First-trimester versus second- and third-trimester pregnancy in prenatal ultrasonographic features of placenta accreta
-
摘要:目的 比较孕早期和孕中晚期胎盘植入的产前超声特点及预后影响因素。方法 回顾性分析120例胎盘植入患者的临床资料, 其中孕早期18例,孕中晚期102例。所有孕妇均行产前超声检查,比较产前超声对不同孕期胎盘植入的诊断效能,分析超声特点。随访产妇预后并分析胎盘植入产妇预后的相关影响因素。结果 与孕中晚期胎盘植入相比,孕早期胎盘植入的超声检出率更低。孕早期胎盘植入的超声特征以妊娠囊位置低为主,其次为前壁肌层变薄,然后是胎盘内低回声区或透声区(类陷窝)、蜕膜-子宫/胎盘-子宫界面不规则。孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声特征以胎盘内漩涡形成为主,其次为胎盘与子宫肌层、宫颈组织界限不清且周围的血流信号丰富,胎盘后间隙消失,胎盘异常增厚。多因素分析显示,剖宫产史、产后出血、前置胎盘均是胎盘植入孕妇预后不良的危险因素,而前壁胎盘、诊断者有经验则是保护性因素。结论 孕早期和孕中晚期胎盘植入的产前超声特征有较大差异,剖宫产史、胎盘附着位置、产后出血、前置胎盘及诊断者经验是影响胎盘植入孕妇预后的主要因素。Abstract:Objective To compare the prenatal ultrasonographic features and prognostic factors of placenta accreta between first-trimester pregnancy and second-, third-trimester pregnancy.Methods The clinical materials of 120 patients with placenta accreta were analyzed retrospectively, including 18 cases in first-trimester pregnancy and 102 cases in second-, third-trimester pregnancy. All the pregnant women were conducted with prenatal ultrasound examination, the efficacy of prenatal ultrasound in diagnosing placenta accreta during different periods of pregnancy was compared, and the ultrasonic characteristics were analyzed. The prognosis of pregnant women was followed up and the related factors of prognosis in pregnant women with placenta accreta were analyzed.Results Compared with pregnant women with placenta accreta in second- and third-trimester pregnancy, the ultrasonic detection rate of placental accreta in the first-trimester pregnancy was lower. The ultrasonic features of placental accreta in the first-trimester pregnancy were mainly the low position of gestational sac, followed by the thinning of anterior wall muscle layer, the low echo area or sound transmission area (lacunae like) in the placenta, and the irregular decidua uterus or placenta uterus interface. The ultrasonic features of placental accreta in the second- and third-trimester pregnancy were mainly the formation of intraplacental vortex, followed by unclear boundary between placenta and uterine myometrium and cervical tissue, rich peripheral blood flow signals, disappearance of retroplacental space and abnormal thickening of placenta. Multivariate analysis showed that the history of cesarean section, postpartum hemorrhage and placenta previa were the risk factors for poor prognosis of pregnant women with placenta accreta, while the anterior wall placenta and the experience of the diagnostician were the protective factors.Conclusion There are great differences in prenatal ultrasonic characteristics of placental accreta between the first-trimester pregnancy and second-, third-trimester pregnancy. The history of cesarean section, placental attachment, postpartum hemorrhage, placenta previa and the experience of the diagnostician are the main factors affecting the prognosis of pregnant women with placental accreta.
-
胎盘植入是由蜕膜基底层发育不良导致胎盘绒毛植入子宫肌层的一种胎盘异常附着情况,临床处理不及时会引发大出血、子宫穿孔、弥散性血管内凝血,威胁孕产妇的生命健康[1]。随着剖宫产手术的普及和生育政策的改变,胎盘植入的临床发病率上升[2]。因此,产前尽早明确诊断,及时采取相关干预措施,对于降低孕产妇的子宫切除、大出血发生率及死亡风险具有积极作用。超声技术是产前诊断胎盘植入的主要手段,具有操作简单、可重复性好、准确性高等优点。研究[3]显示,超声对胎盘植入的诊断准确率差异较大。本研究探讨不同孕期胎盘植入的超声特点,明确影响胎盘植入孕妇预后的相关因素,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
回顾性分析海南省人民医院2010年1月—2021年8月收治的终止妊娠后经病理组织学检查确诊的胎盘植入患者120例的临床资料。病理组织学检查明确为胎盘植入(胎盘小叶侵入肌层,尚未穿透子宫浆膜层)。排除胎盘粘连及穿透性胎盘植入者,合并妊娠期其他并发症者,有器官功能障碍或严重精神疾病者。所有孕产妇均自愿参与研究,并签署了知情同意书。孕妇年龄25~43岁,平均(30.71±3.14)岁,高龄产妇(年龄≥35岁)54例;有人工流产史39例,剖宫产史20例,子宫切开手术史34例,宫腔镜手术史13例;终止妊娠孕周8~38周,平均(25.85±4.96)周;孕早期(孕周 < 14周)18例,孕中晚期(孕周≥14周)102例。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 超声检查方法
所有孕妇均行产前超声检查,仪器选用PHILIPS IU22型或GE VOLUSON E8型彩超诊断仪,探头频率2~5 MHz。检查前孕妇保持膀胱适度充盈,取平卧位,充分暴露腹部,在腹壁放置探头,移动探头对胎儿及附属物进行扫查,明确胎盘大小、厚度、位置、内部回声,胎盘后方与子宫肌壁间回声。扫查子宫前壁胎盘,观察膀胱后壁光滑程度,明确膀胱后壁与子宫前壁的关系。通过彩色多普勒血流显像观察胎盘实质内和胎盘后方血流情况,并测量子宫肌层厚度。对于疑为胎盘植入者,记录胎盘种植区面积、周围血流情况等。以病理组织学结果为金标准,计算超声对孕早期及孕中晚期胎盘植入的诊断准确率,并比较超声图像特点。
1.2.2 诊断标准[4]
通过病理学和临床相结合的方法进行诊断,徒手剥离胎盘困难,胎盘剥离后子宫收缩良好但出血得不到有效控制,子宫平滑肌病理切片显示有绒毛组织,子宫浆膜层病理切片显示无绒毛组织。
1.2.3 干预处理
所有孕妇在超声检查完毕后,由资深妇科医师会诊,根据胎盘植入面积、深度、出血情况等决定行保守治疗或子宫切除术,保守治疗措施包括应用甲氨蝶呤、B超定位下宫腔钳夹、结扎双侧子宫动脉、肠线“8”字结扎缝合出血点、植入病灶切除等。
1.2.4 预后随访
所有孕产妇均在本院产科分娩、终止妊娠或治疗胎盘植入,对孕妇预后进行随访,从产后出血、前壁胎盘、前置胎盘、诊断者经验几方面分析孕妇预后的影响因素。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 23.0软件对数据进行处理,计数资料以[n(%)]表示,数据比较采用χ2检验,符合正态分布的计量资料以(x±s)表示,数据比较采用t检验,对胎盘植入患者预后影响因素进行Logistic回归分析,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 孕早期与孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声诊断情况比较
与孕中晚期胎盘植入相比,孕早期胎盘植入的超声检出率更低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 孕早期与孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声诊断情况比较[n(%)]孕期 检出 未检出 孕早期(n=18) 12(66.67) 6(33.33) 孕中晚期(n=102) 98(96.08)* 4(3.92)* 与孕早期比较, *P < 0.05。 2.2 孕早期与孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声特征比较
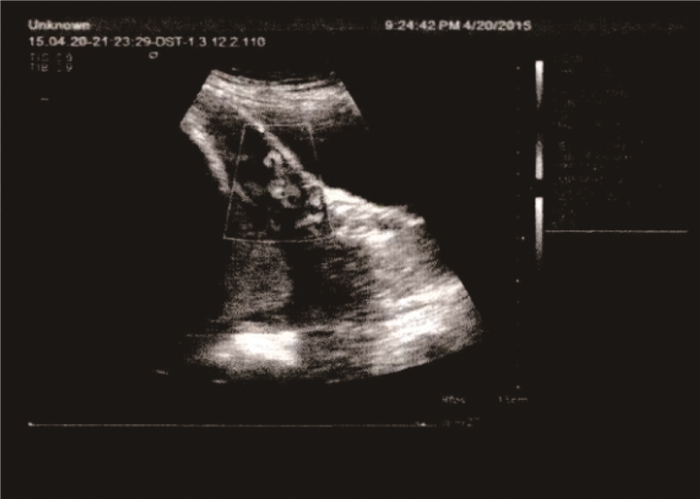
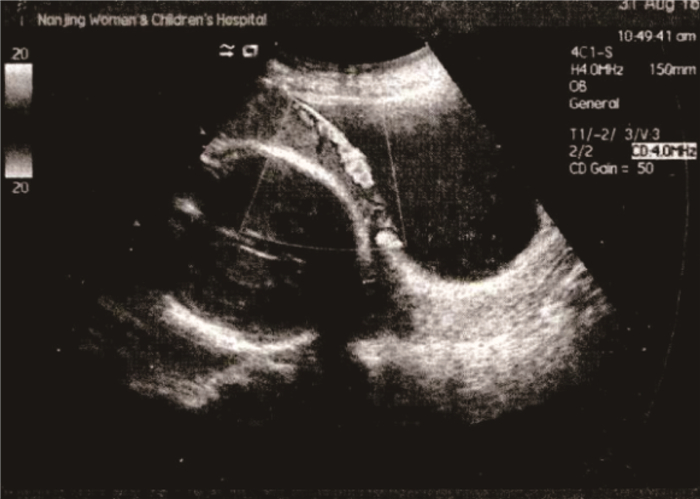
孕早期胎盘植入的超声特征以妊娠囊位置低为主(55.56%), 妊娠囊位置低是指孕囊位于子宫下1/3处(孕8~10周)或子宫内下1/2处(孕周>10周); 其次为前壁肌层变薄(22.22%), 见图 1; 胎盘内低回声区或透声区(类陷窝)、蜕膜-子宫/胎盘-子宫界面不规则检出率均为16.67%。孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声特征以胎盘内漩涡形成为主(59.80%); 其次为胎盘与子宫肌层、宫颈组织界限不清,且周围的血流信号丰富(39.22%), 见图 2; 胎盘后间隙消失占35.29%; 有15.69%可见胎盘异常增厚。见表 2。
表 2 孕早期与孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声特征比较[n(%)]孕期 超声图像特征 检出结果 孕早期 妊娠囊位置低 10(55.56) (n=18) 前壁肌层变薄 4(22.22) 胎盘内低回声区或透声区(类陷窝) 3(16.67) 蜕膜-子宫/胎盘-子宫界面不规则 3(16.67) 孕中晚期 胎盘内漩涡形成 61(59.80) (n=102) 胎盘与子宫肌层、宫颈组织界限不清,且周围的血流信号丰富 40(39.22) 胎盘后间隙消失 36(35.29) 胎盘异常增厚 16(15.69) 2.3 预后情况
产前超声诊断为胎盘植入的110例孕妇中,最终行子宫切除术6例,行保守手术治疗54例,行药物保守治疗50例,预后良好,均未发生严重并发症。10例产前未诊断为胎盘植入的孕妇, 3例经阴道成功分娩, 5例在剖宫产时发现胎盘植入,娩出胎儿后切开子宫将胎盘取出, 2例在阴道分娩时发生大出血而转行剖腹探查发现胎盘植入,后切开子宫将胎盘取出。
2.4 胎盘植入预后的影响因素分析
行子宫切除术、产后大出血均判定为预后不良。预后不良组13例与预后良好组107例在产后出血、剖宫产史、前置胎盘、前壁胎盘、诊断者经验方面比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 见表 3。
表 3 影响胎盘植入孕妇预后的单因素分析[n(%)]因素 n 预后不良组(n=13) 预后良好组(n=107) 产后出血 有 28 10(76.92) 18(16.82)* 无 92 3(23.08) 89(83.18)* 分娩史 有 46 6(46.15) 40(37.38) 无 74 7(53.85) 67(62.62) 剖宫产史 有 31 8(61.54) 23(21.50)* 无 89 5(38.46) 84(78.50)* 前置胎盘 是 50 9(69.23) 41(38.32)* 否 70 4(30.77) 66(61.68)* 前壁胎盘 是 44 3(23.08) 41(38.32)* 否 76 10(76.92) 66(61.78)* 诊断者经验 有 41 1(7.69) 40(37.38)* 无 79 12(92.31) 67(62.62)* 与预后不良组比较, *P < 0.05。 2.5 胎盘植入预后不良的多因素分析
多因素分析显示,产后出血、剖宫产史、前置胎盘均是胎盘植入孕妇预后不良的危险因素(P < 0.05), 前壁胎盘、诊断者有经验是胎盘植入孕妇预后不良的保护性因素(P < 0.05)。见表 4。
表 4 胎盘植入预后不良的多因分析结果变量 β S. E. Wald P OR 95%CI 产后出血 3.514 0.558 11.286 < 0.001 33.582 30.024~38.925 剖宫产史 2.711 0.412 15.605 < 0.001 10.908 8.547~15.998 前置胎盘 2.658 0.305 28.573 < 0.001 14.278 11.589~19.501 前壁胎盘 -1.905 0.214 41.598 < 0.001 6.719 4.362~9.224 诊断者经验 -2.032 0.427 11.145 < 0.001 7.629 5.017~10.804 3. 讨论
超声技术是临床进行产前检查的基础手段,妊娠中晚期胎盘植入的超声影像学特征主要表现为胎盘异常增厚,胎盘内漩涡状血流,周围血流信号丰富及胎盘后间隙完全或部分消失[8-9]。本研究中59.80%的孕中晚期胎盘植入孕妇均可见胎盘内漩涡形成,其形成原因可能为胎盘植入发生后后,高脉压弓形动脉及宫旁血管显著扩张,其形成的腔隙状结构即可在超声图像上表现为漩涡状血流。本研究中39.22%的孕妇可见胎盘与子宫肌层、宫颈组织的界限模糊,周围血流信号丰富,孕晚期胎盘植入孕妇中有35.29%可见胎盘后间隙消失, 15.69%的孕中晚期胎盘植入孕妇可见胎盘异常增厚。超声检查对孕中晚期胎盘植入的检出率为96.08%, 这与相关报道[10]结论相符,可见超声检查对孕中晚期胎盘植入有较高的诊断准确性。
孕早期进行超声观察有助于筛选出胎盘植入高危患者,降低围产期急重症发生风险。孕早期诊断胎盘植入有较大难度,其检出率、准确性均远不及孕中晚期,本研究显示孕早期胎盘植入的超声检出率仅为66.67%,远低于孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声检出率。胎盘植入的孕早期超声征象主要有妊娠囊位置低、胎盘内低回声区或透声区(类陷窝)、前壁肌层变薄、蜕膜-子宫/胎盘-子宫界面模糊。研究[11]指出,孕早期孕囊位置低或胎盘位于前壁瘢痕处的孕妇,仅有部分最终被证实为胎盘植入。另有研究[12]指出,孕早期孕囊在子宫下段着床预示着前置胎盘或胎盘低置,而并不能作为胎盘植入的最终判定标准。胎盘陷窝征在孕中晚期对胎盘植入有较高的敏感性、特异性,孕早期胎盘类陷窝征对胎盘植入的敏感性、特异性尚未证实,但不少研究都指出孕早期类陷窝征往往预示不良结局。胎盘-子宫界面不规则是诊断胎盘植入的超声征象之一,本研究中16.67%可见胎盘-子宫界面不规则,其是提示胎盘异常附着的重要征象。孕中晚期子宫下段前壁肌层变薄往往提示胎盘植入,但由于妊娠晚期子宫充分伸展,肌层变薄,所以仍有一定的假阳性率。在孕早期测量前壁肌层厚度则较为客观,研究[13]指出胎盘植入和瘢痕妊娠病例孕早期的前壁肌层均比正常孕妇更薄。由此提示孕早期前壁肌层变薄可能是诊断胎盘植入的一个重要超声特征,本组病例中有22.22%可见前壁肌层变薄。虽然孕早期的胎盘植入检出率不高,但仍可以筛查出胎盘植入高危病例,指导临床加强监测。
对于胎盘植入较深者,徒手剥离胎盘难度较大,剥离胎盘后血窦持续开放,容易引发产后出血而增加子宫切除风险。临床常通过产后出血量来间接评估胎盘植入深度,所以产后出血是胎盘植入孕妇预后不良的危险因素[14]。本研究还发现剖宫产史、前置胎盘均是胎盘植入孕妇预后不良的危险因素,前壁胎盘、诊断者有经验是胎盘植入孕妇预后不良的保护性因素。胎盘发育不良是前置胎盘与胎盘植入的本质,胎盘植入叠加前置胎盘,尤其是凶险型前置胎盘会使胎盘剥离难度大大增加,从而增加产后大出血及子宫切除风险。胎盘位于子宫前壁时,超声声束近场对胎盘内回声及子宫肌层关系显示清晰,胎盘植入诊断率较高,而胎盘位于其他位置时,超声声束远场显示清晰度不足,再加之胎儿肢体的遮挡,诊断难度较大,所以更易漏诊。有剖宫产史者,子宫切口瘢痕形成、子宫内膜损伤使得绒毛更易侵入子宫肌层,特别是覆盖子宫瘢痕部位的胎盘,更易被绒毛侵入而发生胎盘植入。相比产前检出胎盘植入者,漏诊者可能因准备不足、分娩时机及分娩方式不当等增加不良预后风险[15]。此外诊断者经验也被证实为是影响胎盘植入患者预后的因素之一,有经验的诊断者能够对胎盘植入进行准确判断,并事先采取合理的处理措施,制订周全的分娩干预方案,从而有效地降低胎盘植入患者的不良预后风险。
综上所述,孕早期和孕中晚期胎盘植入的产前超声特征有较大差异,其对孕中晚期胎盘植入的诊断准确性更高。剖宫产史、胎盘附着位置、产后出血、前置胎盘及诊断者经验是影响胎盘植入孕妇预后的主要因素。临床医师尽可能掌握胎盘植入不同孕期的超声征象,提高胎盘植入的诊断准确性,同时结合胎盘植入预后影响因素制订合理的处理措施,可降低不良预后风险,改善产妇结局。
-
表 1 孕早期与孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声诊断情况比较[n(%)]
孕期 检出 未检出 孕早期(n=18) 12(66.67) 6(33.33) 孕中晚期(n=102) 98(96.08)* 4(3.92)* 与孕早期比较, *P < 0.05。 表 2 孕早期与孕中晚期胎盘植入的超声特征比较[n(%)]
孕期 超声图像特征 检出结果 孕早期 妊娠囊位置低 10(55.56) (n=18) 前壁肌层变薄 4(22.22) 胎盘内低回声区或透声区(类陷窝) 3(16.67) 蜕膜-子宫/胎盘-子宫界面不规则 3(16.67) 孕中晚期 胎盘内漩涡形成 61(59.80) (n=102) 胎盘与子宫肌层、宫颈组织界限不清,且周围的血流信号丰富 40(39.22) 胎盘后间隙消失 36(35.29) 胎盘异常增厚 16(15.69) 表 3 影响胎盘植入孕妇预后的单因素分析[n(%)]
因素 n 预后不良组(n=13) 预后良好组(n=107) 产后出血 有 28 10(76.92) 18(16.82)* 无 92 3(23.08) 89(83.18)* 分娩史 有 46 6(46.15) 40(37.38) 无 74 7(53.85) 67(62.62) 剖宫产史 有 31 8(61.54) 23(21.50)* 无 89 5(38.46) 84(78.50)* 前置胎盘 是 50 9(69.23) 41(38.32)* 否 70 4(30.77) 66(61.68)* 前壁胎盘 是 44 3(23.08) 41(38.32)* 否 76 10(76.92) 66(61.78)* 诊断者经验 有 41 1(7.69) 40(37.38)* 无 79 12(92.31) 67(62.62)* 与预后不良组比较, *P < 0.05。 表 4 胎盘植入预后不良的多因分析结果
变量 β S. E. Wald P OR 95%CI 产后出血 3.514 0.558 11.286 < 0.001 33.582 30.024~38.925 剖宫产史 2.711 0.412 15.605 < 0.001 10.908 8.547~15.998 前置胎盘 2.658 0.305 28.573 < 0.001 14.278 11.589~19.501 前壁胎盘 -1.905 0.214 41.598 < 0.001 6.719 4.362~9.224 诊断者经验 -2.032 0.427 11.145 < 0.001 7.629 5.017~10.804 -
[1] 王芊芸, 黄贝尔, 杨慧霞. 胎盘植入发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中华围产医学杂志, 2019, 22(1): 66-69. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-9408.2019.01.014 [2] 杨慧霞, 马京梅. 重视胎盘植入的及早诊断及规范化转诊[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2019, 54(6): 361-362. [3] 赵扬玉, 种轶文. 超声检查对胎盘植入类型与凶险程度的预测作用[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2018, 53(8): 573-576. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2018.08.013 [4] 陈敦金, 杨慧霞. 胎盘植入诊治指南(2015)[J]. 中华产科急救电子杂志, 2016, 5(1): 26-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHCJ201601007.htm [5] 杨雁芬, 唐敏敏, 施如勇. 胎盘植入高风险孕妇妊娠早期超声影像特点分析[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2019, 18(6): 572-575. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2019.06.013 [6] 潘燕芳, 韦华英. 前置胎盘、胎盘粘连及胎盘植入的临床病理研究[J]. 当代医学, 2018, 24(24): 123-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2018.24.049 [7] 曹伟英, 谷宝峰. 产前联合应用二维及彩色多普勒超声对胎盘植入的诊断价值[J]. 医疗装备, 2019, 32(2): 13-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2376.2019.02.009 [8] 张君玲, 栗河舟, 李洁, 等. 胎盘植入超声征象: "胎盘陷窝"的再探讨[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2019, 30(10): 730-733. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201910013.htm [9] 马飞, 高小瞻, 王熙, 等. 超声多普勒子宫动脉血流监测诊断前置胎盘植入的研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(20): 3595-3597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2019.20.042 [10] 杨慧霞, 马京梅. 重视胎盘植入的及早诊断及规范化转诊[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2019, 54(6): 361-362. [11] YEOU-LIH W, SHIH-SHIEN W, WEN-CHU H. First-trimester abortion complicated with placenta accreta: A systematic review[J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol, 2019, 58(1): 10-14. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2018.11.032
[12] 黄泽嫦, 黄苑铭, 黄冬平, 等. 超声在妊娠早期筛查剖宫产后胎盘植入中的应用[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2020, 28(4): 309-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2020.04.018 [13] 冯佩明, 王晓岩, 李博, 等. 超声诊断剖宫产瘢痕妊娠与胎盘植入的关系研究[J]. 中国计划生育和妇产科, 2019, 11(9): 64-67, 97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4020.2019.09.18 [14] 何雪仪, 陈敏霞, 刘国成. 胎盘植入的临床高危因素研究[J]. 广东医学, 2018, 39(z1): 154-155, 158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2018.z1.050 [15] 苏晓力. 彩色多普勒超声在产前胎盘植入中的诊断效果及对预后的影响观察[J]. 实用妇科内分泌电子杂志, 2019, 6(7): 88-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKDZ201907060.htm -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 杨虹,季红珍,黄萍,陈善美. 腹部联合阴道超声用于生育“二孩”或“三孩”瘢痕子宫孕妇孕早期胎盘植入诊断的价值. 生殖医学杂志. 2024(06): 813-816 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谢贤海,郑宗杰. 经阴道彩色多普勒超声心动图诊断宫颈部胎盘植入的效果. 医疗装备. 2023(05): 66-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 时明芳,常书娟,张聪祎. 超声评分法联合血浆人胎盘催乳素水平检测对前置胎盘合并胎盘植入的诊断价值. 中国医药导报. 2023(09): 97-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高莉,张玉琴,薛祖兵,王小漫,徐庆. 产前不同超声特征对瘢痕子宫胎盘植入的评价分析. 生殖医学杂志. 2023(05): 759-762 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙雪,高霞,刘博,周春花,李云鹏. 孕妇胎盘内部血流参数与妊高症关系研究. 西部医学. 2023(05): 765-769 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张敬丽,谷小乐,元丽芝. 二维超声及彩色多普勒超声诊断孕晚期胎盘植入的价值. 临床医学. 2022(10): 81-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
