Efficacy of ultrasound-guided arc-edge needle-knife therapy in the treatment of arthrogenic pain of lumbar facet joint pain of lumbar facet joint after foraminoscopy
-
摘要:目的
观察超声引导下弧刃针刀松解责任腰椎上下关节突周围组织并注射镇痛液治疗椎板间入路椎间孔镜术后腰椎关节突关节源性疼痛的临床疗效以及安全性。
方法选取72例经椎板间入路椎间孔镜术后出现腰椎关节突关节源性疼痛的患者为研究对象,按照随机数字表法分为弧刃针组(n=36)与封闭针组(n=36)。弧刃针组采用超声引导下弧刃针刀松解责任腰椎上下关节突周围组织并注射镇痛液; 封闭针组参照腰椎AP位X线片的体表投影进行定位,责任腰椎上下关节突周围徒手行局部封闭针治疗。分别记录治疗前、治疗后1 d、1个月及3个月后的视觉模拟评分法(VAS)评分和Oswestry功能障碍指数(ODI)评分,通过日本骨科学会(JOA)评分计算治疗总有效率。
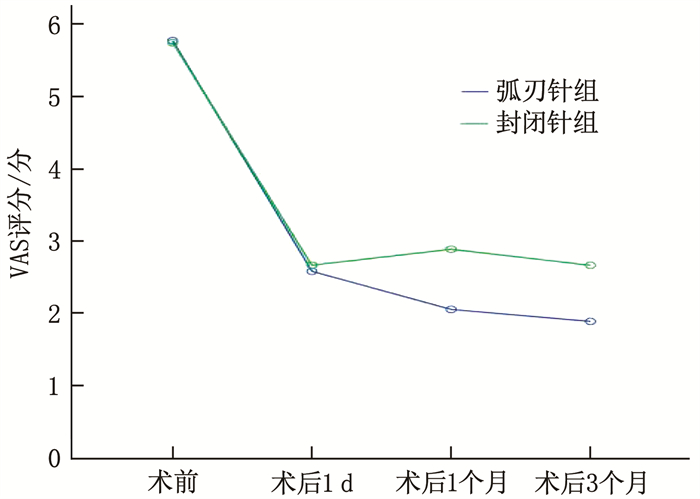
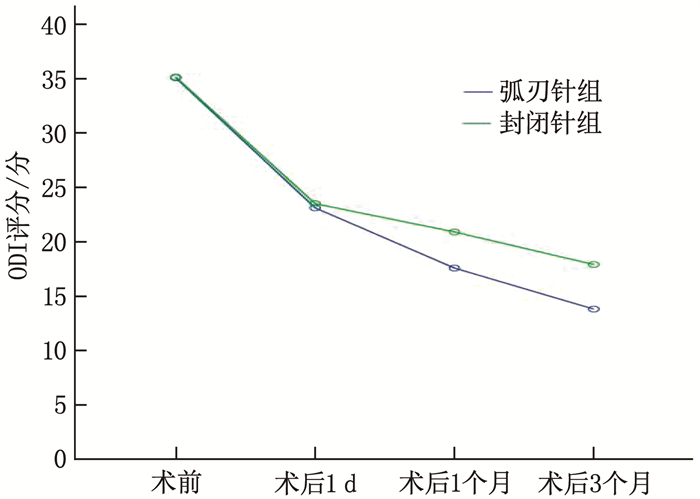
结果弧刃针组穿刺时间短于封闭针组,穿刺调整次数少于封闭针组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。2组治疗后1个月、3个月的VAS评分、ODI评分均优于治疗前及治疗后1 d,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。弧刃针组治疗后1个月和3个月的VAS评分、ODI评分优于封闭针组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。弧刃针组治疗总有效率高于封闭针组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论超声引导下弧刃针刀松解腰椎上下关节突周围组织并注射镇痛液缓解椎板间入路椎间孔镜术后腰椎关节源性疼痛的效果明显,具有持续性减轻疼痛的作用,在改善患者腰部功能有积极意义。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the clinical efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided arc-edge needle-knife therapy for treatment of lumbar arthrogenic pain of lumbar facet joint after foraminoscopy by releasing the tissue around the responsible upper and lower lumbar articular processes and injecting analgesic solution.
MethodsA total of 72 patients who presented with arthrogenic pain of the umbar facet joint after translaminar approach foraminoscopy were selected and divided into arc-edge needle group (n=36) and local anesthesia group (n=36)according to the random number table method. The arc-edge needle group was given ultrasound-guided arc-edge needle-knife therapy to release the tissues around the upper and lower articular processes of the responsible lumbar spine and injected analgesic solution. The local anesthesia group was performed freehand local closed-needle treatment around the upper and lower articular processes of the responsible lumbar spine in the location according to the body surface projection of AP radiographs of the lumbar spine. The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) scores were recorded before treatment, 1 day, 1 month and 3 months after treatment, respectively, and the total effective rate was calculated by the Japanese Orthopaedic Society (JOA) score.
ResultsThe puncture time and puncture adjustment times of the arc-edge needle group were shorter or less than those of the local anesthesia group, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.01). VAS scores and ODI scores of 1 month and 3 months after treatment were better than those before treatment and 1 day after treatment, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The VAS scores and ODI scores of 1 month and 3 months after treatment in the arc-edge needle group were higher than those in the local anesthesia group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The total effective rate of the arc-edge needle group was higher than that of the local anesthesia group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
ConclusionRelease of periarticular tissues around the upper and lower lumbar synapses by ultrasound-guided arc-edge needle-knife therapy and injection of analgesic solution is effective in continuously relieving lumbar arthrogenic pain after foraminoscopy by releasing the tissue around the responsible upper and lower lumbar articular processes, and has positive significance in improving patients' lumbar function.
-
-
表 1 2组一般资料比较(x±s)[n(%)]
组别 性别 年龄/岁 病程/d 责任椎间隙 男 女 L4/5 L5/S1 弧刃针组(n=36) 15(41.67) 21(58.33) 45.44±11.45 34.42±15.05 16(44.44) 20(55.56) 封闭针组(n=36) 17(47.22) 19(52.78) 45.11±10.25 34.31±11.60 19(52.78) 17(47.22) 表 2 2组穿刺效果比较(x±s)
组别 定位穿刺时间/min 穿刺调整次数/次 左 右 左 右 弧刃针组(n=36) 3.42±1.34** 3.33±1.15** 1.28±0.51** 1.36±0.64** 封闭针组(n=36) 8.19±2.21 8.22±2.11 2.19±0.92 2.11±0.78 与封闭针组比较, **P < 0.01。 表 3 2组治疗前后VAS评分、ODI评分比较(x±s)
分 评分 组别 n 治疗前 治疗后1 d 治疗后1个月 治疗后3个月 VAS评分 弧刃针组 36 5.78±0.90 2.58±0.69 2.06±0.67*#△ 1.89±0.67*#△ 封闭针组 36 5.75±0.84 2.67±0.59 2.89±0.71*△ 2.67±0.68*△ ODI评分 弧刃针组 36 35.11±4.23 23.11±2.85 17.56±4.14*#△ 13.78±5.59*#△ 封闭针组 36 35.17±4.31 23.50±2.96 20.89±3.67*△ 17.89±6.21*△ 与治疗前比较, *P < 0.05; 与封闭针组比较, #P < 0.05; 与治疗后1 d比较, △P < 0.05。 表 4 2组治疗总有效率比较[n(%)]
组别 临床控制 显效 有效 无效 总有效 弧刃针组(n=36) 1(2.78) 19(52.78) 13(36.11) 3(8.33) 33(91.67)* 封闭针组(n=36) 0 10(27.78) 18(50.00) 8(22.22) 28(77.78) 与封闭针组比较, *P<0.05。 -
[1] RUETTEN S, KOMP M, MERK H, et al. Use of newly developed instruments and endoscopes: full-endoscopic resection of lumbar disc herniations via the interlaminar and lateral transforaminal approach[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2007, 6(6): 521-530. doi: 10.3171/spi.2007.6.6.2
[2] PAN M M, LI Q F, LI S C, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: indications and complications[J]. Pain Physician, 2020, 23(1): 49-56.
[3] 王冰. 腰椎完全内镜经椎板间入路技术的临床教程[J]. 山东大学学报: 医学版, 2019, 57(5): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYB201905006.htm [4] WON H S, YANG M, KIM Y D. Facet joint injections for management of low back pain: a clinically focused review[J]. Anesth Pain Med, 2020, 15(1): 8-18. doi: 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.8
[5] 时宗庭, 刘恒平, 于栋, 等. 肌骨超声引导下精准针刀治疗腰椎关节突关节源性腰痛35例[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2018, 26(4): 69-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZG201804019.htm [6] 吴承钧. "益髓通督"针刺法联合五籽散中药封包治疗椎间孔镜术后腰痛36例[J]. 浙江中医杂志, 2021, 56(6): 446-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0411-8421.2021.06.034 [7] 钱治, 宋敏, 钱军, 等. 电针及McKenzie疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症椎间孔镜术后残留症状效果比较[J]. 新中医, 2019, 51(1): 189-193. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2019.01.050 [8] SCHIANCHI P M. A new technique to treat facet joint pain with pulsed radiofrequency[J]. Anesth Pain Med, 2015, 5(1): e21061.
[9] 国家中医药管理局. ZY/T001. 1- 94中医病证诊断疗效标准[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2012. [10] 王晓刚, 常洪波, 刘颖, 等. 腰椎及其毗邻结构的超声检查方法与临床意义[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2016, 25(5): 417-421. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2016.05.015 [11] MILLION R, HALL W, HAAVIK NILSEN K, et al. Assessment of the progress of the back-pain patient[J]. Spine, 1982, 7(3): 204-212. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198205000-00004
[12] 郑光新, 赵晓鸥, 刘广林, 等. Oswestry功能障碍指数评定腰痛患者的可信性[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2002, 12(1): 13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-406X.2002.01.004 [13] NAKAMURA M, MIYAMOTO K, SHIMIZU K. Difference in evaluation of patients with low back pain using the Japanese Orthopaedic Association Score for Back Pain and the Japanese Version of the Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire[J]. J Orthop Sci, 2009, 14(4): 367-373. doi: 10.1007/s00776-009-1348-5
[14] TIEBER F, LEWANDROWSKI K U. Technology advancements in spinal endoscopy for staged management of painful spine conditions[J]. J Spine Surg, 2020, 6(S1): S19-S28. doi: 10.21037/jss.2019.10.02
[15] 郑红志, 白雪景, 张桂荣, 等. 百克瑞纱布创面敷料对皮肤浅表脓肿切开引流术后的疗效观察[J]. 河北医药, 2022, 44(13): 2024-2027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2022.13.026 [16] 董蕊, 徐幼苗, 张志利. CT引导下微创介入联合疗法对腰椎间盘突出症患者VAS评分和手术相关并发症的影响[J]. 中国医学装备, 2020, 17(5): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2020.05.019 [17] CHIAROTTO A, KOES B W. Nonspecific Low Back Pain[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 386(18): 1732-1740. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp2032396
[18] 马晟, 曾蕊, 赵学千, 等. 钹针治疗腰椎术后综合征40例临床报道[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2021, 29(12): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZG202112013.htm [19] 徐文嵩, 董宝强. 经筋理论指导下DSA引导针刀"解结法"治疗第三腰椎横突综合征临床观察[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2021, 23(8): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB202108020.htm [20] 都帅刚, 王学昌, 周松林, 等. 弧刃针刀综合疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2019, 39(2): 194-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXJ201902018.htm [21] 戴敏, 李开平, 吴晓亮. 超声可视化针刀技术研究现状和应用优势分析[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2020, 22(6): 170-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB202006044.htm [22] 吴忌, 吴文知, 杨兴勇, 等. 超声引导下针刀松解腰骶韧带联合神经根阻滞治疗L5S1极外侧型椎间盘突出症[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2020, 28(6): 32-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZG202006007.htm [23] 刘涛, 戚洪亮, 王成, 等. 罗哌卡因用于硬膜外麻醉在经皮椎间孔镜手术中的浓度效应[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2018, 39(4): 458-460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYTZ201804020.htm -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 王轶. 注射用盐酸倍他司汀治疗眩晕症的临床效果及对炎性因子的影响. 临床合理用药. 2024(02): 48-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾智本,吴新风. 三联疗法联合倍他司汀治疗耳石症复位后残余头晕的效果观察. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(13): 92-97 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李欣龙,袁琳. 倍他司汀联合阿托伐他汀用于颈动脉斑块伴眩晕患者的疗效观察. 大医生. 2023(05): 41-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 栗冰洁. 半夏白术天麻汤联合氟桂利嗪胶囊治疗周围性眩晕患者的效果. 承德医学院学报. 2023(02): 124-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘钢招,钟丽,沈娟. 倍他司汀联合天麻钩藤饮治疗眩晕症的疗效及对脑血流动力学的影响. 现代诊断与治疗. 2023(05): 644-646 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 金赢政,井睿智,李金江. 天麻钩藤饮联合针灸治疗后循环缺血性眩晕临床研究. 新中医. 2023(22): 53-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘秀. 倍他司汀联合盐酸氟桂利嗪对颈性眩晕患者眩晕症状及血液流变学的影响. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志. 2023(23): 47-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 章恒端,叶旭星,胡建海. 半夏白术天麻汤联合耳穴埋豆治疗颈性眩晕的临床效果. 中国医师杂志. 2022(12): 1832-1836 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 冷静,李红,王孝佳,董阳,韩丽丽. 后循环缺血继发眩晕给予倍他司汀及氟桂利嗪的临床干预效果评析. 中外医疗. 2022(29): 89-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 许电,陈慧珍,邓恺伦. 针刺联合甲磺酸倍他司汀片对颈性眩晕患者疗效及椎基底动脉血流动力学的影响. 医学理论与实践. 2021(18): 3163-3164 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李晓,贺永雄,李世珅. 不同方法治疗颈性眩晕症的临床疗效比较. 内蒙古医学杂志. 2020(12): 1423-1424 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(19)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号