Correlations of platelet-derived growth factor and Beclin1 with vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients
-
摘要:目的
探讨血清血小板衍生生长因子-BB(PDGF-BB)、自噬相关分子Beclin1水平与行维持性血液透析(MHD)患者血管钙化(VC)的相关性。
方法选取100例MHD患者为MHD组,100例健康者为对照组,比较2组血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1水平。按腹主动脉钙化评分(AACS)将MHD患者分为钙化组(48例)和非钙化组(52例)。分析MHD患者发生VC的影响因素;分析血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1水平预测MHD患者VC的价值。
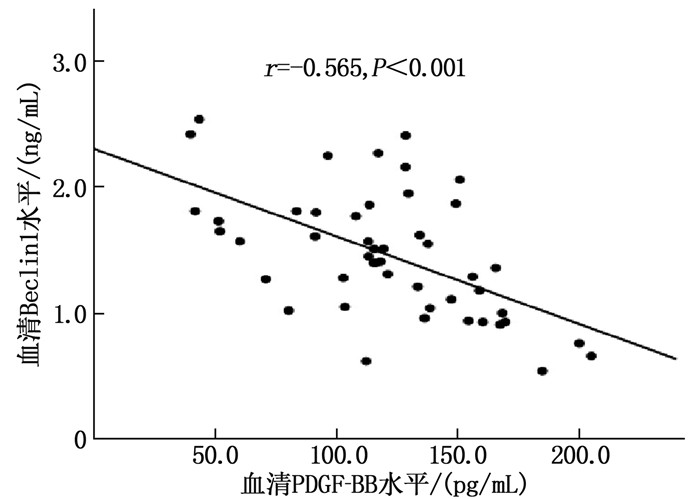
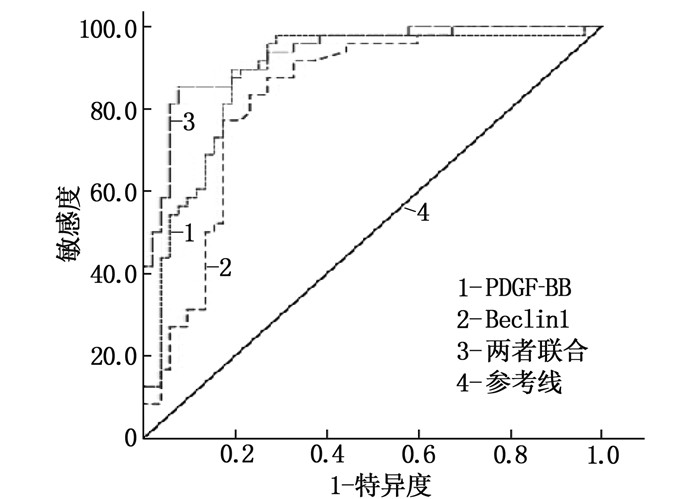
结果MHD组血清PDGF-BB水平[(90.57±31.64)pg/mL]高于对照组[(41.78±13.83)pg/mL],血清Beclin1水平[(2.02±0.68)ng/mL]低于对照组[(3.09±1.04)ng/mL],差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。血磷、PDGF-BB、血钙、TG是影响MHD患者发生VC的危险因素(P < 0.05),Beclin1是影响MHD患者发生VC的保护因素(P < 0.05)。血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1水平预测MHD患者VC的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.885、0.832;血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1水平联合预测MHD患者VC的AUC为0.932,敏感度为85.4%,特异度为92.3%。
结论MHD患者血清PDGF-BB水平较高,Beclin1水平较低,两者均与VC相关。血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1联合预测可能有助于临床预防、评估MHD患者并发VC。
-
关键词:
- 血小板衍生生长因子-BB /
- 维持性血液透析 /
- Beclin1水平 /
- 血管钙化
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the correlations of serum platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) and autophagy-related molecule Beclin1 with vascular calcification (VC) in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD).
MethodsA total of 100 MHD patients were selected as MHD group, and 100 healthy people were selected as control group. The levels of serum PDGF-BB and Beclin1 were compared between the two groups. According to Abdominal Aortic Calcification Score (AACS), MHD patients were divided into calcification group (48 cases) and non-calcification group (52 cases). The influencing factors of VC in MHD patients were analyzed; the value of serum PDGF-BB and Beclin1 levels in predicting VC in MHD patients were analyzed.
ResultsThe level of serum PDGF-BB in the MHD group[(90.57±31.64) pg/mL] was significantly higher than that in the control group[(41.78±13.83) pg/mL], and the level of Beclin1 in MHD group[(2.02±0.68) ng/mL] was significantly lower than that in the control group[(3.09±1.04) ng/mL] (P < 0.05). Blood phosphorus, PDGF-BB, blood calcium and TG were the risk factors for VC in MHD patients (P < 0.05), and Beclin1 was a protective factor for VC in MHD patients (P < 0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) of serum PDGF-BB and Beclin1 levels in predicting VC in MHD patients were 0.885 and 0.832, respectively; the AUC of serum PDGF-BB and Beclin1 in combination to predict VC in MHD patients was 0.932, the sensitivity was 85.4%, and the specificity was 92.3%.
ConclusionThe serum PDGF-BB level is higher and Beclin1 level is lower in MHD patients, both of them were related to VC. The combined prediction of serum PDGF-BB and Beclin1 may help to prevent and evaluate VC in MHD patients.
-
-
表 1 MHD组、对照组血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1水平比较(x±s)
组别 n PDGF-BB/(pg/mL) Beclin1/(ng/mL) 对照组 100 41.78±13.83 3.09±1.04 MHD组 100 90.57±31.64* 2.02±0.68* PDGF-BB: 血小板衍生生长因子-BB。
与对照组比较, *P < 0.05。表 2 钙化组、非钙化组一般资料及血清PDGF-BB、Beclin1水平比较(x±s)
指标 非钙化组(n=52) 钙化组(n=48) 性别 男 27 24 女 25 24 体质量指数/(kg/m2) 22.76±2.28 23.12±2.40 舒张压/mmHg 75.34±10.46 78.57±10.72 血钙/(mmol/L) 2.70±0.54 3.18±0.64* 年龄/岁 47.05±11.83 47.66±12.07 收缩压/mmHg 130.57±17.39 135.26±18.61 血磷/(mmol/L) 1.54±0.52 1.99±0.68* 总胆固醇/(mmol/L) 5.85±1.27 6.95±1.51* 空腹血糖/(mmol/L) 7.38±2.50 7.88±2.64 LDL-C/(mmol/L) 2.76±0.81 2.85±0.83 甘油三酯/(mmol/L) 1.66±0.55 2.90±0.97* 白蛋白/(g/L) 40.41±5.06 38.94±4.88 HDL-C/(mmol/L) 1.04±0.35 0.98±0.33 PDGF-BB/(pg/mL) 63.22±21.05 120.20±41.54* Beclin1/(ng/mL) 2.53±0.85 1.47±0.50* LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;
PDGF-BB: 血小板衍生生长因子-BB。
与非钙化组比较, *P < 0.05。表 3 MHD患者VC影响因素的Logistic回归分析
指标 B SE Wald P OR 95%CI 性别 0.052 0.103 0.251 0.616 1.053 0.861~1.289 BMI 0.088 0.105 0.703 0.402 1.092 0.889~1.342 舒张压 0.113 0.117 0.938 0.333 1.120 0.890~1.409 年龄 0.136 0.107 1.622 0.203 1.146 0.929~1.413 血钙 0.905 0.225 16.165 < 0.001 2.471 1.590~3.841 收缩压 0.093 0.110 0.722 0.395 1.098 0.885~1.362 血磷 0.891 0.212 17.655 < 0.001 2.437 1.608~3.692 TC 0.128 0.108 1.394 0.238 1.136 0.919~1.404 空腹血糖 0.168 0.115 2.136 0.144 1.183 0.944~1.482 LDL-C 0.161 0.112 2.073 0.150 1.175 0.943~1.463 TG 0.756 0.206 13.456 < 0.001 2.129 1.422~3.188 白蛋白 0.041 0.109 0.140 0.708 0.960 0.775~1.189 HDL-C 0.067 0.104 0.418 0.518 0.935 0.763~1.146 PDGF-BB 1.023 0.231 19.605 < 0.001 2.781 1.768~4.374 Beclin1 -0.548 0.102 28.883 < 0.001 0.578 0.473~0.706 BMI: 体质量指数; TC: 总胆固醇; LDL-C: 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇; TG: 甘油三酯; HDL-C: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;
PDGF-BB: 血小板衍生生长因子-BB。 -
[1] RAVINDRAN A, SUNNY A, KUNNATH R P, et al. Assessment of quality of life among end-stage renal disease patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Indian J Palliat Care, 2020, 26(1): 47-53. doi: 10.4103/IJPC.IJPC_141_19
[2] 王明莉, 陈德政. 维持性血液透析患者血清铁蛋白水平与预后的关系[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2019, 19(4): 256-260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2019.04.006 [3] 陈雨, 李旻, 周华, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清IGF-1、SOST与血管钙化的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(25): 85-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY202025024.htm [4] ZHAO W, WANG Y, KONG W, et al. Elevated serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein and the metalloproteinase-ADAMTS7 levels are associated with vascular calcification in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Semin Dial, 2020, 33(4): 322-329. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12885
[5] 薛新月, 畅智慧, 刘兆玉. 血管平滑肌细胞在血管钙化中的调控机制研究进展[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2020, 36(9): 870-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXB202009020.htm [6] OSSAREH S, RAYATNIA M, VAHEDI M, et al. Association of serum fetuin-A with vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients and its' impact on 3-year mortality[J]. Iran J Kidney Dis, 2020, 14(6): 500-509.
[7] 李松, 陈民, 石晓娟. 通瘀煎化方配合雷公藤多苷对糖尿病肾病患者血液流变学及血清TGF-β1、PDGF-BB、CTGF的影响[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2019, 14(1): 74-77, 81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJZX201901026.htm [8] 黄显元, 刘建红, 朱彦儒. α-硫辛酸对糖尿病肾病自噬相关因子LC3、Rab7和Beclin1表达的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2019, 35(17): 2073-2078. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201917006.htm [9] 李大勇, 袁新科, 刘冠兰, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清Irisin、BMP-7水平与血管钙化及钙磷代谢指标的相关性研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2019, 29(15): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXDY201915010.htm [10] 葛均波, 徐永健. 内科学[M]. 8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013: 459-462. [11] 韩蓓, 韩俊岭, 曹靖昊, 等. 全段成纤维细胞生长因子23与维持性血液透析患者肾性贫血的相关性研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(21): 114-118. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20213812 [12] ZBROCH E, BAZYLUK A, MALYSZKO J, et al. The serum concentration of anti-aging proteins, Sirtuin1 and αKlotho in patients with end-stage kidney disease on maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2020, 15: 387-393.
[13] 李志鹏. 活动性肺结核患者外周血PDGF-BB与IP-10水平及其诊断价值[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2019, 24(11): 2000-2003, 2019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFK201911016.htm [14] LEDARD N, LIBOZ A, BLONDEAU B, et al. Slug, a cancer-related transcription factor, is involved in vascular smooth muscle cell transdifferentiation induced by platelet-derived growth factor-BB during atherosclerosis[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2020, 9(2): e014276.
[15] HAN J H, PARK H S, LEE D H, et al. Regulation of autophagy by controlling Erk1/2 and mTOR for platelet-derived growth factor-BB-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype shift[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 267: 118978.
[16] 邱小波, 姚丽, 盛子桐. 自噬影响慢性肾脏病血管钙化的研究进展[J]. 中国血液净化, 2018, 17(5): 321-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJH201805010.htm [17] 张晨红, 章礼久, 宋莎莎. 结直肠癌组织中自噬相关蛋白Beclin1和p62的表达特点及意义[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2020, 36(2): 206-209, 215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYZ202002015.htm [18] ZHU H W, QU Y Q. Expression levels of ARHI and Beclin1 in thyroid cancer and their relationship with clinical pathology and prognosis[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 19(2): 1241-1246.
[19] QIU X B, XU Q, XU T H, et al. Metformin alleviates β-glycerophosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells via AMPK/mTOR-activated autophagy[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 21(1): 58.
[20] XU T H, QIU X B, SHENG Z T, et al. Restoration of microRNA-30b expression alleviates vascular calcification through the mTOR signaling pathway and autophagy[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(8): 14306-14318.
-
期刊类型引用(21)
1. 薛国静,李会敏,马艳文. 精细化手术室护理对骨科手术患者切口感染发生情况的影响. 临床医学工程. 2023(06): 827-828 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郭果. 腰椎椎间融合术联合后路经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术围术期医护一体化快速康复外科护理效果分析. 河南外科学杂志. 2023(04): 79-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王欢,高艳英,郭珊珊. 精细化护理对胫骨近端骨肿瘤患者膝关节功能康复及生活质量的影响. 中国医刊. 2023(09): 1032-1036 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高小凤,鹿秀娟,蒋丹,张莉. 精细化手术室护理在非体外循环冠状动脉搭桥术患者中的应用效果. 护理实践与研究. 2022(01): 129-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吉桂贇. 精细化护理模式对骨科手术患者负性情绪及疼痛程度的影响. 延安大学学报(医学科学版). 2022(02): 110-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 耿静雅,赵刚,金军伟. 术后预见性护理-精细化护理-全程心理护理应用于高龄股骨粗隆间骨折患者的效果观察. 河南外科学杂志. 2022(04): 181-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘婷,马丽,朱红英,商雪辉,王晶,王艳. 简化McGill疼痛问卷用于肺癌癌痛综合评定的研究. 医学信息. 2021(03): 6-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陆彩萍,邓君. 精细化护理模式在骨科手术患者中的干预效果分析. 中国药物与临床. 2021(13): 2398-2400 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 周小兰,刘丹,周琴. 安神镇静膏外敷神阙穴在儿童骨科术前失眠的临床研究. 光明中医. 2021(19): 3346-3348 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张静. 细致化护理模式对手术患者护理质量、情绪以及睡眠质量的影响. 世界睡眠医学杂志. 2021(10): 1791-1793 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 张桂芳. 骨科术后护理中精细化护理模式的运用. 人人健康. 2020(08): 127 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 潘芳. 股骨粗隆间骨折术后精细化护理对老年患者疼痛及生活质量的影响. 河南医学研究. 2020(11): 2087-2089 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 胡维界,李芬,郭晋怀,李毛毛,张晓瑜. 手术室医护一体化管理在降低骨科手术感染风险中的应用. 甘肃中医药大学学报. 2020(02): 108-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 严珍,刘小华. 细致化护理模式对手术患者护理质量、心理情绪及睡眠质量的改善情况. 世界睡眠医学杂志. 2020(07): 1249-1250 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 刘文泸,董俊,王娟. 精细化护理在骨科手术室护理安全管理中的效果分析. 智慧健康. 2020(30): 126-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 张雪,刘佳,金烨鑫,王之宁,敖诗文. 精细化护理在提高手术室护理质量与患者护理满意度的意义分析. 现代养生. 2019(06): 183-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 迟晓阳. 精细化模式应用于骨科手术患者的有效性分析. 世界最新医学信息文摘. 2019(24): 210+216 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 刘文泸. 手术室护理配合对骨科手术切口感染的影响效果分析. 按摩与康复医学. 2019(17): 68-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 刘金玲. 精细化护理模式对剖宫产产妇康复及产科护理质量的应用效果分析. 中国医药指南. 2019(21): 234-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 车莉. 探讨精细化护理对下肢骨折患者术后康复的影响. 中外医疗. 2019(24): 129-131+138 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 郑爱芳. 精细化护理在乳腺手术的应用效果. 福建医药杂志. 2019(06): 169-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号