Study on the mechanism of herbal pair of Banxia-Huanglian in treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease based on molecular docking and network pharmacology
-
摘要:目的 应用网络药理学分析方法及分子对接技术研究半夏-黄连药对治疗胃食管反流病(GERD)的作用机制。方法 应用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)和Genecard数据库分别筛选出半夏、黄连的有效成分和GERD的相关靶点;采用Cytoscape软件绘制药物-疾病靶点的调控网络图;采用STRING数据库构建蛋白互作(PPI)网络;采用AutoDock软件进行分子对接预测药物与疾病靶点的结合性,通过Pymol软件实现对接结果可视化,构建相互对接模式图;运用R软件对有效靶点进行GO基因功能分析及KEGG通路分析。结果 半夏-黄连有效成分共27个,GERD相关靶点2 960个,半夏黄连-GERD取交集后得到106个靶点。分子对接结果显示,苏氨酸蛋白激酶1(AKT1)、半胱天冬酶3(CASP3)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、人原癌基因(JUN)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)与槲皮素、黄芩苷、β-谷甾醇具有较好结合活性,基因功能分析共969条,信号通路121条。结论 半夏-黄连具有多成分、多靶点及多通路的特性,主要通过抑制炎症反应、降低氧化作用、促进肿瘤细胞凋亡等过程发挥治疗GERD的作用。Abstract:Objective To study the mechanism of the herbal pair of Banxia-Huanglian in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) by network pharmacology and molecular docking.Methods Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP) and GeneCard database were used to screen the active components of Banxia-Huanglian and relevant targets of GERD, respectively. Cytoscape software was used to plot the regulatory network of drug pair and disease target. STRING database was used to construct Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) network for protein interaction. AutoDock software was used for molecular docking to predict the combination between drugs and disease targets. Then, Pymol software was used to realize the visualization of docking results and build a mutual docking pattern diagram. The GO gene function and KEGG pathway of the effective target were analyzed by R software.Results There were 27 active components of Banxia-Huanglian and 2 960 targets related to GERD. A total of 106 targets were obtained after the intersection of Banxia-Huanglian-GERD. Molecular docking results showed that threonine protein kinase 1(AKT1), caspases 3(CASP3), vascular endothelial growth factor A(VEGFA), human oncogene (JUN), interleukin-6 (IL-6) had good binding activity with quercetin, baicalin and β-sitosterol, and a total of 969 gene function analyses were performed, and 121 signal pathway were obtained.Conclusion Banxia and Huanglian play roles in the treatment of GERD by inhibiting inflammatory response, reducing oxidation and promoting tumor cell apoptosis based on their multi-component, multi-target and multi-pathway characteristics.
-
Keywords:
- Banxia /
- Huanglian /
- herbal pair /
- gastroesophageal reflux disease /
- molecular docking /
- network pharmacology
-
胃食管反流病(GERD)是由多种因素导致食管下括约肌功能障碍的胃食管动力障碍性疾病,反流、烧心是其典型症状,中国人群流行病学调查显示,每周至少发作1次烧心症状的概率为1.9%~7.0%[1]。GERD的基础治疗方法是调整生活习惯与饮食方式,常用的治疗药物有抑酸药、促胃肠动力药、黏膜保护剂、抗反流药物等。轻度食管炎的短期服药效果较快,但停药后症状易反复,难治性GERD需长期服药,患者依从性差[2]。药物治疗效果不佳的患者可选择胃镜和外科手术进行抗反流,但治疗风险大[3]。张娇等[4-5]对治疗GERD的中药进行聚类分析得出,使用频次最高的药对是半夏-黄连。半夏能燥湿化痰,降逆止呕,具有镇静抗炎、止呕、抗肿瘤等药理作用; 黄连能清热燥湿、泻火解毒,用于湿热痞满、呕吐吞酸、泄痢等疾病。现代研究[6]表明,中药半夏、黄连具有抑制胃液分泌,提高胃内pH值,抑制胃蛋白酶活性,保护胃黏膜的作用,但作用机制尚未明确。本研究采用网络药理学分析方法探讨“半夏-黄连”治疗GERD的活性成分、相关靶点及信号通路,并结合分子对接技术验证有效成分与重要靶点间的亲和关系,为“半夏-黄连”治疗GERD提供参考依据。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 半夏-黄连活性成分及靶点预测
借助中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)( http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmsp.php )设置生物口服利用度(OB)≥30%, 类药性(DL)≥0.18, 筛选半夏、黄连的有效成分及活性靶点,利用通用蛋白质数据库Uniprot(https://www.uniprot.org/)将靶点蛋白全称转换成简称,整合靶点蛋白,删除数据库不存在的蛋白,最终得到半夏-黄连有效成分的靶点。
1.2 疾病靶点预测
以“gastroesophageal reflux disease”为检索关键词, “Homo sapiens”为研究对象在Gene Cards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)中收集GERD的相关基因。
1.3 药物对疾病潜在靶点预测和调控网络图
运用R语言分析软件R3.6.1 (https://www.r-project.org/)对半夏-黄连的靶点蛋白与GERD的相关基因进行取交集操作,找出两者的交集并绘制出Venn图,初步预测半夏-黄连治疗GERD的作用靶点。采用网络拓扑属性分析软件Cytoscape3.7.2(http://cytoscape.org/)构建药物-有效成分-疾病-靶基因思维关系图,并将其关系进行可视化。
1.4 蛋白互作(PPI)网络的构建
采用蛋白质互作平台STRING(https://www.string-db.org/)对“药物有效成分-疾病相交集的蛋白”进行蛋白-蛋白相互作用的PPI网络图绘制并找出核心基因。
1.5 基因本体论(GO)分析与基因和基因组的京都百科全书(KEGG)分析
利用David 6.8数据库(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)对PPI网络中的作用靶点进行GO基因功能分析及KEGG信号通路分析。
1.6 分子对接验证核心靶点与有效成分
采用AutoDock软件对“药物-有效成分-疾病-靶基因”思维关系图中度值前5位的靶点蛋白与重要成分进行分子对接验证。从PDB(https://www.rcsb.org/)数据库下载核心蛋白3D结构,采用PyMol软件分离靶点蛋白中的配体和水分子,将配体和蛋白均保存为pdb格式文件; 其次,运用AutoDock Tools软件将核心蛋白、配体和mol2格式的化合物均转换为pdbqt格式文件,再以配体为中心寻找活性口袋及Grid Box中心坐标; 利用AutoDock Vina软件进行分子对接,最后选取对接结合能最低的结果,运用PyMol软件将其可视化。
2. 结果
2.1 药物有效成分及靶点预测
以OB>30%, DL>0.18为筛选标准,从TCMSP中共检索出27个活性化合物,其中半夏、黄连分别有13、14个有效成分,参数信息见表 1。利用UniProt数据库对半夏-黄连的1 883个靶蛋白进行简称转换、合并去重处理后,两者共同靶点为195个,有活性成分对应的作用靶点186个。
表 1 半夏-黄连药对活性成分来源 分子编号 有效成分 OB/% DL 半夏 MOL001755 24-乙基胆甾-4-en-3-one 36.08 0.76 半夏 MOL002670 卡维丁 35.64 0.81 半夏 MOL002714 黄芩素 33.52 0.21 半夏 MOL002776 黄芩苷 40.12 0.75 半夏 MOL000358 β-谷甾醇 36.91 0.75 半夏 MOL000449 豆甾醇 43.83 0.76 半夏 MOL005030 二十碳烯 30.70 0.20 半夏 MOL000519 松柏苷 31.11 0.32 半夏 MOL006936 10, 13-二十碳二烯酸 39.99 0.20 半夏 MOL006937 12, 13-环氧-9-氢氧基-7, 10-二烯羟酸 42.15 0.24 半夏 MOL006957 (3S, 6S)-3-苯甲基-6-(4-羟甲基)二苯甲基哌嗪-2, 5-醌 46.89 0.27 半夏 MOL003578 环状类固醇 38.69 0.78 半夏 MOL006967 β-D-呋喃糖苷-e, 二羟基嘌呤-9 44.72 0.21 黄连 MOL001454 小檗碱 36.86 0.78 黄连 MOL013352 黄柏酮 43.29 0.77 黄连 MOL002894 小檗红碱 35.74 0.73 黄连 MOL002897 表小檗碱 43.09 0.78 黄连 MOL002903 (R)-氢化小檗碱 55.37 0.77 黄连 MOL002904 小檗浸碱 36.68 0.82 黄连 MOL002907 黄麻甙 104.95 0.78 黄连 MOL000622 广玉兰内酯 63.71 0.19 黄连 MOL000762 棕榈酸脂 35.36 0.65 黄连 MOL000785 巴马汀 64.60 0.65 黄连 MOL000098 槲皮苷 46.43 0.28 黄连 MOL001458 黄连碱 30.67 0.86 黄连 MOL002668 甲基黄连碱 45.83 0.87 黄连 MOL008647 穆坪马兜铃酰胺 86.71 0.26 2.2 半夏-黄连调控GERD网络图
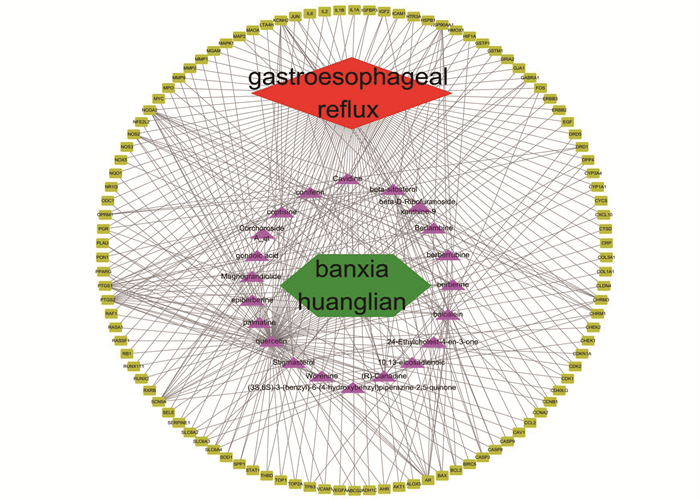
采用Cytoscape软件构建“药物-有效成分-疾病-靶基因”思维关系图,分析结果显示,该网络共有129个节点, 524条边。根据节点度值(Degree)的大小,判断其效果, Degree越大,说明该有效成分连接靶点数目越多,其作用越显著,其中槲皮素(Degree=82)、黄芩苷(Degree=23)、β-谷甾醇(Degree=22)、(R)-氢化小檗碱(Degree=15)、豆甾醇(Degree=15), 见图 1。
2.3 PPI网络及关键靶点
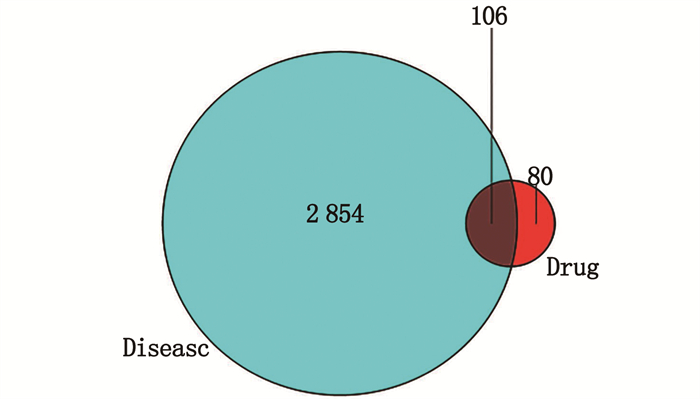
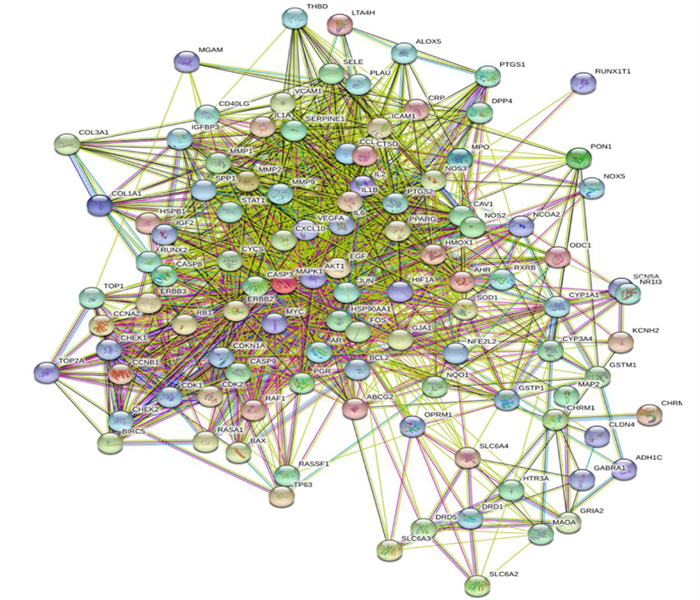
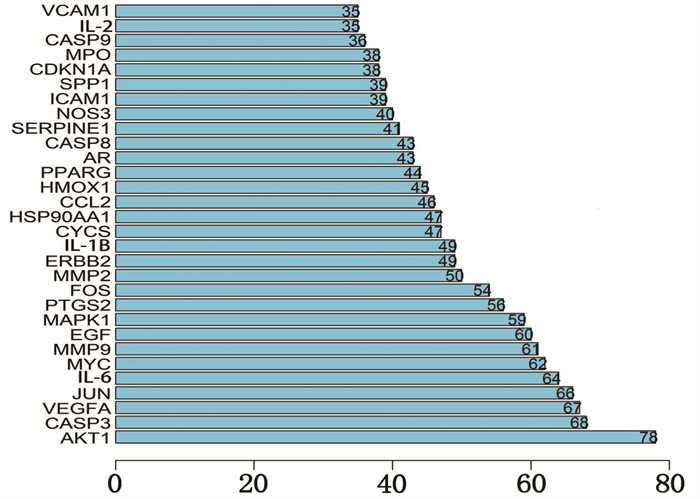
采用R软件对药物的186个作用靶点及疾病的2 960个相关基因取交集后共得到106个交集靶蛋白,见图 2。利用STRING数据平台对交集靶蛋白绘制PPI网络图,图中含有106个靶蛋白和397组互作边,其中胰蛋白酶原(PRSS1) 是游离蛋白,故将其删除。节点代表 1个蛋白,两蛋白之间用边相连,边的度值由蓝色变黄色表示逐渐变小,边越粗表示核心地位越高。其中排名前5位的蛋白分子为苏氨酸蛋白激酶1(AKT1)、半胱天冬酶3(CASP3)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、人原癌基因(JUN)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)。度值越大的蛋白质在整个网络中越起关键作用,同时也是半夏-黄连治疗GERD的关键靶点,见图 3、4。
2.4 “半夏-黄连”关键靶点的分子对接验证
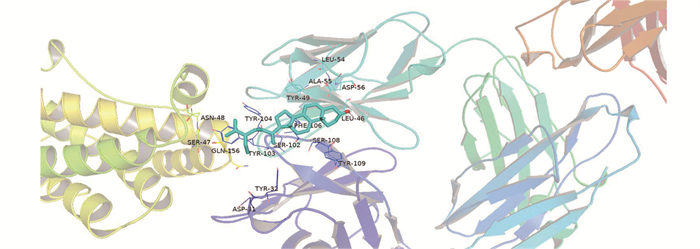
由PPI网络图可知,排名前5名的关键靶点为AKT1、IL-6、CASP3、JUN、VEGFA。采用AutoDock Vina软件对5个关键靶点与活性成分槲皮素、黄芩苷、β-谷甾醇进行分子对接验证。一般认为,配体与受体结合能越低,结合的构象越稳定,结合能小于0说明配体与受体可以自发结合。分析可知,靶点-化合物结合能从小到大排列为: IL-6与β-谷甾醇(-8.3 kcal/mol)、CASP3与β-谷甾醇(-7.1 kcal/mol)、AKT1与黄芩苷(-5.5 kcal/mol)、VEFGA与黄芩苷(-4.4 kcal/mol)、JUN与黄芩苷(-4.8 kcal/mol), 其中IL-6与β-谷甾醇(-8.3 kcal/mol)具有较强的结合力,利用Pymol软件对接结合能最低的化合物进行可视化处理,见图 5。
2.5 GO富集分析和KEGG通路分析
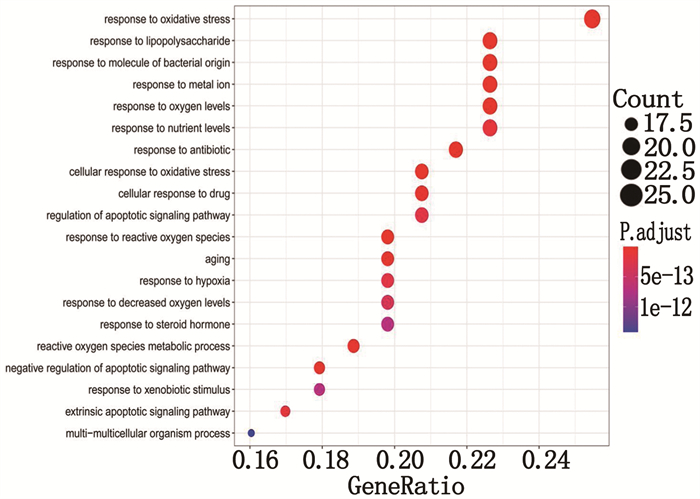
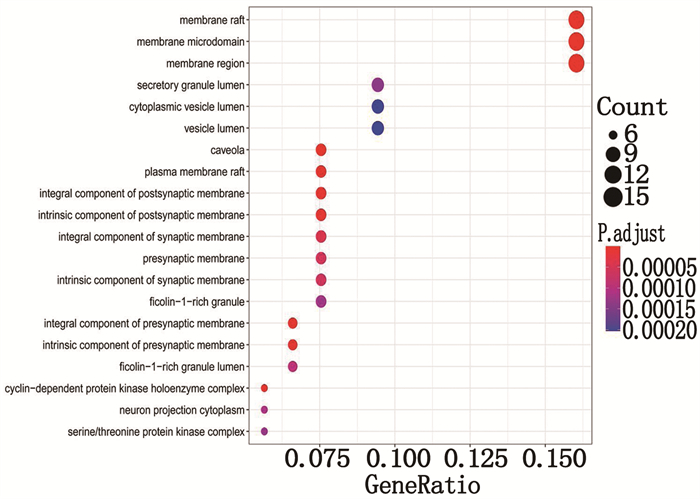
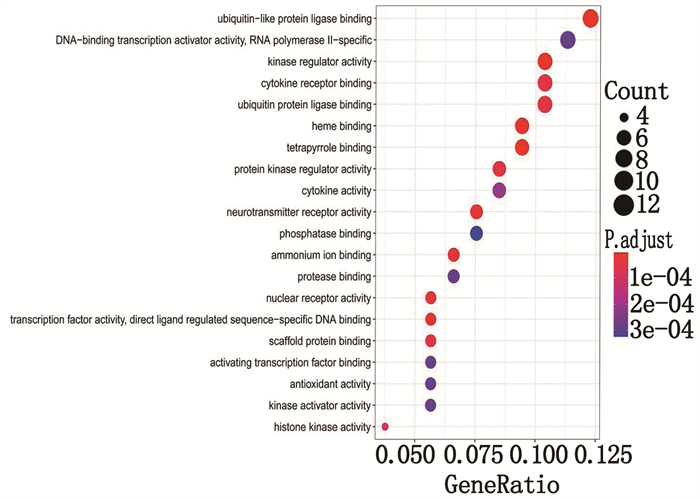
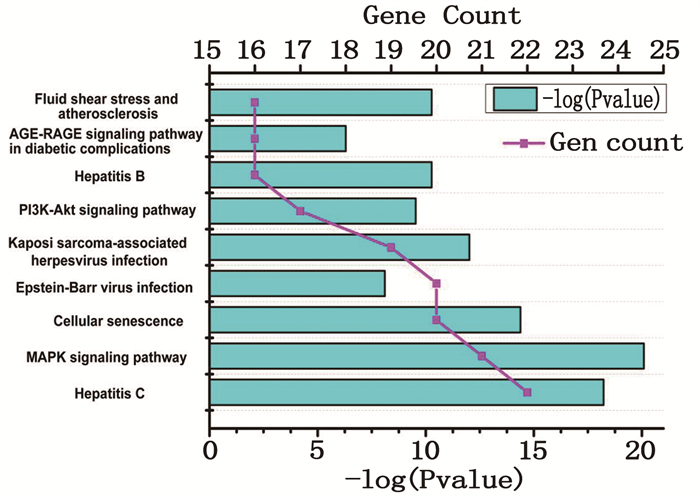
GO基因功能分析共包括969条,生物过程(BP)827条,主要包括氧化应激反应、对脂多糖反应、对细菌来源分子的反应等; 细胞组成(CC)64条,主要包括膜筏、膜微结构域、膜区域等; 分子功能(MF)78条,主要包括泛素样分子链接酶、激酶调节活动、血红素结合等。将P值排序,点越大则富集基因越多, P值越小颜色越红。取前20条通过R软件转化为气泡图,见图 6、7、8。KEGG信号通路分析得到121条通路,主要有丙型肝炎、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路、细胞衰老、PI3K/AKT信号通路等,体现了半夏-黄连治疗过程中参与多通路的特点,见图 9。
3. 讨论
GERD的发病机制包括胃食管交界处结构和功能障碍、食管清除能力与上皮防御功能失衡、食管抗反流功能下降及食管敏感性增高、免疫因素介导食管黏膜损伤等[7-8]。GERD在中医学属“吐酸、食管瘅”范畴,病机多为木郁土虚,湿邪郁阻中焦,气机升降失调,胃气上逆。发病过程中会出现湿郁化热、痰阻气滞等过程,治则是清热燥湿,祛痰降逆,兼以疏肝理气[9]。半夏具有辛温燥热,祛痰降逆功效; 黄连具备苦寒降泄,清热燥湿功能,两药配合,寒热互用以和其阴阳,辛开苦降以调其升降,消湿热之痞,化痰浊之结[4]。
本研究通过网络药理学及分子对接技术对“半夏-黄连”治疗GERD的机制进行初步探讨,共筛选出半夏-黄连活性成分27个,关键靶点186个。根据药物-有效成分-疾病-靶点关系图可知,槲皮素、黄芩苷、β-谷甾醇、(R)-氢化小檗碱、豆甾醇有较多靶点蛋白对应,表明上述化合物可能是治疗GERD的关键活性成分。组胺广泛分布在消化道的各种细胞中, KITANO M等[10]研究表明,组胺可刺激酸分泌和破坏细胞黏膜,槲皮素能有效抑制组胺的浓度,抑制酸的分泌,保护食管黏膜。YOH T等[11]研究发现,单纯抑制胃酸分泌并不能改善食管下括约肌的功能,体内自由基浓度增加可引起脂质过氧化,导致活性氧升高,蛋白质及核酸变性,造成细胞组织损伤从而出现反酸、烧心等症状。槲皮素可有效清除自由基,显著降低脂质过氧化,保护组织黏膜[12]。黄芩苷也具有抗氧化作用,能清除氧自由基的来源,减少组织损伤,延缓细胞衰老[13]。此外,黄芩苷可降低CASP3和Bax水平,调节PI3K/Akt信号通路表达,改善受损的血管内皮功能和调节氧化应激反应[14]。PANDITH H等[15]通过体外试验发现,豆甾醇能抑制脂多糖(LPS)诱导的环氧酶2(COX-2)、诱导型一氧化氮合成酶(iNOS) mRNA水平提高,下调前列腺素E2(PGE2)和NO的释放,维持黏膜屏障功能。β-谷甾醇除具有清除羟自由基的抗氧化作用外,还可增加抗菌肽表达,在细菌作用位点结合,起杀死致病菌的作用; 同样β-谷甾醇通过抑制表皮细胞、巨噬细胞及MAPK信号通路的激活,导致TNF-α、IL-6和白细胞介素-8(IL-8)生成减少从而起到抗炎作用[16]。(R)-氢化小檗碱是黄连素的衍生物,动物实验[17]显示氢化小檗碱具有明显的镇痛抗炎作用。
由PPI网络图可知,相互作用关系较多的靶点是AKT1、CASP3、VEGFA、JUN、IL-6, 这些靶点通过各种联系参与多种生物过程。食管功能改变和食管黏膜损伤是GERD重要发病机制,除外化学损伤还可能涉及自身免疫。研究[18]表明贲门失弛缓症患者的血清和血浆中发现IL-6明显升高, IL-6是重要的免疫调节因子及炎症介质,PALMIERI O等[19]研究证明, IL-6在贲门失弛缓症中造成神经损伤并介导炎症反应的发生。肿瘤血管的形成对实体肿瘤存活至关重要, VEGFA是促进肿瘤血管形成的重要因子,可刺激血管内皮细胞增殖,介导肿瘤血管的形成,主要通过与血管内皮生长因子受体2(VEGFR2)结合激活酪氨酸激酶,使自身磷酸化,触发级联反应,促进肿瘤血管新生[20]。CASP3是细胞凋亡信号通路中的关键位点,介导外部和内在的线粒体通路,催化多种蛋白特异性裂解,降解细胞目标,触发细胞凋亡[21]。AKT1参与细胞增殖生长、代谢和血管生成等多种过程,是PI3K/Akt信号通路上的关键基因, PI3K/Akt信号通路可刺激食管肿瘤细胞增殖转移,而磷酸化AKT1可使食管癌患者局部组织生存期缩短[22]。JUN是活化蛋白1(AP-1)构成单位之一,在食管癌表达中抑制AP-1转录活性,阻断信号通路传导,可抑制食管癌肿瘤细胞增殖[23]。
KEGG通路分析可知,半夏-黄连可通过PI3K/Akt信号通路、MAPK信号通路及NF-κB信号通路发挥治疗GERD的作用。AutoDock Vina分子对接结果显示,半夏-黄连与GERD的作用靶点有较好的结合活性,其中结合力最强的是IL-6与β-谷甾醇。VEGFA信号通路是抗食管癌血管形成的治疗靶点, VEGF是PI3K/Akt信号通路激活的膜受体, VEGF过度活化可诱导食管黏膜组织相关癌变。张锋利等[24]实验证实,降低VEGF表达水平,抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路活化,能够有效抑制正常细胞向癌细胞的增殖分化。MAPK信号通路通过诱导通路上位点Hsp70和Hsp27发挥食管血管内皮细胞对酸性物质的应激反应,减少黏膜损伤[25]。炎症因子是参与破坏食管黏膜屏障的因素之一,人食管黏膜细胞内白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)和IL-8炎症因子的表达,可激活食管黏膜内NF-κB信号通路,该通路的激活促使大量炎症细胞聚集,开启炎症级联反应。同时炎症因子可阻断紧密连接蛋白表达与分布,加重反流对食管黏膜上皮的损害[26]。
本研究通过网络药理学对半夏-黄连药对治疗GERD的有效成分、作用靶点及相关通路进行了初步探索,并通过Autodock分子对接软件验证了半夏-黄连核心成分与关键靶点之间存在较好结合度,有效证明了网络药理学预测靶点的可靠性。结果显示,半夏-黄连可能将活性成分槲皮素、黄芩苷、β-谷甾醇作用于AKT1、IL-6、CASP3等靶点,调控PI3K/Akt信号通路、MAPK信号通路及NF-κB信号通路,参与炎症反应、氧化反应、细胞凋亡等生理病理过程以发挥治疗GERD的作用。但本研究缺乏动物实验验证,且数据库信息更新不及时,因此也具有一定的不足之处。
-
表 1 半夏-黄连药对活性成分
来源 分子编号 有效成分 OB/% DL 半夏 MOL001755 24-乙基胆甾-4-en-3-one 36.08 0.76 半夏 MOL002670 卡维丁 35.64 0.81 半夏 MOL002714 黄芩素 33.52 0.21 半夏 MOL002776 黄芩苷 40.12 0.75 半夏 MOL000358 β-谷甾醇 36.91 0.75 半夏 MOL000449 豆甾醇 43.83 0.76 半夏 MOL005030 二十碳烯 30.70 0.20 半夏 MOL000519 松柏苷 31.11 0.32 半夏 MOL006936 10, 13-二十碳二烯酸 39.99 0.20 半夏 MOL006937 12, 13-环氧-9-氢氧基-7, 10-二烯羟酸 42.15 0.24 半夏 MOL006957 (3S, 6S)-3-苯甲基-6-(4-羟甲基)二苯甲基哌嗪-2, 5-醌 46.89 0.27 半夏 MOL003578 环状类固醇 38.69 0.78 半夏 MOL006967 β-D-呋喃糖苷-e, 二羟基嘌呤-9 44.72 0.21 黄连 MOL001454 小檗碱 36.86 0.78 黄连 MOL013352 黄柏酮 43.29 0.77 黄连 MOL002894 小檗红碱 35.74 0.73 黄连 MOL002897 表小檗碱 43.09 0.78 黄连 MOL002903 (R)-氢化小檗碱 55.37 0.77 黄连 MOL002904 小檗浸碱 36.68 0.82 黄连 MOL002907 黄麻甙 104.95 0.78 黄连 MOL000622 广玉兰内酯 63.71 0.19 黄连 MOL000762 棕榈酸脂 35.36 0.65 黄连 MOL000785 巴马汀 64.60 0.65 黄连 MOL000098 槲皮苷 46.43 0.28 黄连 MOL001458 黄连碱 30.67 0.86 黄连 MOL002668 甲基黄连碱 45.83 0.87 黄连 MOL008647 穆坪马兜铃酰胺 86.71 0.26 -
[1] 中国医师协会消化医师分会胃食管反流病专业委员会, 中华医学会消化内镜学分会食管疾病协作组. 2020年中国胃食管反流病内镜治疗专家共识[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2021, 38(1): 1-12. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321463-20201115-00897 [2] 陆明军, 谭诗云. 难治性胃食管反流病的药物治疗研究进展[J]. 广西医学, 2019, 41(1): 90-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYX201901023.htm [3] 赵小玲, 郑吉敏. 难治性胃食管反流病的治疗研究进展[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(32): 111-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2020.32.030 [4] 张娇, 王凤云, 王安璐, 等. 胃食管反流病的常用方剂及药对规律[J]. 中医杂志, 2015, 29(10): 881-883. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ201510025.htm [5] 何华康. 半夏的化学成分及其药理作用的研究进展[J]. 当代医药论丛, 2020, 18(7): 18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7629.2020.07.013 [6] 张建民, 杨晶. 胃食管反流病常用中药药理作用初析[J]. 中国药业, 2004, 13(8): 77-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2004.08.064 [7] 张晓慧. 胃食管反流病的研究进展[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2011, 11(19): 4570-4571. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWZX201119021.htm [8] BAJBOUJ M. Diagnostik und Therapie atypischer Refluxsymptome Bei fehlendem PPI-Ansprechen[J]. HNO, 2012, 60(3): 193-199. doi: 10.1007/s00106-011-2430-9
[9] 王家平, 周文涛, 顾仁艳, 等. 半夏泻心汤治疗胃食管反流病的临床观察[J]. 中国中医急症, 2016, 25(9): 1828-1829. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2016.09.064 [10] KITANO M, BERNSAND M, KISHIMOTO Y, et al. Ischemia of rat stomach mobilizes ECL cell histamine[J]. American Journal of Physiology, 2005, 288(5): G1084-G1090. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/acc7/f6b4038129108ccbfdbf4aae3bf3511f0f34.pdf
[11] YOH T, SLEE J, OAHN B, et al. Oxidative stress is more important than acid in the pathogenesis of reflux oesophagitis in rats[J]. Gut, 2001, 49(3): 364-371. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.3.364
[12] HU X T, DING C, ZHOU N, et al. Quercetin protects gastric epithelial cell from oxidative damage invitro and in vivo[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2015, 754: 115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.02.007
[13] 郭少英, 程发峰, 钟相根, 等. 黄芩苷的体外抗氧化研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2011, 22(1): 9-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZGY201101005.htm [14] WEI X, ZHU X, HU N, et al. Baicalin attenuates angiotensin Ⅱ-induced endothelial dysfunction[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2015, 465(1): 101-107. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.138
[15] PANDITH H, ZHANG X, THONGPRADITCHOTE S, et al. Effect of Siam weed extract and its bioactive component scutellarein tetramethyl ether on anti-inflammatory activity through NF-κB pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013, 147(2): 434-441. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036224051510_ab9b.html
[16] 陈元堃, 曾奥, 罗振辉, 等. β-谷甾醇药理作用研究进展[J]. 广东药科大学学报, 2021, 37(1): 148-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYX202101039.htm [17] 黄祖良, 韦启后, 汤春荣, 等. 氢化小檗碱镇痛和消炎作用的研究[J]. 江西中医学院学报, 2002, 14(1): 33-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXB200201025.htm [18] CLAYTON S, CAUBLE E, KUMAR A, et al. Plasma levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-γ, IL-12, IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23 in achalasia, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)[J]. BMC Gastroenterology, 2019, 19(1): 28.
[19] PALMIERI O, MAZZA T, MERLA A, et al. Gene expression of muscular and neuronal pathways is cooperatively dysregulated in patients with idiopathic achalasia[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 31549. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4980661?pdf=render
[20] 蔡霄月, 张铭, 周亚宁, 等. 食道通结方对人食管癌裸鼠移植瘤微血管生成的影响[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2021, 55(1): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHZZ202101020.htm [21] ZHANG Z, YU X, GUO Y, et al. Genetic variant in CASP3 affects promoter activity and risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer science, 2012, 103(3): 555-560. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Xuemei_Zhang5/publication/51848574_Genetic_variant_in_CASP3_affects_promoter_activity_and_risk_of_esophageal_squamous_cell_carcinoma/links/5417e9950cf2f48c74a41ccf
[22] 许博文, 李娟, 李杰, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨芪术郁灵汤治疗食管癌的分子生物学机制研究[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2021, 18: 1390-1399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYY202118006.htm [23] 杨鲸蓉, 吴健, 叶仕新, 等. miR-21/PDCD4/AP-1对食管癌细胞增殖、侵袭及迁移的影响[J]. 中国医药导报, 2020, 17(20): 4-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202020003.htm [24] 张锋利, 唐凤英, 沈舒文, 等. 桔梗枳壳汤加味对反流性食管炎模型大鼠PI3K/Akt信号通路及胃肠动力的影响[J]. 中医药导报, 2020, 26(10): 36-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZB202010008.htm [25] 符小聪, 张涛, 赖冬萍, 等. 基于数据挖掘和网络药理学分析旋覆代赭汤治疗反流性食管炎的效用机制[J]. 江西中医药, 2021, 52(4): 69-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXZY202104022.htm [26] 房渝, 黄春, 温剑虎, 等. NF-κB信号通路的激活在胃食管反流破坏食管黏膜上皮屏障功能机制中的作用[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2017, 42(9): 1119-1125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYK201709013.htm -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 陈冠儒,胡铠承. 数据挖掘分析中医药治疗反流性食道炎用药规律. 光明中医. 2024(13): 2574-2577 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王艳璞. 化痰活血方联合西药治疗冠心病伴心力衰竭的研究. 中医研究. 2024(08): 45-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 卢俊伟,祝璟哲,陈鸿儒,解举民. 基于网络药理学与分子对接技术探究木犀草素治疗宫颈癌的分子机制. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(16): 26-33 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 贺晓旭,陈芳,谭晓婵,陈志明. 基于数据挖掘探讨中医药治疗反流性食管炎的核心用药及配伍规律. 浙江中西医结合杂志. 2024(11): 1053-1057 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 付志刚,王振鹏,张刚强. 清热利咽汤联合西药治疗反流性咽喉炎临床研究. 新中医. 2023(11): 140-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 高兴. 埃索美拉唑联合益生菌在胃食管反流治疗中作用及对FNP、FCP蛋白的影响. 医学理论与实践. 2023(15): 2565-2567 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 徐琦,祁双林. 基于数据挖掘探讨国医大师辨治脾胃病的用药规律. 中医药导报. 2022(07): 188-193 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵剑锋,陈凯. 基于网络药理学预测栀子大黄汤抗肝损伤的作用机制. 实用临床医药杂志. 2022(22): 83-89 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号