Methylation status of Septin 9 in peripheral blood and its relationship with colorectal cancer
-
摘要:目的
检测结直肠癌(CRC)患者外周血胞裂蛋白9(Septin 9)的甲基化状态, 分析Septin 9甲基化与CRC的关系。
方法选取120例CRC患者为研究对象,分析其外周血Septin 9甲基化状态与临床资料的关系; 分离CRC患者和健康人群的血清外泌体,采用该外泌体处理CRC细胞,测定CRC细胞的增殖和凋亡情况。
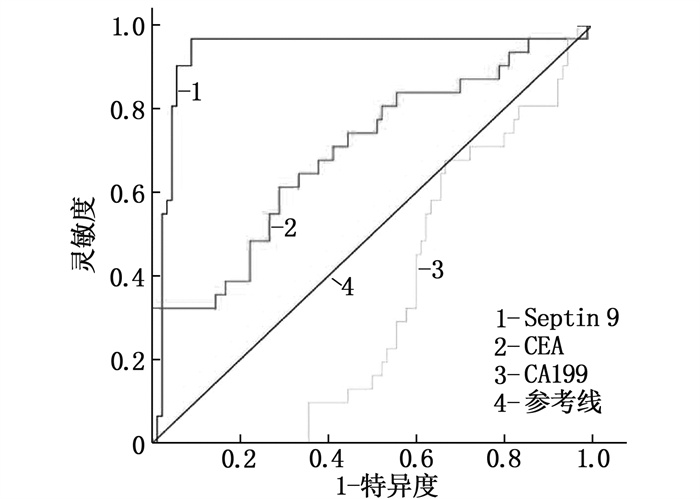
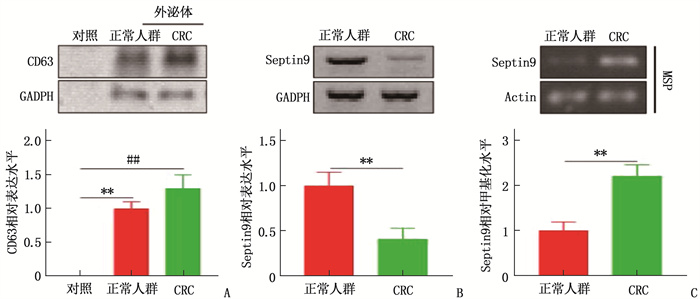
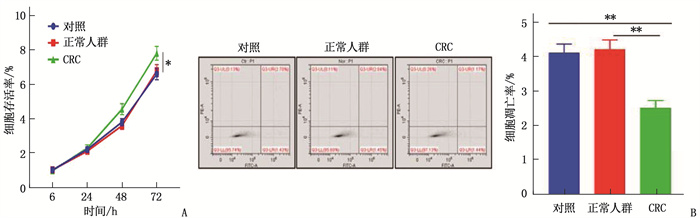
结果共计1586例体检人群接受了Septin 9筛查,其中Seprtin 9甲基化阳性56例,阳性率为3.5%。Sepetin 9阳性者中,胃肠状态异常者(肠胃炎症或者息肉)20例(35.7%), 而Septin 9阴性者胃肠状态异常率仅为5.4%(83/1530), 提示Septin 9在外周血中的甲基化状态与胃肠状态密切相关。120例CRC患者中, Septin 9甲基化阳性率为78.4%(73/93);在不同分化程度的比较中,高分化、中分化、低分化CRC患者的Septin 9甲基化阳性率依次为52.6%(10/19)、79.7%(59/74)、88.9%(24/27), 低分化CRC患者外周血Septin 9甲基化阳性率高于高分化组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.006)。外周血Septin 9甲基化的灵敏度为72.3%, 特异度为92.5%。Western blot结果显示CRC患者外泌体中Septin 9表达较健康人群降低,外泌体中Septin 9甲基化水平较正常人群上升,差异均有统计学意义(P=0.009、0.003)。本研究结果显示, CRC患者血清外泌体可促进细胞增殖,对细胞凋亡有抑制作用,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。
结论Septin 9可作为CRC早期筛查的标志物, CRC患者血清外泌体诱导的CRC增殖、凋亡抵抗可能是Septin 9的作用机制。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo detect the methylation status of Septin 9 in the peripheral blood of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and analyze the relationship between the methylation of Septin 9 and CRC.
MethodsA total of 120 patients with CRC were selected as research objects, and the relationship between the methylation status of Septin 9 in the peripheral blood and the medical materials was analyzed; the serum exosomes isolated from patients with CRC and healthy people were used to treat the CRC cells, and the proliferation and apoptosis of CRC cells were detected.
ResultsA total of 1 586 people with health examinations were screened for Septin 9, and 56 of whom were positive for methylation of Septin 9, with a positive rate of 3.5%. Among patients with Septin 9 positive, there were 20 cases (35.7%) with abnormal gastrointestinal status (gastrointestinal inflammation or polyps), while only 5.4% (83/1 530) of patients with Septin 9 negative had abnormal gastrointestinal status, which indicated that the methylation status of Septin 9 in the peripheral blood was closely related to the gastrointestinal status. Among 120 CRC patients, the positive rate of methylation of Septin 9 was 78.4% (73/93); in the comparison of different differentiation degrees, the positive rates of Septin 9 methylation in patients with highly differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated CRC were 52.6% (10/19), 79.7% (59/74) and 88.9% (24/27) respectively, and the positive rate of Septin 9 methylation in peripheral blood of patients with poorly differentiated CRC was significantly higher than that of patients with highly differentiated CRC (P=0.006). The sensitivity and specificity of Septin 9 methylation in the peripheral blood were 72.3% and 92.5% respectively. Western blot results showed that the expression of Septin 9 in the exosomes of CRC patients was significantly lower than that in the normal people, while the methylation level of Septin 9 in the exosomes was significantly higher than that in the healthy people (P=0.009, 0.003). The results of this study showed that serum exosomes of CRC patients could significantly promote cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01).
ConclusionSeptin 9 can be used as a marker for early screening of CRC, and the mechanism of Septin 9 may be the proliferation and apoptosis resistance of CRC induced by serum exosomes in patients with CRC.
-
Keywords:
- colorectal cancer /
- Septin 9 /
- exosomes /
- carcinoembryonic antigen /
- carbohydrate antigen 199 /
- diagnosis
-
甲状腺癌是来源于甲状腺上皮细胞的恶性肿瘤疾病,主要临床表现为无痛性颈部肿块或结节[1]。甲状腺癌的主要治疗措施包括药物、化疗及手术治疗等,其中手术治疗是目前临床最常用的治疗方式。随着科技的发展,腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术以视野清晰、创口小且位置隐蔽等优点被广泛应用[2-3]。但由于腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术较复杂,手术时间通常较长, 50%~70%的患者在手术过程中会出现低体温现象[4-5]。术中低体温会引发凝血障碍、苏醒恢复延迟等多种手术应激反应,导致治疗效果较差,预后状态不良[6-7]。因此,探究甲状腺癌患者术中低体温的影响因素并及时采取预防措施具有重要的临床意义。本研究收集腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者的临床资料,分析患者术中低体温的影响因素并构建列线图预测模型,以期改善腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术的治疗效果,现报告如下。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2020年1月—2023年6月于淮安市中医院行腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术的336例患者作为研究对象,年龄40~80岁,平均(58.55±6.28)岁。纳入标准: ①经影像学及病理学检查确诊甲状腺癌者; ②初次确诊甲状腺癌者; ③临床资料完整者。排除标准: ①伴有免疫系统疾病或炎性疾病者; ②伴有心脑血管疾病者; ③伴有肝、肾等重要脏器功能障碍者; ④伴有甲状腺功能异常者; ⑤伴有其他恶性肿瘤者。根据术中体温,将所有研究对象分为低体温组195例和正常体温组141例。以鼻咽部作为机体核心温度测量部位,通过麻醉监护仪获取患者自麻醉开始至转运出手术室各时点的体温,任一时点体温≤36 ℃时,则判定该患者发生术中低体温。本研究经医院伦理委员会审核批准。
1.2 研究方法
收集患者的年龄、性别、体质量指数(BMI)、基础疾病史、术前体温等一般资料,并于术后收集手术室室温、麻醉类型、术中出血量、液体输入量、输入液体温度、手术时间等资料。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 20.0统计学软件分析数据,计量资料以(x±s)表示, 2组比较行t检验; 计数资料以[n(%)]表示, 2组间比较行χ2检验。分析低体温组和正常体温组患者一般资料和手术资料的差异; 将差异有统计学意义的因素纳入多因素Logistic回归模型,分析腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温的危险因素; 将筛选出的危险因素导入R3.6.3软件与rms程序包,构建腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温的预测模型; 通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线、校准曲线、Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验评估该列线图模型的预测效能。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 低体温组与正常体温组临床资料比较
低体温组患者的性别、BMI、基础病史、术前体温、手术室室温、麻醉类型、输入液体温度与正常体温组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 低体温组患者的年龄、术中出血量、液体输入量、手术时间与正常体温组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 低体温组与正常体温组患者临床资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]指标 分类 n 低体温组(n=195) 正常体温组(n=141) χ2/t P 年龄 ≤60岁 80 35(17.95) 45(31.91) 8.799 0.003 >60岁 256 160(82.05) 96(68.09) 性别 男 194 106(54.36) 88(63.41) 2.174 0.140 女 142 89(45.64) 53(37.59) 体质量指数 ≤22 kg/m2 134 83(42.56) 51(36.17) 1.395 0.238 >22 kg/m2 202 112(57.44) 90(63.83) 基础疾病史 有 224 137(70.26) 87(61.70) 2.695 0.101 无 112 58(29.74) 54(38.30) 术前体温/℃ — 36.52±0.12 36.55±0.17 1.896 0.059 手术室室温/℃ — 23.56±0.35 23.60±0.32 1.071 0.285 麻醉类型 全麻 152 83(42.56) 69(48.94) 1.341 0.247 全麻联合局麻 184 112(57.44) 72(51.06) 术中出血量 ≤60 mL 173 83(42.56) 90(63.83) 14.816 < 0.001 >60 mL 163 112(57.44) 51(36.17) 液体输入量 ≤1 000 mL 157 72(36.92) 85(60.28) 4.080 0.043 >1 000 mL 179 123(63.08) 56(39.72) 输入液体温度/℃ — 36.09±0.13 36.12±0.16 1.893 0.059 手术时间 ≤2.5 h 163 82(42.05) 81(57.45) 7.765 0.005 >2.5 h 173 113(57.95) 60(42.55) 2.2 腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温的多因素Logistic回归分析
将甲状腺癌患者行腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术时,是否发生术中低体温作为因变量(低体温=1, 正常体温=0), 将年龄(≤60岁=0, >60岁=1)、术中出血量(≤60 mL=0, >60 mL=1)、液体输入量(≤1 000 mL=0, >1 000 mL=1)、手术时间(≤2.5 h=0, >2.5 h=1)作为自变量,纳入多因素Logistic回归分析。分析结果显示,年龄>60岁、术中出血量>60 mL、液体输入量>1 000 mL、手术时间>2.5 h为腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温的危险因素(P < 0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术术中低体温的多因素Logistic回归分析变量 β SE Wald P OR 95%CI 年龄 0.604 0.275 4.836 0.028 1.829 1.068~3.133 术中出血量 0.549 0.246 4.983 0.026 1.731 1.069~2.802 液体输入量 0.645 0.243 7.057 0.008 1.906 1.184~3.067 手术时间 0.557 0.244 5.212 0.022 1.745 1.082~2.815 常量 -1.001 0.281 12.669 < 0.001 0.367 — 2.3 列线图预测模型构建
将术中低体温的危险因素(P < 0.05)引入R软件,构建腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温的列线图预测模型。结果显示,年龄>60岁增加93.5分权重,术中出血量>60 mL增加83.2分权重,液体输入量>1 000 mL增加99.6分权重,手术时间>2.5 h增加84.7分权重,见图 1。
2.4 列线图预测模型验证
采用ROC曲线验证该列线图预测模型的区分度,曲线下面积为0.912(95%CI: 0.884~0.941)。采用校准曲线、Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验验证该列线图预测模型的拟合效度,结果显示校准曲线斜率接近1(χ2=9.140, P=0.243), 见图 2。
3. 讨论
手术是目前治疗甲状腺癌的主要方法之一[8],其中以微创为特点的腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术因具有安全性高、术后康复快、疼痛轻等优点被广泛应用于甲状腺癌治疗中[9-10]。但该类手术患者需接受全身麻醉,影响机体的温度调控能力,加之术中大量输入低温液体以及机体长时间暴露于环境等,均会引发术中低体温。机体体温过低会引起心率异常、呼吸抑制、异常躁动等应激反应[11-12], 还会引起淋巴细胞数量减少,导致淋巴细胞功能障碍,损害免疫系统,增高手术部位的感染发生率,不利于术后恢复,严重时甚至威胁生命安全[13-15]。因此,明确甲状腺癌患者行腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术时发生术中低体温的危险因素,提前采取保暖护理措施[16-17], 将有利于改善腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术的治疗效果。
本研究结果显示, 195例甲状腺癌患者行腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术时发生术中低体温,占比58.04%。本研究进一步分析患者的一般资料及手术相关资料发现, 2组甲状腺癌患者的年龄、术中出血量、液体输入量、手术时间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄>60岁、术中出血量>60 mL、液体输入量>1 000 mL、手术时间>2.5 h为术中低体温的危险因素(P < 0.05)。年龄较大的患者体温中枢调节能力减弱,且对药物耐受性差,血液循环慢,容易出现术中低体温[18]。术中出血会导致热量损失,因此出血量较大会引发术中低体温[19]。当患者失血量过多时,常会输注大量常温或冷藏液体及血液制品来增加血容量,维持内环境及全身血液循环稳定,而液体和血液的输入量较大时,不仅会消耗机体热能,较低的液体温度也会使患者体温降低,导致术中低体温[20-21]。较长的手术时间也是影响术中低体温的重要因素之一,腔镜手术中体腔通常处于开放状态,因此随着手术时间的推移,机体热量长时间散失,易发生术中低体温,此外较长的手术时间通常表示手术复杂程度高,在此过程中也将消耗机体能量,引发术中低体温[22-23]。本研究基于Logistic回归模型筛选出腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温的4项危险因素并构建列线图预测模型,列线图预测模型验证结果显示曲线下面积为0.912(95%CI: 0.884~0.941), 校准曲线斜率接近1, Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验χ2=9.140, P=0.243, 提示此模型对腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者是否发生术中低体温具有较好的预测能力,以便医护人员提前做好保暖措施。
综上所述,基于年龄、术中出血量、液体输入量、手术时间因素构建的列线图预测模型,对腔镜下甲状腺癌根治术患者术中低体温具有较好的预测价值。但本研究纳入的样本量较小,样本选取范围较单一,未来应继续收集样本并扩大样本选择范围对此模型加以验证。
-
表 1 1 586例正常人群Septin 9甲基化与胃肠状态的相关性
指标 分类 Septin 9甲基化状态 阳性(n=56) 阴性(n=1 530) 性别 男 43 982 女 13 548 胃肠状态 正常 36 1 447 异常 20 83 表 2 CRC患者Septin 9检测情况[n(%)]
指标 分类 Septin 9阳性(n=93) Septin 9阴性(n=27) 性别 男 67(79.8) 17(20.2) 女 26(72.2) 10(27.8) 年龄 ≤60岁 51(71.8) 20(28.2) >60岁 42(85.7) 7(14.3) 分化程度 高分化 10(52.6)** 9(47.4) 中分化 59(79.7) 15(20.3) 低分化 24(88.9) 3(11.1) 低分化比较, ** P < 0.01。 表 3 CRC患者Septin 9、CEA、CA199的灵敏度和特异度比较
指标 灵敏度(95%CI) 特异度(95%CI) 曲线下面积 Septin 9 72.3(60.5~80.5) 92.5(75.5~95.5) 0.87 CEA 42.2(32.2~55.6) 75.0(65.5~87.5) 0.59 CA199 20.5(12.1~27.1) 45.0(37.7~55.5) 0.24 -
[1] ZENG H M, ZHENG R S, GUO Y M, et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003-2005: a population-based study[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(8): 1921-1930. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29227
[2] KANG Q, JIN P, YANG L, et al. Significance of Septin 9 gene methylation detection of plasma circulation DNA in colorectal cancer screening[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2014, 94(48): 3839-3841. .
[3] SUN G P, MENG J, DUAN H, et al. Diagnostic ssessment of Septin 9 DNA methylation for colorectal cancer using blood detection: a meta-analysis[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2019, 25(4): 1525-1534. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0559-5
[4] LIU T, ZHANG X, DU L T, et al. Exosome transmitted miR-l 28-3p increase chemosensitivity of oxaliplatin-resistant coloretal cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 43. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0981-7
[5] 谭琪, 宗明, 處珊珊, 等. 联合检测外周血游离Septin 9、SDC2、BCATI基因甲基化在结直肠癌诊断中的意义[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2021, 44(3): 204-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201605028.htm [6] YANQING H, CHENG D, LING X. Serum CA72-4 as a bionarker in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Open Med: Wars, 2018, 13: 164-171. doi: 10.1515/med-2018-0026
[7] 宋慧琴, 张君娜. Septin 9基因、缺氧诱导因子1与结直肠癌发生发展的相关性[J]. 广州医科大学学报, 2021, 49(1): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-9664.2021.01.04 [8] YANG J K, YANG J P, TONG J, et al. Exosomal miR-221 targets DNM3 to induce tumor progression and temozolomide re sistance in glioma[J]. J Neurooncol, 2017, 131(2): 255-265. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2308-5
[9] 陈培, 邓钦木, 李丹丹. 血浆Septin 9甲基化检测在结直肠癌中的诊断价值[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2020, 35(4): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2020.04.003 [10] 宫媛, 王卫华, 杜海涛, 等. 外周血Septin 9基因甲基化检测在结直肠癌诊断中的研究进展[J]. 临床输血与检验, 2021, 23(2): 263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2587.2021.02.028 [11] 张春燕, 于正麟, 王蓓丽, 等. 血浆Septin 9基因甲基化检测性能评价及对结直肠癌患者的筛查价值[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2019, 37(2): 152-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCJY201902018.htm [12] YAN S S, HAN B, GAO S Y, et al. Exsome-encapsulated micro RNAs as circulating biomarkers for colorectal cancer[J] Oncotarget, 2017, 8(36): 60149-60158. . doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18557
[13] 陈越亚, 陈卫昌. 外周血SEPT9基因甲基化检测在结直肠癌中的研究进展[J]. 中国血液流变学杂志, 2021, 31(2): 265-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-881X.2021.02.031 [14] 穆剑强, 高海锋. 外周血Septin9基因甲基化和血清CA199联合检测在结直肠癌筛查中的诊断价值[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2022, 19(4): 526-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYL202204023.htm [15] RICHARDS K E, ZELENIAK A E, FISHEL M L, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(13): 1770-1778.
[16] 赵媛, 陈四明, 蒋益兰, 等. Septin-9基因甲基化检测对结直肠癌诊断价值的meta分析[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2020, 22(6): 852-856. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20200222-00172 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 章明阳,刘京辉,金雁,徐文琪,李斌飞,黄珊,杜李百合,侯亚甜,李小寒. 围手术期低体温风险预测模型的系统评价. 护理学报. 2024(22): 54-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丁旭,曹霞,王鹰,陈雷. 优化术中管理对老年骨科手术患者住院期间发生下肢深静脉血栓的预防作用. 血管与腔内血管外科杂志. 2024(12): 1511-1514+1528 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
