Effect of silencing E26 transformation-specific sequence 4 on proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway
-
摘要:目的
探讨E26转录因子变异体4(ETV4)通过核因子-κB(NF-κB)信号通路对结肠癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响机制。
方法通过用户友好的交互式癌症转录组数据分析资源(UALCAN)数据库分析ETV4在结肠正常组织和癌组织中的表达; 采用逆转录定量聚合酶链式反应(qRT-PCR)和Western blot检测ETV4在正常肠上皮细胞和结肠癌细胞系中的表达; 沉默SW480细胞的ETV4后, 采用qRT-PCR和Western blot检测ETV4的表达以评估转染效率; 采用菌落形成实验和Transwell实验检测沉默ETV4后对结肠癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响; 采用Western blot检测沉默ETV4后对NF-κB通路中的蛋白65(p65)和磷酸化蛋白65(p-p65)的蛋白表达的影响。
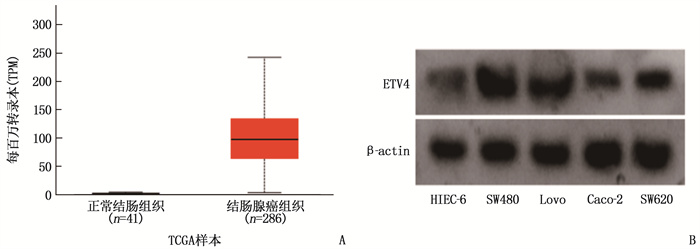
结果UALCAN数据库分析结果显示ETV4在结肠癌组织中高表达。qRT-PCR和Western blot检测显示ETV4在结肠癌细胞系SW480、Lovo、Caco-2和SW620中的表达高于正常肠上皮细胞HIEC-6, 其中SW480细胞中ETV4的表达最高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。菌落形成实验和Transwell实验结果显示,沉默ETV4后显著抑制了结肠癌细胞SW480的增殖和迁移能力(P < 0.001)。Western blot检测结果显示,沉默ETV4显著抑制细胞中p-p65蛋白的表达(P < 0.001)。
结论沉默ETV4可能抑制NF-κB信号通路的激活,进而抑制结肠癌细胞的增殖和迁移。
-
关键词:
- E26转录因子变异体4 /
- 核因子-κB /
- 结肠癌 /
- 细胞增殖 /
- 细胞迁移
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the mechanism of E26 transformation-specific sequence 4 (ETV4) affecting the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells through the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway.
MethodsThe expression level of ETV4 in normal colon tissues and cancer tissues was analyzed by the user-friendly interactive cancer transcriptome data analysis resource (UALCAN) database. Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot were used to detect the expression level of ETV4 in normal intestinal epithelial cells and colon cancer cell lines. After silencing ETV4 in SW480 cells, qRT-PCR and Western blot were performed to detect the expression of ETV4 to assess transfection efficiency; colony formation and Transwell assays were conducted to explore the effects of ETV4 silencing on the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells; the Western blot was used to detect the effects of ETV4 silencing on the protein expression of protein 65 (p65) and phosphorylated protein 65 (p-p65) in the NF-κB pathway.
ResultsThe UALCAN database analysis revealed high expression of ETV4 in colon cancer tissues. The qRT-PCR and Western blot showed that ETV4 expression was significantly higher in the colon cancer cell lines SW480, Lovo, Caco-2, and SW620 than in normal intestinal epithelial cells HIEC-6, with the highest expression in SW480 cells (P < 0.001). Colony formation and Transwell assay results indicated that silencing ETV4 significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration of colon cancer SW480 cells (P < 0.001). Western blot results showed that silencing ETV4 significantly inhibited the expression of p-p65 protein in the cells (P < 0.001).
ConclusionSilencing ETV4 may inhibit the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells.
-
-
表 1 各细胞中 ETV4 mRNA和ETV4蛋白相对表达(x±s)
细胞 ETV4 mRNA相对表达 ETV4蛋白相对表达 HIEC-6 1.00±0.15 0.26±0.03 SW480 3.22±0.36*** 0.95±0.08*** Lovo 2.64±0.19*** 0.59±0.07*** Caco-2 1.67±0.15* 0.42±0.04* SW620 2.44±0.14*** 0.51±0.06** ETV4: E26转录因子变异体4。
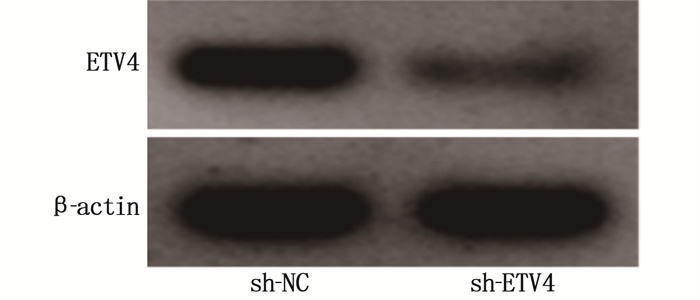
与HIEC-6比较, * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01, * * * P < 0.001表 2 sh-NC组与sh-ETV4组 ETV4 mRNA和ETV4蛋白表达比较(x±s)
组别 ETV4 mRNA相对表达 ETV4蛋白相对表达 sh-NC组 1.00±0.11 0.84±0.07 sh-ETV4组 0.38±0.04*** 0.28±0.04*** 与sh-NC组比较, * * * P < 0.001。 -
[1] SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, FUCHS H E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022 [J]. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2022, 72(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
[2] DE NES L C F, VAN DER HEIJDEN J A G, VERSTEGEN M G, et al. Predictors of undergoing multivisceral resection, margin status and survival in Dutch patients with locally advanced colorectal cancer[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2022, 48(5): 1144-1152. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.11.004
[3] LUO Y, YAO Q. Circ_0085315 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in colon cancer through miR-1200/MAP3K1 signaling pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2022, 21(11): 1194-1211. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2044137
[4] KOLB J M, MOLMENTI C L, PATEL S G, et al. Increased risk of colorectal cancer tied to advanced colorectal polyps: an untapped opportunity to screen first-degree relatives and decrease cancer burden[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(7): 980-988. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000639
[5] BENZ S R, FEDER I S, VOLLMER S, et al. Complete mesocolic excision for right colonic cancer: prospective multicentre study[J]. Br J Surg, 2022, 110(1): 98-105. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znac379
[6] XIE M, LIN Z Y, JI X Y, et al. FGF19/FGFR4-mediated elevation of ETV4 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by upregulating PD-L1 and CCL2[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79(1): 109-125. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.02.036
[7] QI D D, LU M, XU P F, et al. Transcription factor ETV4 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by driving hepatic TNF-α signaling[J]. Cancer Commun, 2023, 43(12): 1354-1372. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12482
[8] GAO X L, JIANG M Z, CHU Y, et al. ETV4 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis through activation of the CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling axis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2022, 524: 42-56. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.09.026
[9] CAI L S, CHEN Q X, FANG S Y, et al. ETV4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through regulating KDM5D[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(5): 2442-2451.
[10] YAO D, BAO Z M, QIAN X, et al. ETV4 transcriptionally activates HES1 and promotes Stat3 phosphorylation to promote malignant behaviors of colon adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2021, 45(10): 2129-2139. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11669
[11] MOSAAD H, AHMED M M, ELAIDY M M, et al. Down-regulated MiRNA 29-b as a diagnostic marker in colorectal cancer and its correlation with ETV4 and Cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2023, 37(3): 179-189. doi: 10.3233/CBM-220349
[12] ZHANG W L, HUANG Z C, XIAO Z G, et al. NF-κB downstream miR-1262 disturbs colon cancer cell malignant behaviors by targeting FGFR1[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2023, 55(11): 1819-1832. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023235
[13] SUN G, ZHENG C, DENG Z, et al. TRAF5 promotes the occurrence and development of colon cancer via the activation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 2020, 34(4): 1257-1268.
[14] BENSON A B, VENOOK A P, AL-HAWARY M M, et al. Colon cancer, version 2.202 1, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2021, 19(3): 329-359. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0012
[15] SIEGEL REBECCA L, MILLER KIMBERLY D, ANN G S, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA a Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(3): 145-164. doi: 10.3322/caac.21601
[16] AL-SARAIREH Y M, ALSHAMMARI F O F O, YOUSSEF A M M, et al. Cytochrome 4Z1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in colon cancer patients[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2021, 14: 5249-5260. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S332037
[17] SIEGEL R, WAGLE N S, CERCEK A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73: 233-254. doi: 10.3322/caac.21772
[18] WANG H, DAI Y Y, WANG F X. ETV4-mediated transcriptional activation of SLC12A5 exacerbates ferroptosis resistance and glucose metabolism reprogramming in breast cancer cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2024, 30(6): 217. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13341
[19] ELUARD B, THIEBLEMONT C, BAUD V. NF-κB in the new era of cancer therapy[J]. Trends Cancer, 2020, 6(8): 677-687. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.04.003
[20] WENG G X, LING T, HOU W, et al. Mitochondrial DUT-M potentiates RLR-mediated antiviral signaling by enhancing VISA and TRAF2 association[J]. Mol Immunol, 2021, 132: 117-125. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.01.023
[21] DIMITRAKOPOULOS F D, KOTTOROU A E, KALOFONOU M, et al. The fire within: NF-κB involvement in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(19): 4025-4036. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3578
[22] REN C E, HAN X, LU C, et al. Ubiquitination of NF-κB p65 by FBXW2 suppresses breast cancer stemness, tumorigenesis, and paclitaxel resistance[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2022, 29(2): 381-392. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00862-4
[23] DU F, QI X, ZHANG A T, et al. MRTF-A-NF-κB/p65 axis-mediated PDL1 transcription and expression contributes to immune evasion of non-small-cell lung cancer via TGF-Β[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2021, 53(9): 1366-1378. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00670-3
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 郑潇潇,李鑫月,于晓兰,史小京. 人工流产术前患者焦虑抑郁现状及影响因素调查. 生殖医学杂志. 2023(12): 1790-1797 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:



 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
