂养不耐受及预防医院感染的效果. 中华医院感染学杂志. 2022(04): 595-599 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
