Automatic temperature control moxibustion box based on modular design
-
摘要:目的
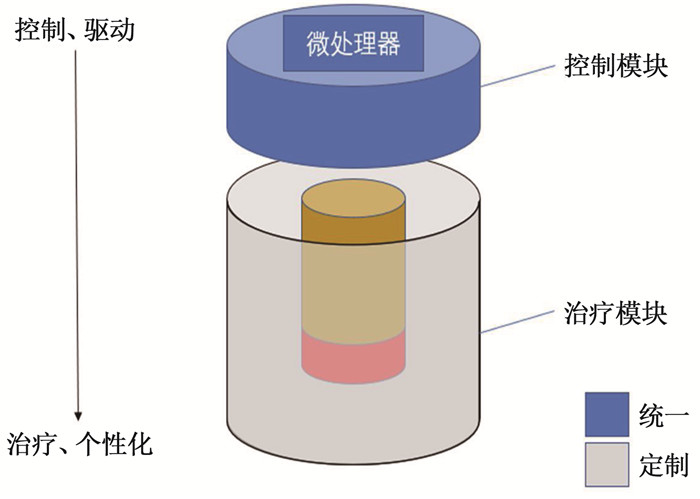
针对中医临床艾灸疗法“三因制宜”思想与疗法创新的需求,探索一种模块化艾灸盒的设计方案,研发具有功能切换和个性化定制的模块,使用传统艾条并能自动控温的模块化艾灸盒。
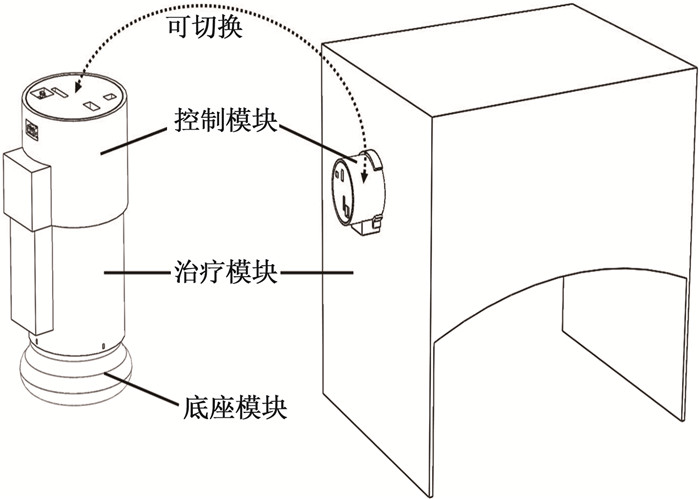
方法应用模块化设计方法,将艾灸盒分为控制和治疗模块。结合微纳温度传感器与脉冲带宽调制芯片实现传统艾条的自动控温功能。
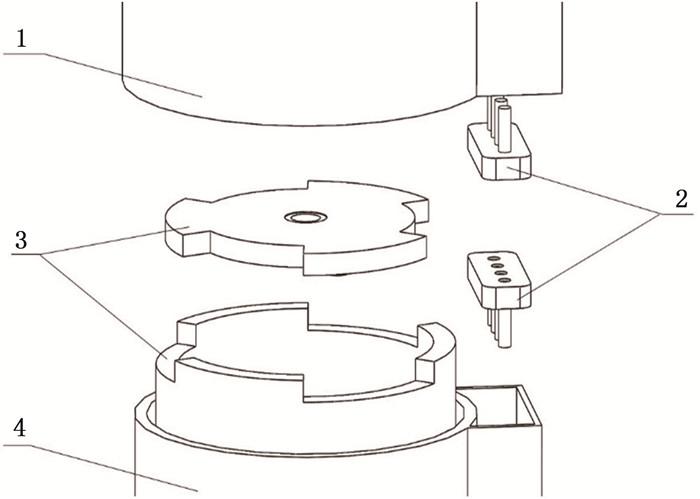
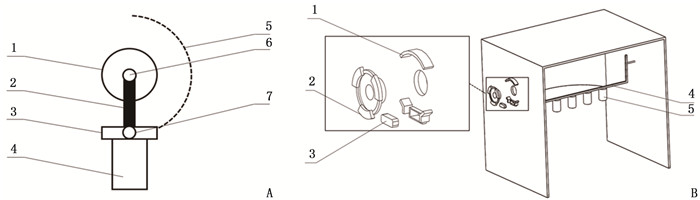
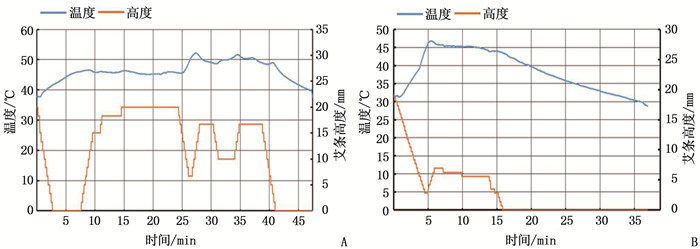
结果设计了单穴位灸和多穴位灸2种治疗模块,拆装模块实现切换施灸部位以及个性化调整的功能,验证了模块化艾灸盒在结构上的可行性;经过温度测试,在点燃艾条的情况下,单穴位灸与多穴位灸在设置45℃条件下测试的平稳期平均温度分别为45.68℃和45.12℃。
结论设计的艾灸盒能够保留传统艾条施灸功能,实现智能控制温度的效果,基于模块化方法可适应多种使用场景,具有较高的性价比和较大的应用潜力,为艾灸盒甚至中医诊疗设备的设计提供了新的方法及思路。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore a modular moxibustion box design scheme according to the thought of "developing appropriate treatment according to three disease causes" and the demand of therapy innovation to develop a modular moxibustion box with function switching and personalized customization, which uses traditional moxa sticks and can automatically control temperature.
MethodsThe moxibustion box was divided into control module and treatment module by modular design method. Combining micro- and nano-temperature sensor and pulse bandwidth modulation chip, the automatic temperature control function of traditional moxa stick was realized.
ResultsSingle point moxibustion and multi-point moxibustion were designed. The functions of switching moxibustion sites and personalized adjustment were realized by disassembling and assembling the module, and the feasibility of modular moxibustion box in structure was verified. After the temperature test, the average temperature of single point moxibustion and multi-point moxibustion at 45℃ in the test stationary period was 45.68℃ and 45.12℃ respectively under the condition of firing moxa stick.
ConclusionThe moxibustion box designed retains the function of traditional moxibustion with moxa sticks and realizes intelligent temperature control. Based on the modular method, it can adapt to a variety of use scenarios, with high cost performance and great application potential. It provides a new method and idea for the design of moxibustion box and even traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis and treatment equipment.
-
-
表 1 温控测试结果
穴位灸 最低温度/℃ 最高温度/℃ 自动模式45℃ 自动模式50℃ 平均温度*/℃ 标准差* 占比**/% 平均温度*/℃ 标准差* 占比**/% 单穴位灸 42.9 61.1 45.70 0.465 62.59 49.96 0.992 56.20 多穴位灸 37.5 46.4 45.12 0.763 57.38 - - - 平均温度*和标准差*是在温度平稳的区间的平均温度及标准差; 占比**指在设定温度正负1 ℃区间温度的占比(如45 ℃的温度范围为44 ~46 ℃)。 -
[1] 邓凯烽, 毛文倩, 陈晓强, 等. 基于《黄帝内经》三因制宜理论浅析针灸的临床应用[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2021, 48(7): 70-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNZY202107020.htm [2] 连艳萍, 李红芳. 耳穴埋豆联合艾灸促进胃肠道术后肠功能恢复的护理分析[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2018, 22(12): 75-77. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201812022 [3] 刘爽, 何其英, 汤亚箐, 等. 中医综合疗法联合中医特色护理防治肛肠术后尿潴留的效果[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(16): 24-29. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20220519 [4] 戴云飞, 杨洁, 朱开宇, 等. 灸具研发的现状与展望[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(7): 4142-4144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202107093.htm [5] 石文韬, 孟青云, 喻洪流, 等. 一种模块化的腕关节康复训练器设计与仿真[J]. 软件导刊, 2021, 20(2): 135-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJDK202102026.htm [6] 余鑫, 杨帆, 杨浩. 可自动进艾调温艾灸盒的研制[J]. 按摩与康复医学, 2019, 10(19): 35-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AMYD201919016.htm [7] 金煜昊, 易荣, 孟江琼, 等. 一种自动控温艾灸仪器设计与应用[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2018, 34(11): 70-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJLC201811020.htm [8] 夏世林, 佃松宜, 张浛芮, 等. 一种适用于多关节艾灸机械臂艾灸器的设计与应用[J]. 中国针灸, 2021, 41(2): 221-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE202102031.htm [9] 李菲菲, 臧蕾, 李欣荣, 等. 一种可温显、定时和恒温的新型艾灸盒的研制[J]. 医学信息, 2019, 32(12): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXXX201912001.htm [10] 徐炜君, 刘凤辉, 陶东华. 一种智能艾灸设备的研制与应用[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2017, 51(5): 17-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHZZ201705005.htm [11] 陈祥林, 龙韵翔, 杨丹, 等. 一种基于LED红外技术的智能光灸环设备的研制[J]. 生物医学工程研究, 2019, 38(4): 472-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDSG201904020.htm [12] 王晓颖, 张玉杰, 杜美玲, 等. 新型艾灸仪研究进展[J]. 河南中医, 2020, 40(10): 1618-1620. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZY202010042.htm [13] 张国鑫, 苗晋玲, 张中原, 等. 电针不同腧穴组方对高脂血症大鼠血脂的调节作用[J]. 中国针灸, 2014, 34(9): 894-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE201409028.htm [14] 刘菊娥, 曾艳艳, 王琼娜. 艾灸关元穴联合穴位按摩在宫缩乏力性产后出血护理中的应用[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2020, 24(20): 130-132. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.202020036 [15] 徐素娥, 姜九. 艾灸疗法治疗高血压前期患者的临床观察[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2020, 24(14): 115-118. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.202014032 [16] 杨国芳, 方朝晖, 王静, 等. 温和灸联合穴位按摩治疗糖尿病性骨质疏松症的临床效果[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2021, 25(2): 59-62. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20200804 [17] 张绪初. 艾灸法治疗腹股沟疝术后尿潴留的疗效观察[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2017, 21(19): 160-160, 162. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.201719054 [18] 吴珍梅, 严晓岚, 谢洁珊, 等. 多功能电子艾灸仪辅助治疗脑瘫患儿的效果观察[J]. 按摩与康复医学, 2021, 12(10): 36-37, 40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AMYD202110014.htm [19] TUOHETI A, AIASSA S, CRISCUOLO F, et al. New approach for making standard the development of biosensing devices by a modular multi-purpose design[J]. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience, 2020, 19(3): 339-346.
[20] UKTVERIS T, JUSAS V. Development of a modular board for EEG signal acquisition[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2018, 18(7): 2140.
[21] PAULSON C, CHIEN D, LIN F, et al. A novel modular headmount design for non-invasive scalp EEG recordings in awake animal models[J]. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, 2018, 2018: 5422-5425.




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
