Efficacy of modified transvaginal rectal repair for patients with rectocele
-
摘要:目的
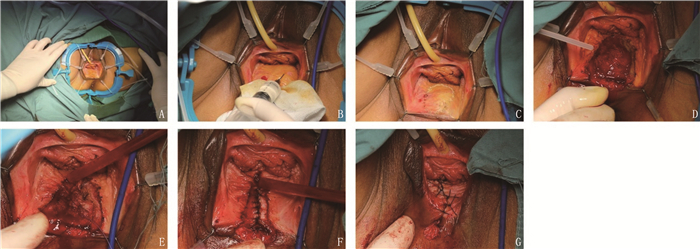
分析改良经阴道后壁切开直肠前突修补术(MTVRR)对中重度直肠前突(RC)患者的疗效。
方法回顾性分析行MTVRR治疗的21例女性RC患者的临床资料。术前及术后3、6、12、24个月, 采用便秘评分系统(CSS)量表评估患者的便秘症状,记录患者症状改善有效率。观察RC患者术后并发症发生情况。
结果21例患者顺利完成手术,手术时间为25~135 min, 平均为(83.14±30.39) min; 住院时间为10~21 d, 平均为(14.10±2.34) d。术后, 21例患者中, 1例患者失访。20例患者术后CSS量表评分低于术前,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。20例患者术后3、6、12个月的便秘症状改善总有效率分别为100.00%、90.00%、80.00%。20例患者中, 15例患者完成术后24个月的随访,其术后CSS量表评分低于术前,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。15例患者术后24个月便秘症状改善总有效率为80.00%。术后随访显示,无1例患者出现并发症。
结论MTVRR可改善中重度RC患者的便秘症状,且疗效较好。
-
关键词:
- 便秘 /
- 直肠前突 /
- 改良经阴道后壁切开直肠前突修补术 /
- 便秘 /
- 便秘评分系统
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the efficacy of modified transvaginal rectal repair (MTVRR) in patients with moderate to severe rectocele (RC).
MethodsA retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 21 female patients with RC who underwent MTVRR. The Constipation Scoring System (CSS) scale was used to assess patients' constipation symptoms before surgery and at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after surgery, and the efficiency of symptom improvement was recorded. The occurrence of postoperative complications in RC patients was observed.
ResultsAll 21 patients successfully underwent the surgery, with surgical duration ranging from 25 to 135 minutes, with average of (83.14±30.39) minutes, and hospital stay ranging from 10 to 21 days, with average of (14.10±2.34) days. Postoperatively, one patient was lost during follow-up among 21 patients. The CSS scores of the remaining 20 patients were lower than those before surgery, with a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The overall effective rates of constipation symptom improvement at 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively were 100.00%, 90.00% and 80.00%, respectively. Among 20 patients, 15 patients completed 24-month follow-up after surgery, and the CSS score after surgery was lower than that before surgery, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The CSS scores of the remaining 15 patients were lower than those before surgery, with a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The overall effective rate of constipation symptom improvement at 24 months postoperatively was 80.00% among 15 patients. During postoperative follow-up, it revealed that no complications occurred in any patient.
ConclusionMTVRR can improve constipation symptoms in patients with RC, demonstrating good therapeutic efficacy.
-
-
表 1 患者术前一般资料(n=21)[n(%)]
资料 分类 数据 产次 0次 1(4.76) 1次 11(52.38) 2次 8(38.10) 4次 1(19.05) 既往盆底手术史 子宫切除术 3(14.29) 痔切除术 3(14.29) 卵巢囊肿切除术 1(4.76) 肛周脓肿切除术 1(4.76) 经阴道后壁膨出修补术 1(4.76) 绝经 12(57.14) 表 1 患者术前一般资料(n=21)[n(%)]
资料 分类 数据 产次 0次 1(4.76) 1次 11(52.38) 2次 8(38.10) 4次 1(19.05) 既往盆底手术史 子宫切除术 3(14.29) 痔切除术 3(14.29) 卵巢囊肿切除术 1(4.76) 肛周脓肿切除术 1(4.76) 经阴道后壁膨出修补术 1(4.76) 绝经 12(57.14) 表 2 患者术前与术后CSS量表评分比较(x±s)
分 n 术前CSS量表评分 术后CSS量表评分 20 17.85±1.66 5.60±1.90*a 20 17.85±1.66 8.90±3.52*b 20 17.85±1.66 9.50±4.07*c 15 18.27±1.34 9.40±3.91*d a: 术后3个月; b: 术后6个月; c: 术后12个月; d: 术后24个月。与术前比较, *P < 0.05。 表 2 患者术前与术后CSS量表评分比较(x±s)
分 n 术前CSS量表评分 术后CSS量表评分 20 17.85±1.66 5.60±1.90*a 20 17.85±1.66 8.90±3.52*b 20 17.85±1.66 9.50±4.07*c 15 18.27±1.34 9.40±3.91*d a: 术后3个月; b: 术后6个月; c: 术后12个月; d: 术后24个月。与术前比较, *P < 0.05。 表 3 患者术后便秘症状改善情况[n(%)]
时点 n 痊愈 显效 有效 无效 总有效 术后3个月 20 0 11(55.0) 9(45.0) 0 20(100.0) 术后6个月 20 0 4(20.0) 14(70.0) 2(10.0) 18(90.0) 术后12个月 20 0 3(15.0) 13(65.0) 4(20.0) 16(80.0) 术后24个月 15 0 3(20.0) 9(60.0) 3(20.0) 12(80.0) 表 3 患者术后便秘症状改善情况[n(%)]
时点 n 痊愈 显效 有效 无效 总有效 术后3个月 20 0 11(55.0) 9(45.0) 0 20(100.0) 术后6个月 20 0 4(20.0) 14(70.0) 2(10.0) 18(90.0) 术后12个月 20 0 3(15.0) 13(65.0) 4(20.0) 16(80.0) 术后24个月 15 0 3(20.0) 9(60.0) 3(20.0) 12(80.0) -
[1] 中国医师协会肛肠医师分会, 中国医师协会肛肠医师分会临床指南工作委员会, 中国中西医结合学会大肠肛门病专业委员会, 等. 出口梗阻型便秘诊治中国专家共识(2022版)[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2022, 25(12): 1045-1057. [2] 汪建平主编李春雨. 肛肠外科手术学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015: 1-15. [3] MUSTAIN W C. Functional disorders: rectocele[J]. Clin Colon Rectal Surg, 2017, 30(1): 63-75.
[4] DIETZ H P, GÓMEZ M, ATAN I K, et al. Association between vaginal parity and rectocele[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2018, 29(10): 1479-1483. doi: 10.1007/s00192-017-3552-8
[5] GUZMÁN ROJAS R, QUINTERO C, SHEK K L, et al. Does childbirth play a role in the etiology of rectocele[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2015, 26(5): 737-741. doi: 10.1007/s00192-014-2560-1
[6] TAN C, TAN M, GENG J, et al. Rectal-vaginal pressure gradient in patients with pelvic organ prolapse and symptomatic rectocele[J]. BMC Womens Health, 2021, 21(1): 165. doi: 10.1186/s12905-021-01304-6
[7] TAN C, GENG J, TANG J, et al. The relationship between obstructed defecation and true rectocele in patients with pelvic organ prolapse[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 5599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62376-2
[8] 卢任华. 排粪造影在直肠肛管疾病诊断中的应用[J]. 大肠肛门病外科杂志, 1995(1): 18-22. [9] 中国医师协会肛肠医师分会. 便秘外科诊治指南(2017)[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2017, 20(3): 241-243. [10] 郑筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则: 试行[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002: 15-19. [11] DIETZ H P, ZHANG X, SHEK K L, et al. How large does a rectocele have to be to cause symptoms A 3D/4D ultrasound study[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2015, 26(9): 1355-1359. doi: 10.1007/s00192-015-2709-6
[12] WALLACE S L, TOROSIS M, ROGO-GUPTA L. Does rectocele on defecography equate to rectocele on physical examination in patients with defecatory symptoms[J]. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg, 2021, 27(1): 18-22. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0000000000000719
[13] HALLIGAN S, BARTRAM C I. Is Barium trapping in rectoceles significant[J]. Dis Colon Rectum, 1995, 38(7): 764-768. doi: 10.1007/BF02048038
[14] AUBERT M, MEGE D, LE HUU NHO R, et al. Surgical management of the rectocele-An update[J]. J Visc Surg, 2021, 158(2): 145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2020.10.001
[15] FERRARI L, CUINAS K, HAINSWORTH A, et al. Transvaginal rectocoele repair for the surgical treatment of a "symptomatic" rectocoele when conservative measures fail: a 12 year experience of 215 patients[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2022, 34(11): e14343. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14343
[16] GROSSI U, CARRINGTON E V, BHARUCHA A E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy study of anorectal manometry for diagnosis of dyssynergic defecation[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(3): 447-455. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308835
[17] 李婧婧, 陈茜, 周惠芬, 等. 基于经会阴超声及肛管直肠测压分析女性排便梗阻综合征患者盆底形态与功能特征[J]. 中华消化病与影像杂志: 电子版, 2024, 14(3): 229-234. [18] SUN G, DE HAAS R J, TRZPIS M, et al. A possible physiological mechanism of rectocele formation in women[J]. Abdom Radiol, 2023, 48(4): 1203-1214. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-03807-2




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
